二叉树的直径
树的直径(有时称为宽度)是两个末端节点之间最长路径上的节点数。下图显示了两棵直径为 9 的树,形成最长路径末端的叶子带有阴影(请注意,每棵长度为 9 的树中有多个路径,但路径不超过 9 个节点)。
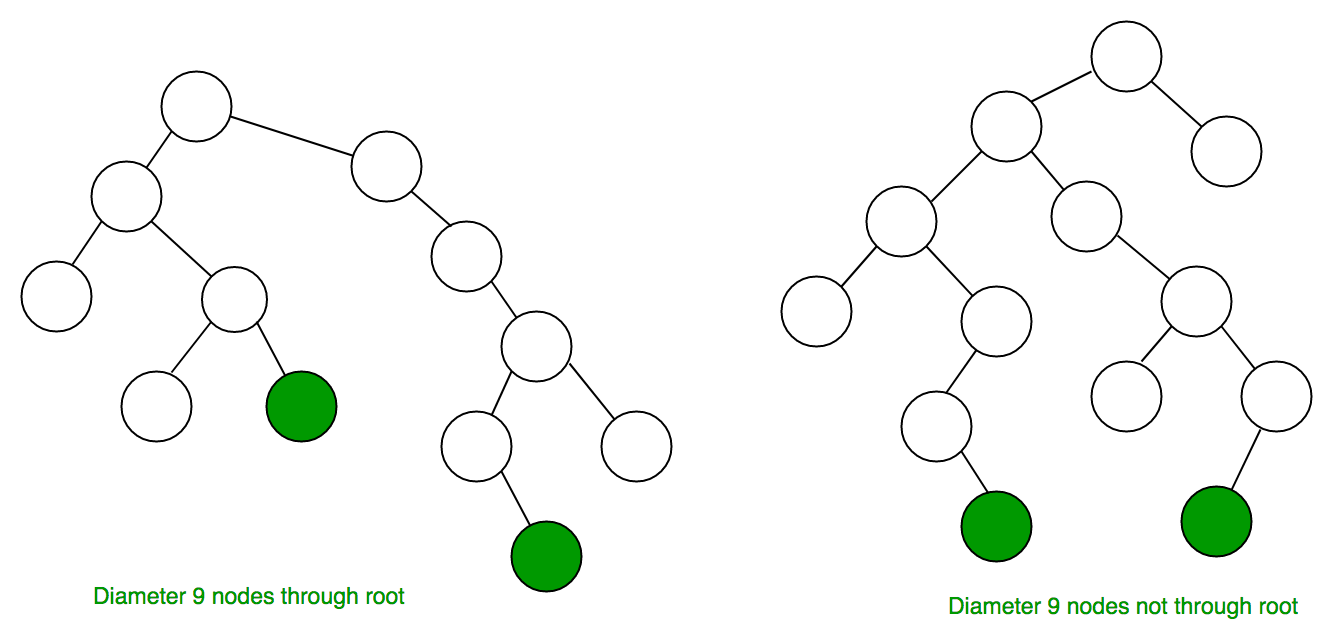
一棵树的直径 T 是下列量中最大的一个:
- T 的左子树的直径。
- T 的右子树的直径。
- 通过 T 的根的叶子之间的最长路径(这可以从 T 的子树的高度计算)
执行:
C++
// Recursive optimized C program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
// and a pointer to right child
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// function to create a new node of tree and returns pointer
struct node* newNode(int data);
// returns max of two integers
int max(int a, int b) { return (a > b) ? a : b; }
// function to Compute height of a tree.
int height(struct node* node);
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
int diameter(struct node* tree)
{
// base case where tree is empty
if (tree == NULL)
return 0;
// get the height of left and right sub-trees
int lheight = height(tree->left);
int rheight = height(tree->right);
// get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
int ldiameter = diameter(tree->left);
int rdiameter = diameter(tree->right);
// Return max of following three
// 1) Diameter of left subtree
// 2) Diameter of right subtree
// 3) Height of left subtree + height of right subtree + 1
return max(lheight + rheight + 1,
max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
// UTILITY FUNCTIONS TO TEST diameter() FUNCTION
// The function Compute the "height" of a tree. Height is
// the number f nodes along the longest path from the root
// node down to the farthest leaf node.
int height(struct node* node)
{
// base case tree is empty
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 + max of left
// height and right heights
return 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right));
}
// Helper function that allocates a new node with the
// given data and NULL left and right pointers.
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* Constructed binary tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
*/
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
// Function Call
cout << "Diameter of the given binary tree is " <<
diameter(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 C
// Recursive optimized C program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
#include
#include
// A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
// and a pointer to right child
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// function to create a new node of tree and returns pointer
struct node* newNode(int data);
// returns max of two integers
int max(int a, int b) { return (a > b) ? a : b; }
// function to Compute height of a tree.
int height(struct node* node);
// Function to get diameter of a binary tree
int diameter(struct node* tree)
{
// base case where tree is empty
if (tree == NULL)
return 0;
// get the height of left and right sub-trees
int lheight = height(tree->left);
int rheight = height(tree->right);
// get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
int ldiameter = diameter(tree->left);
int rdiameter = diameter(tree->right);
// Return max of following three
// 1) Diameter of left subtree
// 2) Diameter of right subtree
// 3) Height of left subtree + height of right subtree + 1
return max(lheight + rheight + 1,
max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
// UTILITY FUNCTIONS TO TEST diameter() FUNCTION
// The function Compute the "height" of a tree. Height is
// the number f nodes along the longest path from the root
// node down to the farthest leaf node.
int height(struct node* node)
{
// base case tree is empty
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 + max of left
// height and right heights
return 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right));
}
// Helper function that allocates a new node with the
// given data and NULL left and right pointers.
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* Constructed binary tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
*/
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
// Function Call
printf("Diameter of the given binary tree is %d\n",
diameter(root));
return 0;
} Java
// Recursive optimized Java program to find the diameter of
// a Binary Tree
// Class containing left and right child of current
// node and key value
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
// Class to print the Diameter
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
// Method to calculate the diameter and return it to
// main
int diameter(Node root)
{
// base case if tree is empty
if (root == null)
return 0;
// get the height of left and right sub-trees
int lheight = height(root.left);
int rheight = height(root.right);
// get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
int ldiameter = diameter(root.left);
int rdiameter = diameter(root.right);
/* Return max of following three
1) Diameter of left subtree
2) Diameter of right subtree
3) Height of left subtree + height of right subtree + 1
*/
return Math.max(lheight + rheight + 1,
Math.max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
// A wrapper over diameter(Node root)
int diameter() { return diameter(root); }
// The function Compute the "height" of a tree. Height
// is the number of nodes along the longest path from the
// root node down to the farthest leaf node.
static int height(Node node)
{
// base case tree is empty
if (node == null)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 + max of
// left height and right heights
return (1
+ Math.max(height(node.left),
height(node.right)));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// creating a binary tree and entering the nodes
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
// Function Call
System.out.println(
"The diameter of given binary tree is : "
+ tree.diameter());
}
}Python3
# Python3 program to find the diameter of binary tree
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# The function Compute the "height" of a tree. Height is the
# number of nodes along the longest path from the root node
# down to the farthest leaf node.
def height(node):
# Base Case : Tree is empty
if node is None:
return 0
# If tree is not empty then height = 1 + max of left
# height and right heights
return 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right))
# Function to get the diameter of a binary tree
def diameter(root):
# Base Case when tree is empty
if root is None:
return 0
# Get the height of left and right sub-trees
lheight = height(root.left)
rheight = height(root.right)
# Get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
ldiameter = diameter(root.left)
rdiameter = diameter(root.right)
# Return max of the following tree:
# 1) Diameter of left subtree
# 2) Diameter of right subtree
# 3) Height of left subtree + height of right subtree +1
return max(lheight + rheight + 1, max(ldiameter, rdiameter))
# Driver Code
"""
Constructed binary tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
"""
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
# Function Call
print(diameter(root))
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// Recursive optimized C# program to find the diameter of
// a Binary Tree
// Class containing left and right child of current
// node and key value
using System;
namespace Tree
{
class Tree
{
public Tree(T value)
{
this.value = value;
}
public T value { get; set; }
public Tree left { get; set; }
public Tree right { get; set; }
}
public class TreeDiameter
{
Tree root;
// The function Compute the "height" of a tree. Height
// is the number of nodes along the longest path from the
// root node down to the farthest leaf node.
int Height(Tree node)
{
if (node == null) return 0;
return 1 + Math.Max(Height(node.left),
Height(node.right));
}
int Diameter(Tree root)
{
if (root == null) return 0;
// get the height of left and right sub-trees
int lHeight = Height(root.left);
int rHeight = Height(root.right);
// get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
int lDiameter = Diameter(root.left);
int rDiameter = Diameter(root.right);
// Return max of following three
//1) Diameter of left subtree
//2) Diameter of right subtree
//3) Height of left subtree + height of right subtree + 1
return Math.Max(lHeight + rHeight + 1,
Math.Max(lDiameter, rDiameter));
}
// A wrapper over diameter(Node root)
int Diameter() { return Diameter(root); }
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// creating a binary tree and entering the nodes
TreeDiameter tree = new TreeDiameter();
tree.root = new Tree(1);
tree.root.left = new Tree(2);
tree.root.right = new Tree(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Tree(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Tree(5);
Console.WriteLine($"The diameter of given binary tree is : {tree.Diameter()}");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by krishaccot Javascript
C++
// Recursive optimized C++ program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
// and a pointer to right child
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// function to create a new node of tree and returns pointer
struct node* newNode(int data);
int diameterOpt(struct node* root, int* height)
{
// lh --> Height of left subtree
// rh --> Height of right subtree
int lh = 0, rh = 0;
// ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
// rdiameter --> Diameter of right subtree
int ldiameter = 0, rdiameter = 0;
if (root == NULL) {
*height = 0;
return 0; // diameter is also 0
}
// Get the heights of left and right subtrees in lh and
// rh And store the returned values in ldiameter and
// ldiameter
ldiameter = diameterOpt(root->left, &lh);
rdiameter = diameterOpt(root->right, &rh);
// Height of current node is max of heights of left and
// right subtrees plus 1
*height = max(lh, rh) + 1;
return max(lh + rh + 1, max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
// Helper function that allocates a new node with the
// given data and NULL left and right pointers.
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* Constructed binary tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
*/
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
int height = 0;
// Function Call
cout << "Diameter of the given binary tree is " << diameterOpt(root, &height);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by probinsah. C
// Recursive C program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
#include
// the second parameter is to store the height of tree.
// Initially, we need to pass a pointer to a location with
// value as 0. So, function should be used as follows:
// int height = 0;
// struct node *root = SomeFunctionToMakeTree();
// int diameter = diameterOpt(root, &height);
int diameterOpt(struct node* root, int* height)
{
// lh --> Height of left subtree
// rh --> Height of right subtree
int lh = 0, rh = 0;
// ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
// rdiameter --> Diameter of right subtree
int ldiameter = 0, rdiameter = 0;
if (root == NULL) {
*height = 0;
return 0; // diameter is also 0
}
// Get the heights of left and right subtrees in lh and
// rh And store the returned values in ldiameter and
// ldiameter
ldiameter = diameterOpt(root->left, &lh);
rdiameter = diameterOpt(root->right, &rh);
// Height of current node is max of heights of left and
// right subtrees plus 1
*height = max(lh, rh) + 1;
return max(lh + rh + 1, max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
} Java
// Recursive Java program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
// Class containing left and right child of current
// node and key value
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
// A utility class to pass height object
class Height {
int h;
}
// Class to print the Diameter
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
// define height =0 globally and call
// diameterOpt(root,height) from main
int diameterOpt(Node root, Height height)
{
// lh --> Height of left subtree
// rh --> Height of right subtree
Height lh = new Height(), rh = new Height();
if (root == null) {
height.h = 0;
return 0; // diameter is also 0
}
/*
ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
rdiameter --> Diameter of right subtree
Get the heights of left and right subtrees in lh and rh.
And store the returned values in ldiameter and ldiameter*/
int ldiameter = diameterOpt(root.left, lh);
int rdiameter = diameterOpt(root.right, rh);
// Height of current node is max of heights of left
// and right subtrees plus 1
height.h = Math.max(lh.h, rh.h) + 1;
return Math.max(lh.h + rh.h + 1,
Math.max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
// A wrapper over diameter(Node root)
int diameter()
{
Height height = new Height();
return diameterOpt(root, height);
}
// The function Compute the "height" of a tree. Height
// is
// the number f nodes along the longest path from the
// root node down to the farthest leaf node.
static int height(Node node)
{
// base case tree is empty
if (node == null)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 + max of
// left height and right heights
return (1
+ Math.max(height(node.left),
height(node.right)));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// creating a binary tree and entering the nodes
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
// Function Call
System.out.println(
"The diameter of given binary tree is : "
+ tree.diameter());
}
}Python3
# Python3 program to find the diameter of a binary tree
# A binary tree Node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new Node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
# utility class to pass height object
class Height:
def __init(self):
self.h = 0
# Optimised recursive function to find diameter
# of binary tree
def diameterOpt(root, height):
# to store height of left and right subtree
lh = Height()
rh = Height()
# base condition- when binary tree is empty
if root is None:
height.h = 0
return 0
# ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
# rdiameter --> diameter of right subtree
# height of left subtree and right subtree is obtained from lh and rh
# and returned value of function is stored in ldiameter and rdiameter
ldiameter = diameterOpt(root.left, lh)
rdiameter = diameterOpt(root.right, rh)
# height of tree will be max of left subtree
# height and right subtree height plus1
height.h = max(lh.h, rh.h) + 1
# return maximum of the following
# 1)left diameter
# 2)right diameter
# 3)left height + right height + 1
return max(lh.h + rh.h + 1, max(ldiameter, rdiameter))
# function to calculate diameter of binary tree
def diameter(root):
height = Height()
return diameterOpt(root, height)
# Driver Code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
"""
Constructed binary tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
"""
# Function Call
print(diameter(root))
# This code is contributed by Shweta Singh(shweta44)C#
// Recursive C# program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Class containing left and right child of current
// node and key value
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
// A utility class to pass height object
class Height {
public int h;
}
// Class to print the Diameter
class BinaryTree {
public Node root;
// define height =0 globally and call
// diameterOpt(root,height) from main
public int diameterOpt(Node root, Height height)
{
// lh --> Height of left subtree
// rh --> Height of right subtree
Height lh = new Height(), rh = new Height();
if (root == null) {
height.h = 0;
return 0; // diameter is also 0
}
// ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
// rdiameter --> Diameter of right subtree
// Get the heights of left and right subtrees in lh
/*and rh And store the returned values in ldiameter
and ldiameter */
int ldiameter = diameterOpt(root.left, lh);
int rdiameter = diameterOpt(root.right, rh);
// Height of current node is max of heights of left
// and right subtrees plus 1
height.h = Math.Max(lh.h, rh.h) + 1;
return Math.Max(lh.h + rh.h + 1,
Math.Max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
// A wrapper over diameter(Node root)
public int diameter()
{
Height height = new Height();
return diameterOpt(root, height);
}
// The function Compute the "height" of a tree. Height
// is
// the number f nodes along the longest path from the
// root node down to the farthest leaf node.
public int height(Node node)
{
// base case tree is empty
if (node == null)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 + max of
// left height and right heights
return (1
+ Math.Max(height(node.left),
height(node.right)));
}
// Driver Code
static void Main()
{
// creating a binary tree and entering the nodes
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
// Function Call
Console.Write("The diameter of given binary tree is : " + tree.diameter());
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.Javascript
输出
Diameter of the given binary tree is 4时间复杂度: O(n 2 )优化实现:上面的实现可以通过在同一个递归中计算高度来优化,而不是单独调用一个height()。感谢 Amar 建议这个优化版本。这种优化将时间复杂度降低到 O(n)。
C++
// Recursive optimized C++ program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
// and a pointer to right child
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// function to create a new node of tree and returns pointer
struct node* newNode(int data);
int diameterOpt(struct node* root, int* height)
{
// lh --> Height of left subtree
// rh --> Height of right subtree
int lh = 0, rh = 0;
// ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
// rdiameter --> Diameter of right subtree
int ldiameter = 0, rdiameter = 0;
if (root == NULL) {
*height = 0;
return 0; // diameter is also 0
}
// Get the heights of left and right subtrees in lh and
// rh And store the returned values in ldiameter and
// ldiameter
ldiameter = diameterOpt(root->left, &lh);
rdiameter = diameterOpt(root->right, &rh);
// Height of current node is max of heights of left and
// right subtrees plus 1
*height = max(lh, rh) + 1;
return max(lh + rh + 1, max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
// Helper function that allocates a new node with the
// given data and NULL left and right pointers.
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* Constructed binary tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
*/
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
int height = 0;
// Function Call
cout << "Diameter of the given binary tree is " << diameterOpt(root, &height);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by probinsah.
C
// Recursive C program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
#include
// the second parameter is to store the height of tree.
// Initially, we need to pass a pointer to a location with
// value as 0. So, function should be used as follows:
// int height = 0;
// struct node *root = SomeFunctionToMakeTree();
// int diameter = diameterOpt(root, &height);
int diameterOpt(struct node* root, int* height)
{
// lh --> Height of left subtree
// rh --> Height of right subtree
int lh = 0, rh = 0;
// ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
// rdiameter --> Diameter of right subtree
int ldiameter = 0, rdiameter = 0;
if (root == NULL) {
*height = 0;
return 0; // diameter is also 0
}
// Get the heights of left and right subtrees in lh and
// rh And store the returned values in ldiameter and
// ldiameter
ldiameter = diameterOpt(root->left, &lh);
rdiameter = diameterOpt(root->right, &rh);
// Height of current node is max of heights of left and
// right subtrees plus 1
*height = max(lh, rh) + 1;
return max(lh + rh + 1, max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
Java
// Recursive Java program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
// Class containing left and right child of current
// node and key value
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
// A utility class to pass height object
class Height {
int h;
}
// Class to print the Diameter
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
// define height =0 globally and call
// diameterOpt(root,height) from main
int diameterOpt(Node root, Height height)
{
// lh --> Height of left subtree
// rh --> Height of right subtree
Height lh = new Height(), rh = new Height();
if (root == null) {
height.h = 0;
return 0; // diameter is also 0
}
/*
ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
rdiameter --> Diameter of right subtree
Get the heights of left and right subtrees in lh and rh.
And store the returned values in ldiameter and ldiameter*/
int ldiameter = diameterOpt(root.left, lh);
int rdiameter = diameterOpt(root.right, rh);
// Height of current node is max of heights of left
// and right subtrees plus 1
height.h = Math.max(lh.h, rh.h) + 1;
return Math.max(lh.h + rh.h + 1,
Math.max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
// A wrapper over diameter(Node root)
int diameter()
{
Height height = new Height();
return diameterOpt(root, height);
}
// The function Compute the "height" of a tree. Height
// is
// the number f nodes along the longest path from the
// root node down to the farthest leaf node.
static int height(Node node)
{
// base case tree is empty
if (node == null)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 + max of
// left height and right heights
return (1
+ Math.max(height(node.left),
height(node.right)));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// creating a binary tree and entering the nodes
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
// Function Call
System.out.println(
"The diameter of given binary tree is : "
+ tree.diameter());
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to find the diameter of a binary tree
# A binary tree Node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new Node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
# utility class to pass height object
class Height:
def __init(self):
self.h = 0
# Optimised recursive function to find diameter
# of binary tree
def diameterOpt(root, height):
# to store height of left and right subtree
lh = Height()
rh = Height()
# base condition- when binary tree is empty
if root is None:
height.h = 0
return 0
# ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
# rdiameter --> diameter of right subtree
# height of left subtree and right subtree is obtained from lh and rh
# and returned value of function is stored in ldiameter and rdiameter
ldiameter = diameterOpt(root.left, lh)
rdiameter = diameterOpt(root.right, rh)
# height of tree will be max of left subtree
# height and right subtree height plus1
height.h = max(lh.h, rh.h) + 1
# return maximum of the following
# 1)left diameter
# 2)right diameter
# 3)left height + right height + 1
return max(lh.h + rh.h + 1, max(ldiameter, rdiameter))
# function to calculate diameter of binary tree
def diameter(root):
height = Height()
return diameterOpt(root, height)
# Driver Code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
"""
Constructed binary tree is
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
"""
# Function Call
print(diameter(root))
# This code is contributed by Shweta Singh(shweta44)
C#
// Recursive C# program to find the diameter of a
// Binary Tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Class containing left and right child of current
// node and key value
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
// A utility class to pass height object
class Height {
public int h;
}
// Class to print the Diameter
class BinaryTree {
public Node root;
// define height =0 globally and call
// diameterOpt(root,height) from main
public int diameterOpt(Node root, Height height)
{
// lh --> Height of left subtree
// rh --> Height of right subtree
Height lh = new Height(), rh = new Height();
if (root == null) {
height.h = 0;
return 0; // diameter is also 0
}
// ldiameter --> diameter of left subtree
// rdiameter --> Diameter of right subtree
// Get the heights of left and right subtrees in lh
/*and rh And store the returned values in ldiameter
and ldiameter */
int ldiameter = diameterOpt(root.left, lh);
int rdiameter = diameterOpt(root.right, rh);
// Height of current node is max of heights of left
// and right subtrees plus 1
height.h = Math.Max(lh.h, rh.h) + 1;
return Math.Max(lh.h + rh.h + 1,
Math.Max(ldiameter, rdiameter));
}
// A wrapper over diameter(Node root)
public int diameter()
{
Height height = new Height();
return diameterOpt(root, height);
}
// The function Compute the "height" of a tree. Height
// is
// the number f nodes along the longest path from the
// root node down to the farthest leaf node.
public int height(Node node)
{
// base case tree is empty
if (node == null)
return 0;
// If tree is not empty then height = 1 + max of
// left height and right heights
return (1
+ Math.Max(height(node.left),
height(node.right)));
}
// Driver Code
static void Main()
{
// creating a binary tree and entering the nodes
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
// Function Call
Console.Write("The diameter of given binary tree is : " + tree.diameter());
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
Javascript
输出
The diameter of given binary tree is : 4时间复杂度: O(n)
- O(n)中二叉树的直径[一种新方法]
- N叉树的直径
被问到:亚马逊、Cadence、MakeMyTrip、微软、甲骨文、飞利浦、Prop Tiger、Sales Force、Snapdeal、VMWare