给定 N 元树的顶点V和整数K ,任务是打印树中给定顶点的第K个祖先。如果不存在任何这样的祖先,则打印-1 。
例子:
Input: K = 2, V = 4
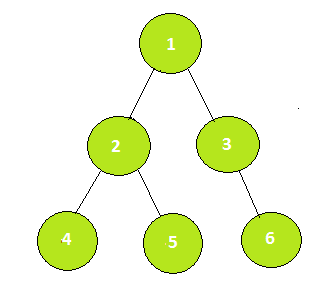
Output: 1
2nd parent of vertex 4 is 1.
Input: K = 3, V = 4
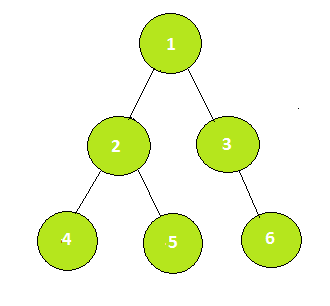
Output: -1
方法:这个想法是使用二元提升技术。这种技术基于这样一个事实,即每个整数都可以用二进制形式表示。通过预处理,可以计算出一个稀疏表table[v][i] ,其中存储了顶点v 的第2个父节点,其中0 ≤ i ≤ log 2 N 。这个预处理需要O(NlogN)时间。
为了找到顶点V 的第K个父节点,让K = b 0 b 1 b 2 …b n是二进制表示中的n位数字,让p 1 , p 2 , p 3 , …, p j是索引其中位值为1,则K可以表示为K = 2 p 1 + 2 p 2 + 2 p 3 + … + 2 p j 。因此,为了到达V 的第K个父节点,我们必须以任意顺序跳转到2 pth 1 、 2 pth 2 、 2 pth 3到2 pth j父节点。这可以通过之前在O(logN)中计算的稀疏表有效地完成。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// CPP implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Table for storing 2^ith parent
int **table;
// To store the height of the tree
int height;
// initializing the table and
// the height of the tree
void initialize(int n)
{
height = (int)ceil(log2(n));
table = new int *[n + 1];
}
// Filling with -1 as initial
void preprocessing(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
table[i] = new int[height + 1];
memset(table[i], -1, sizeof table[i]);
}
}
// Calculating sparse table[][] dynamically
void calculateSparse(int u, int v)
{
// Using the recurrence relation to
// calculate the values of table[][]
table[v][0] = u;
for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++)
{
table[v][i] = table[table[v][i - 1]][i - 1];
// If we go out of bounds of the tree
if (table[v][i] == -1)
break;
}
}
// Function to return the Kth ancestor of V
int kthancestor(int V, int k)
{
// Doing bitwise operation to
// check the set bit
for (int i = 0; i <= height; i++)
{
if (k & (1 << i))
{
V = table[V][i];
if (V == -1)
break;
}
}
return V;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 6;
// initializing
initialize(n);
// Pre-processing
preprocessing(n);
// Calculating ancestors of v
calculateSparse(1, 2);
calculateSparse(1, 3);
calculateSparse(2, 4);
calculateSparse(2, 5);
calculateSparse(3, 6);
int K = 2, V = 5;
cout << kthancestor(V, K) << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.Arrays;
class GfG {
// Table for storing 2^ith parent
private static int table[][];
// To store the height of the tree
private static int height;
// Private constructor for initializing
// the table and the height of the tree
private GfG(int n)
{
// log(n) with base 2
height = (int)Math.ceil(Math.log10(n) / Math.log10(2));
table = new int[n + 1][height + 1];
}
// Filling with -1 as initial
private static void preprocessing()
{
for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) {
Arrays.fill(table[i], -1);
}
}
// Calculating sparse table[][] dynamically
private static void calculateSparse(int u, int v)
{
// Using the recurrence relation to
// calculate the values of table[][]
table[v][0] = u;
for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++) {
table[v][i] = table[table[v][i - 1]][i - 1];
// If we go out of bounds of the tree
if (table[v][i] == -1)
break;
}
}
// Function to return the Kth ancestor of V
private static int kthancestor(int V, int k)
{
// Doing bitwise operation to
// check the set bit
for (int i = 0; i <= height; i++) {
if ((k & (1 << i)) != 0) {
V = table[V][i];
if (V == -1)
break;
}
}
return V;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 6;
// Calling the constructor
GfG obj = new GfG(n);
// Pre-processing
preprocessing();
// Calculating ancestors of v
calculateSparse(1, 2);
calculateSparse(1, 3);
calculateSparse(2, 4);
calculateSparse(2, 5);
calculateSparse(3, 6);
int K = 2, V = 5;
System.out.print(kthancestor(V, K));
}
}Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
import math
class GfG :
# Private constructor for initializing
# the table and the height of the tree
def __init__(self, n):
# log(n) with base 2
# To store the height of the tree
self.height = int(math.ceil(math.log10(n) / math.log10(2)))
# Table for storing 2^ith parent
self.table = [0] * (n + 1)
# Filling with -1 as initial
def preprocessing(self):
i = 0
while ( i < len(self.table)) :
self.table[i] = [-1]*(self.height + 1)
i = i + 1
# Calculating sparse table[][] dynamically
def calculateSparse(self, u, v):
# Using the recurrence relation to
# calculate the values of table[][]
self.table[v][0] = u
i = 1
while ( i <= self.height) :
self.table[v][i] = self.table[self.table[v][i - 1]][i - 1]
# If we go out of bounds of the tree
if (self.table[v][i] == -1):
break
i = i + 1
# Function to return the Kth ancestor of V
def kthancestor(self, V, k):
i = 0
# Doing bitwise operation to
# check the set bit
while ( i <= self.height) :
if ((k & (1 << i)) != 0) :
V = self.table[V][i]
if (V == -1):
break
i = i + 1
return V
# Driver code
# Number of vertices
n = 6
# Calling the constructor
obj = GfG(n)
# Pre-processing
obj.preprocessing()
# Calculating ancestors of v
obj.calculateSparse(1, 2)
obj.calculateSparse(1, 3)
obj.calculateSparse(2, 4)
obj.calculateSparse(2, 5)
obj.calculateSparse(3, 6)
K = 2
V = 5
print(obj.kthancestor(V, K))
# This code is contributed by Arnab KunduC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
class GfG
{
// Table for storing 2^ith parent
private static int [,]table ;
// To store the height of the tree
private static int height;
// Private constructor for initializing
// the table and the height of the tree
private GfG(int n)
{
// log(n) with base 2
height = (int)Math.Ceiling(Math.Log10(n) / Math.Log10(2));
table = new int[n + 1, height + 1];
}
// Filling with -1 as initial
private static void preprocessing()
{
for (int i = 0; i < table.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < table.GetLength(1); j++)
{
table[i, j] = -1;
}
}
}
// Calculating sparse table[,] dynamically
private static void calculateSparse(int u, int v)
{
// Using the recurrence relation to
// calculate the values of table[,]
table[v, 0] = u;
for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++)
{
table[v, i] = table[table[v, i - 1], i - 1];
// If we go out of bounds of the tree
if (table[v, i] == -1)
break;
}
}
// Function to return the Kth ancestor of V
private static int kthancestor(int V, int k)
{
// Doing bitwise operation to
// check the set bit
for (int i = 0; i <= height; i++)
{
if ((k & (1 << i)) != 0)
{
V = table[V, i];
if (V == -1)
break;
}
}
return V;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 6;
// Calling the constructor
GfG obj = new GfG(n);
// Pre-processing
preprocessing();
// Calculating ancestors of v
calculateSparse(1, 2);
calculateSparse(1, 3);
calculateSparse(2, 4);
calculateSparse(2, 5);
calculateSparse(3, 6);
int K = 2, V = 5;
Console.Write(kthancestor(V, K));
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01Javascript
输出:
1时间复杂度: O(NlogN) 用于预处理和 logN 用于查找祖先。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。