顺序电路是具有内部状态概念的电路。这种内部状态的概念是必要的,因为在时序电路中,电路的输出是当前输入和过去输入的函数。时序电路的内部状态只不过是电路过去输入的反映。现在,顺序电路的内部状态由许多状态变量表示。每个状态变量可以处于 2 种可能状态中的一种。这是因为 State Variables 是在 Flip-Flops 的帮助下物理实现的,每个 Flip-Flop 只能代表 2 种可能的状态。因此,如果我们有“N”个触发器,我们最多可以表示 2 N个状态。
最大限度。 ‘N’ 触发器的状态数 = ![]()
这意味着最多可以有一个具有“N”个触发器的顺序电路![]() 内部状态。
内部状态。
现在让我们以使用 T 触发器的同步和异步 2 位二进制递增计数器为例,说明同步和异步顺序电路之间的区别。

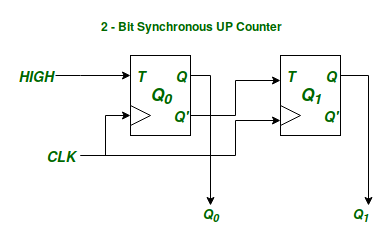
在上述两个电路中![]() 是表示上述每个电路的内部状态的状态变量。由于有 2 个状态变量,上述时序电路可以处于 4 种可能的状态,而计数器的函数是按特定顺序循环遍历这 4 种状态。
是表示上述每个电路的内部状态的状态变量。由于有 2 个状态变量,上述时序电路可以处于 4 种可能的状态,而计数器的函数是按特定顺序循环遍历这 4 种状态。
现在同步和异步电路之间的区别在于电路如何从一个内部状态到下一个内部状态。在同步顺序电路中,所有代表电路内部状态的状态变量都会随着给定的输入时钟信号同时改变它们的状态,以实现下一个状态。
另一方面,在异步电路的情况下,所有状态变量可能不会同时改变其状态以实现下一个稳定的内部状态。换句话说,状态变量不与任何通用时钟信号同步。
比较——
| Synchronous Circuit | Asynchronous Circuit |
|---|---|
| All the State Variable changes are synchronized with a universal clock signal. | The State Variables are not synchronized to change simulteneously and may change at anytime irrespective of each other to achieve the next Steady Internal State |
| Since all the Internal State changes are in the strict control of a master clock source they are less prone to failure or to a race condition and hence are more reliable. | Since there is no such universal clock source, the internal state changes as soon as any of the inputs change and hence are more prone to a race condition. |
| Timings of the internal state changes are in our control. | The changes in the internal state of an asynchronous circuit are not in our control. |