给定一个图G补充图是通过从具有与G相同节点数的完整图中去除G 中包含的边来获得的。
例子:
初始图 G:
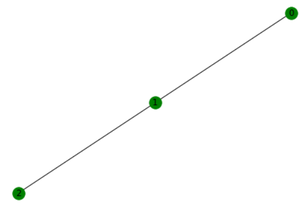
G
G的补:
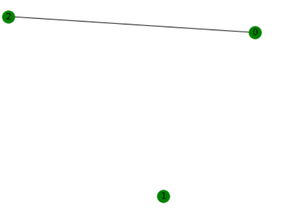
G补
使用Python实现补码:
我们将使用networkx.complement()函数来完成我们的任务
句法:
networkx.complement()
- Returns the complement of the graph object passed.
- The value returned is of the same type of the value passed i.e networkx graph object.
- G is the initial object passed.
- Although the complement is being created but no self-loops and parallel edges are created.
补(G)函数:
如果满足以下条件,则将边 (n,n2)(其中 n 是用于迭代 G 的迭代器)添加到补充图:
- n 和 n2 不是邻居,即 n2 在 n 的邻接表中,反之亦然。
- 并且 n != n2。
- n 和 n2 都是 G 的一部分。
方法:
- 我们将使用别名nx导入networkx 。
- 使用path_graph()函数创建示例图形对象 G。
- 然后我们将调用补充函数,将G作为参数传递。
- 我们将在另一个对象G_C 中捕获补码函数返回的对象。
- 然后我们将调用draw()函数,传递G_C作为参数,它将显示补码图。
Python3
# importing networkx module
import networkx as nx
# creating sample graph object
G = nx.path_graph(3)
# complement of G and saving in G_C
G_C = nx.complement(G)
# calling draw() to visualize the original graph
nx.draw(G, node_color='Green', with_labels=True)
# calling draw() to visualize the complement graph
nx.draw(G_C, node_color='Green', with_labels=True)输出:
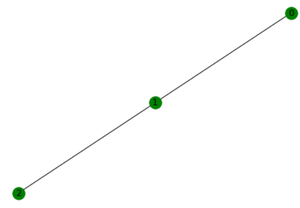
原始图
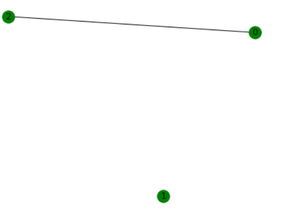
补图
通过使用complement()方法,G 中的所有边都被删除了,所有其他可能性都被添加到G 的补集中并打印出来。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。