给定N个顶点和M 条边的无向图,任务是为给定的 M 条边分配方向,使该图成为强连通分量。如果图形不能转换为强连通分量,则打印“-1” 。
例子:
Input: N = 5, Edges[][] = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 }, { 1, 2 }, { 1, 4 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 } }
Output:
0->1
2->0
4->1
3->4
2->3
1->2
Explanation:
Below is the assigned edges to the above undirected graph:
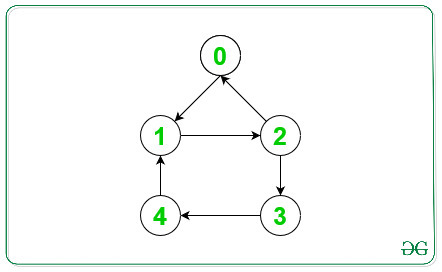
Input: N = 5, Edges[][] = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 } }
Output: -1
Explanation:
Below is the graph for the above information:
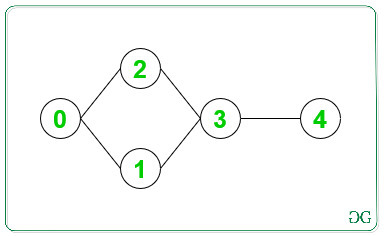
Since there is a bridge present in the above-undirected graph. Therefore, this graph can’t be converted into SCCs.
方法:我们知道在任何有向图中都被称为在强连通分量(SCC)中,如果该图的所有顶点都是某个循环的一部分。当且仅当图中包含任何桥时,给定的无向图不会形成 SCC。以下是步骤:
- 我们将使用数组mark[]来存储 DFS 遍历期间的访问节点,使用order[]存储访问节点的索引号,以及使用bridge_detect[]存储给定图中存在的任何桥。
- 从顶点1开始 DFS 遍历。
- 遍历当前 Node 的 Adjacency 列表并执行以下操作:
- 如果在任何 DFS 调用时再次遍历任何边,则忽略该边。
- 如果子节点(节点 u )的顺序大于父节点(节点 v )的顺序,则忽略此当前边,因为Edges(v, u)已被处理。
- 如果找到任何后边缘,则将当前父节点(节点 v )的桥边缘更新为:
bridge_detect[v] = min(order[u], bridge_detect[v]);- 否则对当前子节点执行 DFS 遍历,并为当前节点重复步骤 3。
- 将当前节点的 DFS 调用后的网桥检测更新为:
bridge_detect[v] = min(bridge_detect[u], bridge_detect[v])- 将当前的Edges(v, u) 对作为从节点 v 到节点 u 的有向边存储在一对数组中(比如arr[][] )。
- 如果给定图中存在任何桥接,则打印“-1” 。
- 否则打印存储在arr[][] 中的有向边。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// To store the assigned Edges
vector > ans;
// Flag variable to check Bridges
int flag = 1;
// Function to implement DFS Traversal
int dfs(vector adj[],
int* order, int* bridge_detect,
bool* mark, int v, int l)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
mark[v] = 1;
// Update the order of node v
order[v] = order[l] + 1;
// Update the bridge_detect for node v
bridge_detect[v] = order[v];
// Traverse the adjacency list of
// Node v
for (int i = 0; i < adj[v].size(); i++) {
int u = adj[v][i];
// Ignores if same edge is traversed
if (u == l) {
continue;
}
// Ignores the edge u --> v as
// v --> u is already processed
if (order[v] < order[u]) {
continue;
}
// Finds a back Edges, cycle present
if (mark[u]) {
// Update the bridge_detect[v]
bridge_detect[v]
= min(order[u],
bridge_detect[v]);
}
// Else DFS traversal for current
// node in the adjacency list
else {
dfs(adj, order, bridge_detect,
mark, u, v);
}
// Update the bridge_detect[v]
bridge_detect[v]
= min(bridge_detect[u],
bridge_detect[v]);
// Store the current directed Edge
ans.push_back(make_pair(v, u));
}
// Condition for Bridges
if (bridge_detect[v] == order[v]
&& l != 0) {
flag = 0;
}
// Return flag
return flag;
}
// Function to print the direction
// of edges to make graph SCCs
void convert(vector adj[], int n)
{
// Arrays to store the visited,
// bridge_detect and order of
// Nodes
int order[n] = { 0 };
int bridge_detect[n] = { 0 };
bool mark[n];
// Initialise marks[] as false
memset(mark, false, sizeof(mark));
// DFS Traversal from vertex 1
int flag = dfs(adj, order,
bridge_detect,
mark, 1, 0);
// If flag is zero, then Bridge
// is present in the graph
if (flag == 0) {
cout << "-1";
}
// Else print the direction of
// Edges assigned
else {
for (auto& it : ans) {
cout << it.first << "->"
<< it.second << '\n';
}
}
}
// Function to create graph
void createGraph(int Edges[][2],
vector adj[],
int M)
{
// Traverse the Edges
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int u = Edges[i][0];
int v = Edges[i][1];
// Push the edges in an
// adjacency list
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// N vertices and M Edges
int N = 5, M = 6;
int Edges[M][2]
= { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 2 }, { 1, 4 },
{ 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 } };
// To create Adjacency List
vector adj[N];
// Create an undirected graph
createGraph(Edges, adj, M);
// Function Call
convert(adj, N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG{
// To store the assigned Edges
static ArrayList ans;
// Flag variable to check Bridges
static int flag = 1;
// Function to implement DFS Traversal
static int dfs(ArrayList> adj,
int[] order, int[] bridge_detect,
boolean[] mark, int v, int l)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
mark[v] = true;
// Update the order of node v
order[v] = order[l] + 1;
// Update the bridge_detect for node v
bridge_detect[v] = order[v];
// Traverse the adjacency list of
// Node v
for(int i = 0; i < adj.get(v).size(); i++)
{
int u = adj.get(v).get(i);
// Ignores if same edge is traversed
if (u == l)
{
continue;
}
// Ignores the edge u --> v as
// v --> u is already processed
if (order[v] < order[u])
{
continue;
}
// Finds a back Edges, cycle present
if (mark[u])
{
// Update the bridge_detect[v]
bridge_detect[v] = Math.min(order[u],
bridge_detect[v]);
}
// Else DFS traversal for current
// node in the adjacency list
else
{
dfs(adj, order, bridge_detect,
mark, u, v);
}
// Update the bridge_detect[v]
bridge_detect[v] = Math.min(bridge_detect[u],
bridge_detect[v]);
// Store the current directed Edge
ans.add(new int[]{v, u});
}
// Condition for Bridges
if (bridge_detect[v] == order[v] && l != 0)
{
flag = 0;
}
// Return flag
return flag;
}
// Function to print the direction
// of edges to make graph SCCs
static void convert(ArrayList> adj,
int n)
{
// Arrays to store the visited,
// bridge_detect and order of
// Nodes
int[] order = new int[n];
int[] bridge_detect = new int[n];
boolean mark[] = new boolean[n];
// DFS Traversal from vertex 1
int flag = dfs(adj, order,
bridge_detect,
mark, 1, 0);
// If flag is zero, then Bridge
// is present in the graph
if (flag == 0)
{
System.out.print("-1");
}
// Else print the direction of
// Edges assigned
else
{
for(int[] it : ans)
{
System.out.println(it[0] + "->" +
it[1]);
}
}
}
// Function to create graph
static void createGraph(int Edges[][],
ArrayList> adj,
int M)
{
// Traverse the Edges
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
int u = Edges[i][0];
int v = Edges[i][1];
// Push the edges in an
// adjacency list
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// N vertices and M Edges
int N = 5, M = 6;
int Edges[][] = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 2 }, { 1, 4 },
{ 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 } };
// To create Adjacency List
ArrayList> adj = new ArrayList<>();
ans = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
// Create an undirected graph
createGraph(Edges, adj, M);
// Function Call
convert(adj, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for
# the above approach
# To store the assigned
# Edges
ans = []
# Flag variable to
# check Bridges
flag = 1;
# Function to implement
# DFS Traversal
def dfs(adj, order,
bridge_detect,
mark, v, l):
global flag
# Mark the current
# node as visited
mark[v] = 1;
# Update the order of
# node v
order[v] = order[l] + 1;
# Update the bridge_detect
# for node v
bridge_detect[v] = order[v];
# Traverse the adjacency list of
# Node v
for i in range(len(adj[v])):
u = adj[v][i];
# Ignores if same edge
# is traversed
if (u == l):
continue;
# Ignores the edge u --> v as
# v --> u is already processed
if (order[v] < order[u]):
continue;
# Finds a back Edges,
# cycle present
if (mark[u]):
# Update the bridge_detect[v]
bridge_detect[v] = min(order[u],
bridge_detect[v]);
# Else DFS traversal for current
# node in the adjacency list
else:
dfs(adj, order,
bridge_detect,
mark, u, v);
# Update the bridge_detect[v]
bridge_detect[v] = min(bridge_detect[u],
bridge_detect[v]);
# Store the current
# directed Edge
ans.append([v, u]);
# Condition for Bridges
if (bridge_detect[v] ==
order[v] and l != 0):
flag = 0;
# Return flag
return flag;
# Function to print the
# direction of edges to
# make graph SCCs
def convert(adj, n):
# Arrays to store the visited,
# bridge_detect and order of
# Nodes
order = [0 for i in range(n)]
bridge_detect = [0 for i in range(n)]
mark = [False for i in range(n)]
# DFS Traversal from
# vertex 1
flag = dfs(adj, order,
bridge_detect,
mark, 1, 0);
# If flag is zero, then Bridge
# is present in the graph
if (flag == 0):
print(-1)
# Else print the direction
# of Edges assigned
else:
for it in ans:
print("{} -> {}".format(it[0],
it[1]))
# Function to create graph
def createGraph(Edges,adj, M):
# Traverse the Edges
for i in range(M):
u = Edges[i][0];
v = Edges[i][1];
# Push the edges in an
# adjacency list
adj[u].append(v);
adj[v].append(u);
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# N vertices and M Edges
N = 5
M = 6;
Edges = [[0, 1], [0, 2],
[1, 2], [1, 4],
[2, 3], [3, 4]];
# To create Adjacency List
adj = [[] for i in range(N)]
# Create an undirected graph
createGraph(Edges, adj, M);
# Function Call
convert(adj, N);
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// To store the assigned Edges
static ArrayList ans;
// Flag variable to check Bridges
static int flag = 1;
// Function to implement DFS Traversal
static int dfs(ArrayList adj,
int[] order, int[] bridge_detect,
bool[] mark, int v, int l)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
mark[v] = true;
// Update the order of node v
order[v] = order[l] + 1;
// Update the bridge_detect for node v
bridge_detect[v] = order[v];
// Traverse the adjacency list of
// Node v
for(int i = 0;
i < ((ArrayList)adj[v]).Count;
i++)
{
int u = (int)((ArrayList)adj[v])[i];
// Ignores if same edge is traversed
if (u == l)
{
continue;
}
// Ignores the edge u --> v as
// v --> u is already processed
if (order[v] < order[u])
{
continue;
}
// Finds a back Edges, cycle present
if (mark[u])
{
// Update the bridge_detect[v]
bridge_detect[v] = Math.Min(order[u],
bridge_detect[v]);
}
// Else DFS traversal for current
// node in the adjacency list
else
{
dfs(adj, order, bridge_detect,
mark, u, v);
}
// Update the bridge_detect[v]
bridge_detect[v] = Math.Min(bridge_detect[u],
bridge_detect[v]);
// Store the current directed Edge
ans.Add(new int[]{v, u});
}
// Condition for Bridges
if (bridge_detect[v] == order[v] && l != 0)
{
flag = 0;
}
// Return flag
return flag;
}
// Function to print the direction
// of edges to make graph SCCs
static void convert(ArrayList adj,
int n)
{
// Arrays to store the visited,
// bridge_detect and order of
// Nodes
int[] order = new int[n];
int[] bridge_detect = new int[n];
bool []mark = new bool[n];
// DFS Traversal from vertex 1
int flag = dfs(adj, order,
bridge_detect,
mark, 1, 0);
// If flag is zero, then Bridge
// is present in the graph
if (flag == 0)
{
Console.Write("-1");
}
// Else print the direction of
// Edges assigned
else
{
foreach(int[] it in ans)
{
Console.WriteLine(it[0] + "->" +
it[1]);
}
}
}
// Function to create graph
static void createGraph(int [,]Edges,
ArrayList adj,
int M)
{
// Traverse the Edges
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
int u = Edges[i, 0];
int v = Edges[i, 1];
// Push the edges in an
// adjacency list
((ArrayList)adj[u]).Add(v);
((ArrayList)adj[v]).Add(u);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// N vertices and M Edges
int N = 5, M = 6;
int [,]Edges = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 2 }, { 1, 4 },
{ 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 } };
// To create Adjacency List
ArrayList adj = new ArrayList();
ans = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
adj.Add(new ArrayList());
// Create an undirected graph
createGraph(Edges, adj, M);
// Function Call
convert(adj, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham760->1
2->0
4->1
3->4
2->3
1->2时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。