给定一个只包含一个循环的N个顶点和N 个边的无向图,以及一个大小为N的数组arr[] ,其中arr[i]表示第i个节点的值,任务是检查循环是否可以分成两个分量,使得两个分量中所有节点值的总和相同。
例子:
Input: N = 10, arr[] = {4, 2, 3, 3, 1, 2, 6, 2, 2, 5}, edges[] = {{1, 2}, {1, 5}, {1, 3}, {2, 6}, {2, 7}, {2, 4}, {4, 8}, {4, 3}, {3, 9}, {9, 10} }
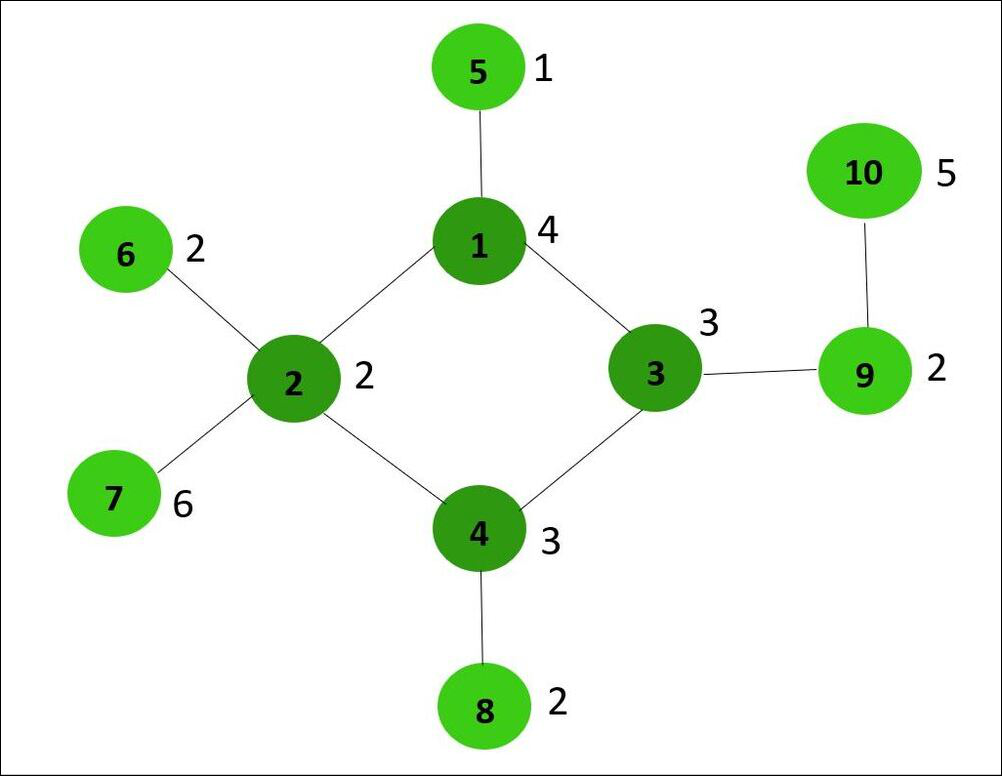
Output: Yes
Explanation: By removing the edges 1-2 and 3-4, the sum of all the node values of both the generated components is equal to 15.

Input: N= 4, arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 3}, edges[] = {{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {2, 4}}

Output: No
Explanation: No possible way exists to obtain two equal sum components by removing an edges from the cycle.
方法:解决这个问题的想法是首先找到属于循环的节点。然后,将不属于循环的每个节点的值添加到循环中其最近的节点。最后一步涉及检查循环是否可以分为两个相等的和分量。以下是步骤:
- 第一步是使用 DFS 在无向图中使用检测循环找到属于循环的所有节点。
- 在给定的图形上执行 DFS 遍历并执行以下操作:
- 将当前节点标记为已访问。对于连接到当前节点的每个未访问节点,递归地为每个节点执行 DFS 遍历。
- 如果当前节点的相邻节点已经被访问过并且与当前节点的前一个节点不同,那么这意味着当前节点是循环的一部分。回溯直到到达这个特定的相邻节点以找到属于循环的所有节点并将它们存储在向量inCycle[] 中。
- 找到inCycle[] 中每个节点的值的总和,并将该总和添加到当前的inCycle[]节点值中。
- 找到inCycle[] 中存在的所有节点的值的总和,并将其存储在变量totalSum 中。如果totalSum 的值为奇数,则打印“否”,因为具有奇数和的循环不能分为两个相等的和分量。
- 否则,检查inCycle[] 中是否存在totalSum/2的值,然后打印“Yes”否则打印“No” 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Recursive function to find all the
// nodes that are part of the cycle
void findNodesinCycle(int u, bool* vis,
int* prev,
vector adj[],
vector& inCycle)
{
// Mark current node as visited
vis[u] = true;
for (int v : adj[u]) {
// If node v is not visited
if (!vis[v]) {
prev[v] = u;
// Recursively find cycle
findNodesinCycle(v, vis, prev,
adj, inCycle);
// If cycle is detected then
// return the previous node
if (!inCycle.empty())
return;
}
// If node is already visited
// and not equal to prev[u]
else if (v != prev[u]) {
int curr = u;
inCycle.push_back(curr);
// Backtrack all vertices
// that are part of cycle
// and store them in inCycle
while (curr != v) {
curr = prev[curr];
inCycle.push_back(curr);
}
// As the cycle is detected
// return the previous node
return;
}
}
}
// Function to add the value of each
// node which is not part of the cycle
// to its nearest node in the cycle
int sumOfnonCycleNodes(
int u, vector adj[],
vector inCycle, bool* vis,
int arr[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited
vis[u] = true;
// Stores the value of required sum
int sum = 0;
for (int v : adj[u]) {
// If v is not already visited
// and not present in inCycle
if (!vis[v]
&& find(inCycle.begin(),
inCycle.end(), v)
== inCycle.end()) {
// Add to sum and call the
// function recursively
sum += (arr[v - 1]
+ sumOfnonCycleNodes(
v, adj, inCycle,
vis, arr));
}
}
// Return the value of sum
return sum;
}
// Function that add the edges
// to the graph
void addEdge(vector adj[],
int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
// Utility Function to check if the cycle
// can be divided into two same sum
bool isBreakingPossible(vector adj[],
int arr[], int N)
{
// Stores all the nodes that are
// part of the cycle
vector inCycle;
// Array to check if a node is
// already visited or not
bool vis[N + 1];
// Initialize vis to false
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
// Array to store the previous node
// of the current node
int prev[N + 1];
// Initialize prev to 0
memset(prev, 0, sizeof prev);
// Recursive function call
findNodesinCycle(1, vis, prev,
adj, inCycle);
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
// Update value of each inCycle
// node
for (int u : inCycle) {
// Add sum of values of all
// required node to current
// inCycle node value
arr[u - 1] += sumOfnonCycleNodes(
u, adj, inCycle, vis, arr);
}
// Stores total sum of values of
// all nodes present in inCycle
int tot_sum = 0;
// Find the total required sum
for (int node : inCycle) {
tot_sum += arr[node - 1];
}
// If value of tot_sum is odd
// then return false
if (tot_sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
int req_sum = tot_sum / 2;
// Create an empty map
unordered_map map;
// Initialise map[0]
map[0] = -1;
// Maintain the sum of values of
// nodes so far
int curr_sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < inCycle.size(); i++) {
// Add the current node value
// to curr_sum
curr_sum += arr[inCycle[i] - 1];
// If curr_sum - req_sum in map
// then there is a subarray of
// nodes with sum of their values
// equal to req_sum
if (map.find(curr_sum - req_sum)
!= map.end()) {
return true;
}
map[curr_sum] = i;
}
// If no such subarray exists
return false;
}
// Function to check if the cycle can
// be divided into two same sum
void checkCycleDivided(int edges[][2],
int arr[],
int N)
{
vector adj[N + 1];
// Traverse the given edges
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
// Add the edges
addEdge(adj, u, v);
}
// Print the result
cout << (isBreakingPossible(
adj, arr, N)
? "Yes"
: "No");
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 10;
int edges[][2] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 5 }, { 1, 3 }, { 2, 6 }, { 2, 7 }, { 2, 4 }, { 4, 8 }, { 4, 3 }, { 3, 9 }, { 9, 10 } };
int arr[] = { 4, 2, 3, 3, 1,
2, 6, 2, 2, 5 };
// Function Call
checkCycleDivided(edges, arr, N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Recursive function to find all the
// nodes that are part of the cycle
static void findNodesinCycle(int u, boolean[] vis,
int[] prev,
ArrayList> adj,
ArrayList inCycle)
{
// Mark current node as visited
vis[u] = true;
for (int v : adj.get(u))
{
// If node v is not visited
if (!vis[v])
{
prev[v] = u;
// Recursively find cycle
findNodesinCycle(v, vis, prev,
adj, inCycle);
// If cycle is detected then
// return the previous node
if (inCycle.size() > 0)
return;
}
// If node is already visited
// and not equal to prev[u]
else if (v != prev[u])
{
int curr = u;
inCycle.add(curr);
// Backtrack all vertices
// that are part of cycle
// and store them in inCycle
while (curr != v)
{
curr = prev[curr];
inCycle.add(curr);
}
// As the cycle is detected
// return the previous node
return;
}
}
}
// Function to add the value of each
// node which is not part of the cycle
// to its nearest node in the cycle
static int sumOfnonCycleNodes(
int u, ArrayList> adj,
ArrayList inCycle, boolean[] vis,
int arr[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited
vis[u] = true;
// Stores the value of required sum
int sum = 0;
for (int v : adj.get(u))
{
// If v is not already visited
// and not present in inCycle
if (!vis[v]
&& !inCycle.contains(v))
{
// Add to sum and call the
// function recursively
sum += (arr[v - 1] + sumOfnonCycleNodes(
v, adj, inCycle, vis, arr));
}
}
// Return the value of sum
return sum;
}
// Utility Function to check if the cycle
// can be divided into two same sum
static boolean isBreakingPossible(ArrayList> adj,
int arr[], int N)
{
// Stores all the nodes that are
// part of the cycle
ArrayList inCycle = new ArrayList<>();
// Array to check if a node is
// already visited or not
boolean[] vis = new boolean[N + 1];
// Array to store the previous node
// of the current node
int[] prev = new int[N + 1];
// Recursive function call
findNodesinCycle(1, vis, prev,
adj, inCycle);
Arrays.fill(vis,false);
// Update value of each inCycle
// node
for (Integer u : inCycle)
{
// Add sum of values of all
// required node to current
// inCycle node value
arr[u - 1] += sumOfnonCycleNodes(
u, adj, inCycle, vis, arr);
}
// Stores total sum of values of
// all nodes present in inCycle
int tot_sum = 0;
// Find the total required sum
for (int node : inCycle)
{
tot_sum += arr[node - 1];
}
// If value of tot_sum is odd
// then return false
if (tot_sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
int req_sum = tot_sum / 2;
// Create an empty map
Map map = new HashMap<>();
// Initialise map[0]
map.put(0, -1);
// Maintain the sum of values of
// nodes so far
int curr_sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < inCycle.size(); i++)
{
// Add the current node value
// to curr_sum
curr_sum += arr[inCycle.get(i) - 1];
// If curr_sum - req_sum in map
// then there is a subarray of
// nodes with sum of their values
// equal to req_sum
if (map.containsKey(curr_sum - req_sum))
{
return true;
}
map.put(curr_sum, i);
}
// If no such subarray exists
return false;
}
// Function to check if the cycle can
// be divided into two same sum
static void checkCycleDivided(int edges[][],
int arr[], int N)
{
ArrayList> adj = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
// Traverse the given edges
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
// Add the edges
adj.get(u).add(v);
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
// Print the result
System.out.print(isBreakingPossible(
adj, arr, N) ? "Yes" : "No");
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int N = 10;
int edges[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 5 },
{ 1, 3 }, { 2, 6 },
{ 2, 7 }, { 2, 4 },
{ 4, 8 }, { 4, 3 },
{ 3, 9 }, { 9, 10 } };
int arr[] = { 4, 2, 3, 3, 1,
2, 6, 2, 2, 5 };
// Function Call
checkCycleDivided(edges, arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Recursive function to find all the
# nodes that are part of the cycle
def findNodesinCycle(u):
global adj, pre, inCycle, vis
vis[u] = True
for v in adj[u]:
# If node v is not visited
if (not vis[v]):
pre[v] = u
# Recursively find cycle
findNodesinCycle(v)
# If cycle is detected then
# return the previous node
if (len(inCycle) > 0):
return
# If node is already visited
# and not equal to prev[u]
elif (v != pre[u]):
curr = u
inCycle.append(curr)
# Backtrack all vertices
# that are part of cycle
# and store them in inCycle
while (curr != v):
curr = pre[curr]
inCycle.append(curr)
# As the cycle is detected
# return the previous node
return
# Function to add the value of each
# node which is not part of the cycle
# to its nearest node in the cycle
def sumOfnonCycleNodes(u, arr):
global adj, pre, inCycle, vis
vis[u] = True
# Stores the value of required sum
sum = 0
for v in adj[u]:
# If v is not already visited
# and not present in inCycle
if (not vis[v]) and (v not in inCycle):
# Add to sum and call the
# function recursively
sum += (arr[v - 1] + sumOfnonCycleNodes(v, arr))
# Return the value of sum
return sum
# Function that add the edges
# to the graph
def addEdge(u, v):
global adj
adj[u].append(v)
adj[v].append(u)
# Utility Function to check if the cycle
# can be divided into two same sum
def isBreakingPossible(arr, N):
# Stores all the nodes that are
global adj, vis, pre
# Recursive function call
findNodesinCycle(1,)
for i in range(N + 1):
vis[i] = False
# Update value of each inCycle
# node
for u in inCycle:
# Add sum of values of all
# required node to current
# inCycle node value
arr[u - 1] += sumOfnonCycleNodes(u, arr)
# Stores total sum of values of
# all nodes present in inCycle
tot_sum = 0
# Find the total required sum
for node in inCycle:
tot_sum += arr[node - 1]
# If value of tot_sum is odd
# then return false
if (tot_sum % 2 != 0):
return False
req_sum = tot_sum // 2
# Create an empty map
map = {}
# Initialise map[0]
map[0] = -1
# Maintain the sum of values of
# nodes so far
curr_sum = 0
for i in range(len(inCycle)):
# Add the current node value
# to curr_sum
curr_sum += arr[inCycle[i] - 1]
# If curr_sum - req_sum in map
# then there is a subarray of
# nodes with sum of their values
# equal to req_sum
if ((curr_sum - req_sum) in map):
return True
map[curr_sum] = i
# If no such subarray exists
return False
# Function to check if the cycle can
# be divided into two same sum
def checkCycleDivided(edges, arr, N):
global adj
# Traverse the given edges
for i in range(N):
u = edges[i][0]
v = edges[i][1]
# Add the edges
addEdge(u, v)
# Print the result
print("Yes" if isBreakingPossible(arr, N) else "No")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 10
edges= [[1, 2], [1, 5], [1, 3],
[2, 6], [2, 7], [2, 4],
[4, 8], [4, 3], [3, 9],
[9, 10]]
arr, adj, vis = [4, 2, 3, 3, 1,
2, 6, 2, 2, 5], [[] for i in range(N + 1)], [False for i in range(N+1)]
inCycle, pre =[], [0 for i in range(N+1)]
checkCycleDivided(edges, arr, N)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
// Recursive function to find all the
// nodes that are part of the cycle
static void findNodesinCycle(int u, bool[] vis,int[] prev,
List> adj,List inCycle)
{
// Mark current node as visited
vis[u] = true;
foreach(int v in adj[u])
{
// If node v is not visited
if (!vis[v])
{
prev[v] = u;
// Recursively find cycle
findNodesinCycle(v, vis, prev,adj, inCycle);
// If cycle is detected then
// return the previous node
if (inCycle.Count > 0)
return;
}
// If node is already visited
// and not equal to prev[u]
else if (v != prev[u])
{
int curr = u;
inCycle.Add(curr);
// Backtrack all vertices
// that are part of cycle
// and store them in inCycle
while (curr != v)
{
curr = prev[curr];
inCycle.Add(curr);
}
// As the cycle is detected
// return the previous node
return;
}
}
}
// Function to add the value of each
// node which is not part of the cycle
// to its nearest node in the cycle
static int sumOfnonCycleNodes(int u, List> adj,List inCycle, bool[] vis,int[] arr)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
vis[u] = true;
// Stores the value of required sum
int sum = 0;
foreach(int v in adj[u])
{
// If v is not already visited
// and not present in inCycle
if (!vis[v] && !inCycle.Contains(v))
{
// Add to sum and call the
// function recursively
sum += (arr[v - 1] + sumOfnonCycleNodes(v, adj, inCycle, vis, arr));
}
}
// Return the value of sum
return sum;
}
// Utility Function to check if the cycle
// can be divided into two same sum
static bool isBreakingPossible(List> adj,int[] arr, int N)
{
// Stores all the nodes that are
// part of the cycle
List inCycle = new List();
// Array to check if a node is
// already visited or not
bool[] vis = new bool[N + 1];
// Array to store the previous node
// of the current node
int[] prev = new int[N + 1];
// Recursive function call
findNodesinCycle(1, vis, prev, adj, inCycle);
// Update value of each inCycle
// node
foreach(int u in inCycle)
{
// Add sum of values of all
// required node to current
// inCycle node value
arr[u - 1] += sumOfnonCycleNodes(u, adj, inCycle, vis, arr);
}
// Stores total sum of values of
// all nodes present in inCycle
int tot_sum = 0;
// Find the total required sum
foreach(int node in inCycle)
{
tot_sum += arr[node - 1];
}
// If value of tot_sum is odd
// then return false
if (tot_sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
int req_sum = tot_sum / 2;
// Create an empty map
Dictionary map = new Dictionary();
// Initialise map[0]
map.Add(0, -1);
// Maintain the sum of values of
// nodes so far
int curr_sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < inCycle.Count; i++)
{
// Add the current node value
// to curr_sum
curr_sum += arr[inCycle[i] - 1];
// If curr_sum - req_sum in map
// then there is a subarray of
// nodes with sum of their values
// equal to req_sum
if (map.ContainsKey(curr_sum - req_sum))
{
return true;
}
map.Add(curr_sum, i);
}
// If no such subarray exists
return false;
}
// Function to check if the cycle can
// be divided into two same sum
static void checkCycleDivided(int[,] edges,int[] arr, int N)
{
List> adj = new List>();
for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
{
adj.Add(new List());
}
// Traverse the given edges
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int u = edges[i,0];
int v = edges[i,1];
// Add the edges
adj[u].Add(v);
adj[v].Add(u);
}
// Print the result
Console.Write(isBreakingPossible(adj, arr, N) ? "Yes" : "No");
}
// Driver code
static public void Main (){
int N = 10;
int[,] edges = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 5 },
{ 1, 3 }, { 2, 6 },
{ 2, 7 }, { 2, 4 },
{ 4, 8 }, { 4, 3 },
{ 3, 9 }, { 9, 10 } };
int[] arr = { 4, 2, 3, 3, 1,
2, 6, 2, 2, 5 };
// Function Call
checkCycleDivided(edges, arr, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 Javascript
Yes时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。