给定一个加权的有向图G ,一个由顶点组成的数组 V[] ,任务是找到通过集合V 的所有顶点的最小成本路径,从给定的源S到目的地D 。
例子:
Input: V = {7}, S = 0, D = 6
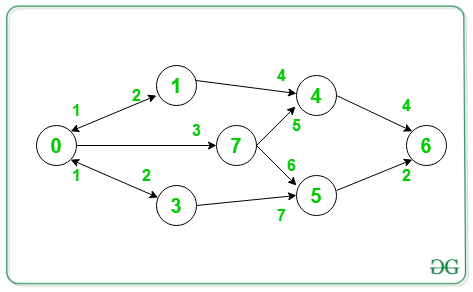
Output: 11
Explanation:
Minimum path 0->7->5->6.
Therefore, the cost of the path = 3 + 6 + 2 = 11
Input: V = {7, 4}, S = 0, D = 6
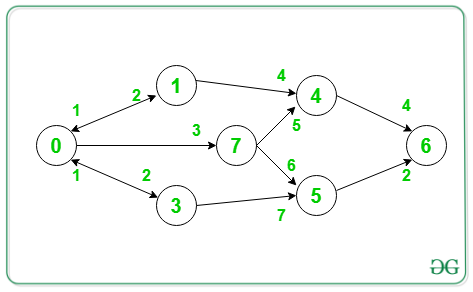
Output: 12
Explanation:
Minimum path 0->7->4->6.
Therefore the cost of the path = 3 + 5 + 4 = 12
方法:
为了解决这个问题,想法是使用广度优先搜索遍历。 BFS一般用于寻找图中的最短路径,BFS 可以从这些节点计算出所有节点到 Source、中间节点和 Destination 的最小距离。
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 将minSum初始化为INT_MAX 。
- 使用BFS从源节点S遍历图。
- 将源的每个相邻节点标记为新源,并从该节点执行BFS 。
- 一旦遇到目标节点D ,则检查是否访问了所有中间节点。
- 如果访问了所有中间节点,则更新minSum并返回最小值。
- 如果没有访问所有中间节点,则返回minSum 。
- 将源标记为未访问。
- 打印得到的minSum的最终值。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Stores minimum-cost of path from source
int minSum = INT_MAX;
// Function to Perform BFS on graph g
// starting from vertex v
void getMinPathSum(unordered_map > >& graph,
vector& visited,
vector necessary,
int src, int dest, int currSum)
{
// If destination is reached
if (src == dest) {
// Set flag to true
bool flag = true;
// Visit all the intermediate nodes
for (int i : necessary) {
// If any intermediate node
// is not visited
if (!visited[i]) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// If all intermediate
// nodes are visited
if (flag)
// Update the minSum
minSum = min(minSum, currSum);
return;
}
else {
// Mark the current node
// visited
visited[src] = true;
// Traverse adjacent nodes
for (auto node : graph[src]) {
if (!visited[node.first]) {
// Mark the neighbour visited
visited[node.first] = true;
// Find minimum cost path
// considering the neighbour
// as the source
getMinPathSum(graph, visited,
necessary, node.first,
dest, currSum + node.second);
// Mark the neighbour unvisited
visited[node.first] = false;
}
}
// Mark the source unvisited
visited[src] = false;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Stores the graph
unordered_map > >
graph;
graph[0] = { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 2 } };
graph[1] = { { 4, 4 }, { 0, 1 } };
graph[2] = { { 4, 5 }, { 5, 6 } };
graph[3] = { { 5, 7 }, { 0, 1 } };
graph[4] = { { 6, 4 } };
graph[5] = { { 6, 2 } };
graph[6] = { { 7, 11 } };
// Number of nodes
int n = 7;
// Source
int source = 0;
// Destination
int dest = 6;
// Keeps a check on visited
// and unvisited nodes
vector visited(n, false);
// Stores intemediate nodes
vector necessary{ 2, 4 };
getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary,
source, dest, 0);
// If no path is found
if (minSum == INT_MAX)
cout << "-1\n";
else
cout << minSum << '\n';
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
pair(int f, int s)
{
this.first = f;
this.second = s;
}
}
// Stores minimum-cost of path from source
static int minSum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Function to Perform BFS on graph g
// starting from vertex v
static void getMinPathSum(Map> graph,
boolean[] visited,
ArrayList necessary,
int source, int dest, int currSum)
{
// If destination is reached
if (src == dest)
{
// Set flag to true
boolean flag = true;
// Visit all the intermediate nodes
for(int i : necessary)
{
// If any intermediate node
// is not visited
if (!visited[i])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// If all intermediate
// nodes are visited
if (flag)
// Update the minSum
minSum = Math.min(minSum, currSum);
return;
}
else
{
// Mark the current node
// visited
visited[src] = true;
// Traverse adjacent nodes
for(pair node : graph.get(src))
{
if (!visited[node.first])
{
// Mark the neighbour visited
visited[node.first] = true;
// Find minimum cost path
// considering the neighbour
// as the source
getMinPathSum(graph, visited,
necessary, node.first,
dest, currSum + node.second);
// Mark the neighbour unvisited
visited[node.first] = false;
}
}
// Mark the source unvisited
visited[src] = false;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Stores the graph
Map> graph = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i <= 6; i++)
graph.put(i, new ArrayList());
graph.get(0).add(new pair(1, 2));
graph.get(0).add(new pair(2, 3));
graph.get(0).add(new pair(3, 2));
graph.get(1).add(new pair(4, 4));
graph.get(1).add(new pair(0, 1));
graph.get(2).add(new pair(4, 5));
graph.get(2).add(new pair(5, 6));
graph.get(3).add(new pair(5, 7));
graph.get(3).add(new pair(0, 1));
graph.get(4).add(new pair(6, 4));
graph.get(5).add(new pair(4, 2));
graph.get(6).add(new pair(7, 11));
// Number of nodes
int n = 7;
// Source
int source = 0;
// Destination
int dest = 6;
// Keeps a check on visited
// and unvisited nodes
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
// Stores intemediate nodes
ArrayList necessary = new ArrayList<>(
Arrays.asList(2, 4));
getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary,
source, dest, 0);
// If no path is found
if (minSum == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
System.out.println(-1);
else
System.out.println(minSum);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 Program to implement
# the above approach
# Stores minimum-cost of path from source
minSum = 1000000000
# Function to Perform BFS on graph g
# starting from vertex v
def getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary,
source, dest, currSum):
global minSum
# If destination is reached
if (src == dest):
# Set flag to true
flag = True;
# Visit all the intermediate nodes
for i in necessary:
# If any intermediate node
# is not visited
if (not visited[i]):
flag = False;
break;
# If all intermediate
# nodes are visited
if (flag):
# Update the minSum
minSum = min(minSum, currSum);
return;
else:
# Mark the current node
# visited
visited[src] = True;
# Traverse adjacent nodes
for node in graph[src]:
if not visited[node[0]]:
# Mark the neighbour visited
visited[node[0]] = True;
# Find minimum cost path
# considering the neighbour
# as the source
getMinPathSum(graph, visited,
necessary, node[0],
dest, currSum + node[1]);
# Mark the neighbour unvisited
visited[node[0]] = False;
# Mark the source unvisited
visited[src] = False;
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Stores the graph
graph=dict()
graph[0] = [ [ 1, 2 ], [ 2, 3 ], [ 3, 2 ] ];
graph[1] = [ [ 4, 4 ], [ 0, 1 ] ];
graph[2] = [ [ 4, 5 ], [ 5, 6 ] ];
graph[3] = [ [ 5, 7 ], [ 0, 1 ] ];
graph[4] = [ [ 6, 4 ] ];
graph[5] = [ [ 6, 2 ] ];
graph[6] = [ [ 7, 11 ] ];
# Number of nodes
n = 7;
# Source
source = 0;
# Destination
dest = 6;
# Keeps a check on visited
# and unvisited nodes
visited=[ False for i in range(n + 1)]
# Stores intemediate nodes
necessary = [ 2, 4 ];
getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary,
source, dest, 0);
# If no path is found
if (minSum == 1000000000):
print(-1)
else:
print(minSum)
# This code is contributed by pratham76C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int f, int s)
{
this.first = f;
this.second = s;
}
}
// Stores minimum-cost of path from source
static int minSum = 100000000;
// Function to Perform BFS on graph g
// starting from vertex v
static void getMinPathSum(Dictionary graph,
bool[] visited, ArrayList necessary,
int source, int dest, int currSum)
{
// If destination is reached
if (src == dest)
{
// Set flag to true
bool flag = true;
// Visit all the intermediate nodes
foreach(int i in necessary)
{
// If any intermediate node
// is not visited
if (!visited[i])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// If all intermediate
// nodes are visited
if (flag)
// Update the minSum
minSum = Math.Min(minSum, currSum);
return;
}
else
{
// Mark the current node
// visited
visited[src] = true;
// Traverse adjacent nodes
foreach(pair node in graph)
{
if (!visited[node.first])
{
// Mark the neighbour visited
visited[node.first] = true;
// Find minimum cost path
// considering the neighbour
// as the source
getMinPathSum(graph, visited,
necessary, node.first,
dest, currSum + node.second);
// Mark the neighbour unvisited
visited[node.first] = false;
}
}
// Mark the source unvisited
visited[src] = false;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Stores the graph
Dictionary graph = new Dictionary();
for(int i = 0; i <= 6; i++)
graph[i] = new ArrayList();
graph[0].Add(new pair(1, 2));
graph[0].Add(new pair(2, 3));
graph[0].Add(new pair(3, 2));
graph[1].Add(new pair(4, 4));
graph[1].Add(new pair(0, 1));
graph[2].Add(new pair(4, 5));
graph[2].Add(new pair(5, 6));
graph[3].Add(new pair(5, 7));
graph[3].Add(new pair(0, 1));
graph[4].Add(new pair(6, 4));
graph[5].Add(new pair(4, 2));
graph[6].Add(new pair(7, 11));
// Number of nodes
int n = 7;
// Source
int source = 0;
// Destination
int dest = 6;
// Keeps a check on visited
// and unvisited nodes
bool[] visited = new bool[n];
// Stores intemediate nodes
ArrayList necessary = new ArrayList();
necessary.Add(2);
necessary.Add(4);
getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, 0);
// If no path is found
if (minSum == 100000000)
Console.WriteLine(-1);
else
Console.WriteLine(minSum);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56 Javascript
输出:
12时间复杂度: O(N+M)
辅助空间: O(N+M)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。