给定成本矩阵 cost[][] 和在 cost[][] 中的位置 (m, n),编写一个函数,返回从 (0, 0) 到达 (m, n) 的最小成本路径的成本。矩阵的每个单元格表示遍历该单元格的成本。到达路径的总成本 (m, n) 是该路径(包括源和目的地)上所有成本的总和。您只能从给定的单元格向下、向右和斜下方的单元格遍历,即从给定的单元格 (i, j)、单元格 (i+1, j)、(i, j+1) 和 (i+1, j+1) 可以遍历。您可以假设所有成本都是正整数。
例如,在下图中,到 (2, 2) 的最小成本路径是什么? 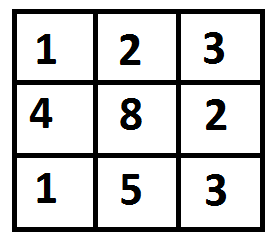
下图突出显示了成本最低的路径。路径是(0, 0) –> (0, 1) –> (1, 2) –> (2, 2)。路径的成本是 8 (1 + 2 + 2 + 3)。
/* Java program for Dynamic Programming implementation
of Min Cost Path problem */
import java.util.*;
class MinimumCostPath {
/* A utility function that returns minimum of 3 integers */
private static int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z) ? x : z;
else
return (y < z) ? y : z;
}
private static int minCost(int cost[][], int m, int n)
{
int i, j;
int tc[][] = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
tc[i][0] = tc[i - 1][0] + cost[i][0];
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j - 1] + cost[0][j];
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i - 1][j - 1],
tc[i - 1][j],
tc[i][j - 1])
+ cost[i][j];
return tc[m][n];
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
int cost[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 8, 2 },
{ 1, 5, 3 } };
System.out.println("minimum cost to reach" +
" (2, 2) = " + minCost(cost, 2, 2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Pankaj Kumar
输出:
minimum cost to reach (2, 2) = 8
请参阅关于动态规划的完整文章 |设置 6(最小成本路径)了解更多详情!
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。