给定N条垂直线(平行于Y轴)的x坐标和从(x1,y1)延伸到(x2,y2)的M条线段,任务是找到线段与垂直线的交点总数.
例子:
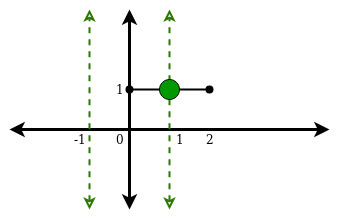
Input: N = 2, M = 1, lines[] = {-1, 1}, Segments[][4] = {0, 1, 2, 1}
Output: 1
Explanation:
There is only one point of intersection (1, 1)
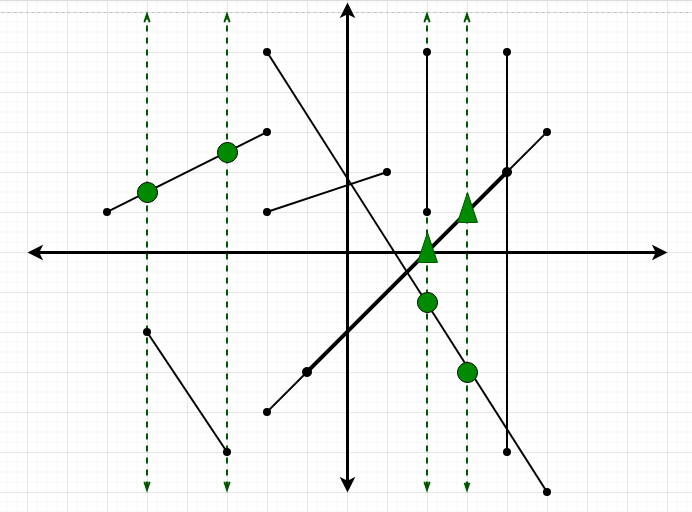
Input: N = 4, M = 8, lines[] = {-5, -3, 2, 3}, segments[][4] = {{-2, 5, 5, -6}, {-5, -2, -3, -5}, {-2, 3, -6, 1}, {-1, -3, 4, 2}, { 2, 5, 2, 1}, { 4, 5, 4, -5}, {-2, -4, 5, 3}, { 1, 2, -2, 1}};
Output: 8
Explanation:
There are total of 8 intersections.
Dotted lines are the vertical lines.
A green circle denote a single point of intersection and
a green triangle denotes that two line segments
intersect same vertical line at that point.
天真的方法:
最简单的方法是,对于每个查询,检查垂直线是否落在两点的x 坐标之间。因此,每个段将具有 O(N) 计算复杂度。
时间复杂度: O(N * M)
方法二:思路是使用Prefix Sum来高效解决这个问题。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 我们可以做出的第一个观察是y 坐标无关紧要。此外,我们可以观察到,仅仅接触垂直线不算作交叉点。
- 首先,计算到目前为止垂直线出现次数的前缀数组,然后从数字中减去直到x2-1的出现次数(我们不考虑 x2,因为它只是作为触摸而不是交集)直到x1的出现次数。因此,对于每个段,计算复杂度降低到O(1) 。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ implementation for the
// above approach.
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to create prefix sum array
void createPrefixArray(int n, int arr[],
int prefSize,
int pref[])
{
// Initialize the prefix array
// to remove garbage values
for (int i = 0; i < prefSize; i++) {
pref[i] = 0;
}
// Marking the occurences of
// vertical lines
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// x is the value after
// Index mapping
int x = arr[i] + 1000000;
pref[x]++;
}
// Creating the prefix array
for (int i = 1; i < prefSize; i++) {
pref[i] += pref[i - 1];
}
}
// Function returns the count of
// total intersection
int pointsOfIntersection(int m,
int segments[][4],
int size,
int pref[])
{
// ans is the number of points of
// intersection of the line segments
// with the vertical lines
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x1 = segments[i][0];
int x2 = segments[i][2];
// Index mapping
x1 = x1 + 1000000;
x2 = x2 + 1000000;
// We don't consider a vertical
// line segment because even if
// it falls on a verticale line
// then it just touches it and
// not intersects.
if (x1 != x2) {
// We have assumed that x1
// will be left and x2 right
// but if not then we just
// swap them
if (x1 > x2) {
swap(x1, x2);
}
int Occ_Till_Right = pref[x2 - 1];
int Occ_Till_Left = pref[x1];
ans = ans + (Occ_Till_Right
- Occ_Till_Left);
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
// N is the number of vertical lines
// M is the number of line segments
int N = 4;
int M = 8;
int size = 2000000 + 2;
int pref[size];
int lines[N] = { -5, -3, 2, 3 };
// Format : x1, y1, x2, y1
int segments[M][4] = { { -2, 5, 5, -6 },
{ -5, -2, -3, -5 },
{ -2, 3, -6, 1 },
{ -1, -3, 4, 2 },
{ 2, 5, 2, 1 },
{ 4, 5, 4, -5 },
{ -2, -4, 5, 3 },
{ 1, 2, -2, 1 } };
// First create the prefix array
createPrefixArray(N, lines, size, pref);
// Print the total number of intersections
cout << pointsOfIntersection(M, segments,
size, pref)
<< endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation for the
// above approach.
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to create prefix sum array
static void createPrefixArray(int n, int arr[],
int prefSize,
int pref[])
{
// Initialize the prefix array
// to remove garbage values
for(int i = 0; i < prefSize; i++)
{
pref[i] = 0;
}
// Marking the occurences of
// vertical lines
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// x is the value after
// Index mapping
int x = arr[i] + 1000000;
pref[x]++;
}
// Creating the prefix array
for(int i = 1; i < prefSize; i++)
{
pref[i] += pref[i - 1];
}
}
// Function returns the count of
// total intersection
static int pointsOfIntersection(int m,
int segments[][],
int size,
int pref[])
{
// ans is the number of points of
// intersection of the line segments
// with the vertical lines
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x1 = segments[i][0];
int x2 = segments[i][2];
// Index mapping
x1 = x1 + 1000000;
x2 = x2 + 1000000;
// We don't consider a vertical
// line segment because even if
// it falls on a verticale line
// then it just touches it and
// not intersects.
if (x1 != x2)
{
// We have assumed that x1
// will be left and x2 right
// but if not then we just
// swap them
if (x1 > x2)
{
int temp = x1;
x1 = x2;
x2 = temp;
}
int Occ_Till_Right = pref[x2 - 1];
int Occ_Till_Left = pref[x1];
ans = ans + (Occ_Till_Right -
Occ_Till_Left);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// N is the number of vertical lines
// M is the number of line segments
int N = 4;
int M = 8;
int size = 2000000 + 2;
int []pref = new int[size];
int lines[] = { -5, -3, 2, 3 };
// Format : x1, y1, x2, y1
int segments[][] = { { -2, 5, 5, -6 },
{ -5, -2, -3, -5 },
{ -2, 3, -6, 1 },
{ -1, -3, 4, 2 },
{ 2, 5, 2, 1 },
{ 4, 5, 4, -5 },
{ -2, -4, 5, 3 },
{ 1, 2, -2, 1 } };
// First create the prefix array
createPrefixArray(N, lines, size, pref);
// Print the total number of intersections
System.out.print(pointsOfIntersection(M, segments,
size, pref) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit KatiyarPython3
# Python3 implementation for the
# above approach
# Function to create prefix sum array
def createPrefixArray(n, arr, prefSize, pref):
# Initialize the prefix array
# to remove garbage values
for i in range(prefSize):
pref[i] = 0
# Marking the occurances
# of vertical lines
for i in range(n):
x = arr[i] + 1000000
pref[x] += 1
# Creating the prefix array
for i in range(1, prefSize):
pref[i] += pref[i - 1]
# Function that returns the count
# of total intersection
def pointOfIntersection(m, segments, size, pref):
# ans is the number of points of
# intersection of the line segments
# with the vertical lines
ans = 0
for i in range(m):
x1 = segments[i][0]
x2 = segments[i][2]
# Index mapping
x1 = x1 + 1000000
x2 = x2 + 1000000
# we don't consider a vertical
# line segment because even if
# it falls on a vertical line
# then it just touches it and
# not intersects.
if (x1 != x2):
# We have assumed that x1
# will be left and x2 right
# but if not then just swap
if (x1 > x2):
x1, x2 = x2, x1
Occ_Till_Right = pref[x2 - 1]
Occ_Till_Left = pref[x1]
ans += (Occ_Till_Right - Occ_Till_Left)
return ans
# Driver code
# Number of vertical lines
N = 4
# Number of line segments
M = 8
size = 2000000 + 2
pref = [0] * size
lines = [ -5, -3, 2, 3 ]
# Format : x1, y1, x2, y2
segments = [ [ -2, 5, 5, -6 ],
[ -5, -2, -3, -5 ],
[ -2, 3, -6, 1 ],
[ -1, -3, 4, 2 ],
[ 2, 5, 2, 1 ],
[ 4, 5, 4, -5 ],
[ -2, -4, 5, 3 ],
[ 1, 2, -2, 1 ] ]
# First create the prefix array
createPrefixArray(N, lines, size, pref)
# Print the total number of intersections
print(pointOfIntersection(M, segments, size, pref))
# This code is contributed by himanshu77C#
// C# implementation for the
// above approach.
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to create prefix sum array
static void createPrefixArray(int n, int []arr,
int prefSize,
int []pref)
{
// Initialize the prefix array
// to remove garbage values
for(int i = 0; i < prefSize; i++)
{
pref[i] = 0;
}
// Marking the occurences of
// vertical lines
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// x is the value after
// Index mapping
int x = arr[i] + 1000000;
pref[x]++;
}
// Creating the prefix array
for(int i = 1; i < prefSize; i++)
{
pref[i] += pref[i - 1];
}
}
// Function returns the count of
// total intersection
static int pointsOfIntersection(int m,
int [,]segments,
int size,
int []pref)
{
// ans is the number of points of
// intersection of the line segments
// with the vertical lines
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x1 = segments[i, 0];
int x2 = segments[i, 2];
// Index mapping
x1 = x1 + 1000000;
x2 = x2 + 1000000;
// We don't consider a vertical
// line segment because even if
// it falls on a verticale line
// then it just touches it and
// not intersects.
if (x1 != x2)
{
// We have assumed that x1
// will be left and x2 right
// but if not then we just
// swap them
if (x1 > x2)
{
int temp = x1;
x1 = x2;
x2 = temp;
}
int Occ_Till_Right = pref[x2 - 1];
int Occ_Till_Left = pref[x1];
ans = ans + (Occ_Till_Right -
Occ_Till_Left);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// N is the number of vertical lines
// M is the number of line segments
int N = 4;
int M = 8;
int size = 2000000 + 2;
int []pref = new int[size];
int []lines = { -5, -3, 2, 3 };
// Format : x1, y1, x2, y1
int [,]segments = { { -2, 5, 5, -6 },
{ -5, -2, -3, -5 },
{ -2, 3, -6, 1 },
{ -1, -3, 4, 2 },
{ 2, 5, 2, 1 },
{ 4, 5, 4, -5 },
{ -2, -4, 5, 3 },
{ 1, 2, -2, 1 } };
// First create the prefix array
createPrefixArray(N, lines, size, pref);
// Print the total number of intersections
Console.Write(pointsOfIntersection(M, segments,
size, pref) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit KatiyarJavascript
C++
// C++ implementation for the
// above approach.
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to create map that stores
// the number of occurences of the
// vertical lines till now.
map createMap(int n,
int arr[])
{
map mp;
sort(arr, arr + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
mp.insert({ arr[i], i + 1 });
}
return mp;
}
// Function returns the count of
// total intersections
int pointsOfIntersection(int m,
int segments[][4],
int n,
map pref)
{
// ans stores the number
// of intersections
int ans = 0;
// Loop over all the segments
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x1 = segments[i][0];
int x2 = segments[i][2];
if (x1 == x2) {
continue;
}
// For convenience we make x1 as
// x co-ordinate of left point
// and x2 as x co-ordinate of
// right point.
if (x1 > x2) {
swap(x1, x2);
}
auto it1 = *pref.lower_bound(x1 + 1);
auto it2 = *pref.upper_bound(x2 - 1);
int intersections = 0;
// If x co-ordinate of the left point
// is after the last vertical line
// then we dont add anything.
if (pref.lower_bound(x1 + 1)
== pref.end()) {
intersections = 0;
}
// If there is no occurence of any
// vertical line after (x2-1)
// then we can mark the
// number of intersections as
// n - occurrences till x1
// because the total occurrences
// are n and all of them
// will fall before x2.
else if (pref.upper_bound(x2 - 1)
== pref.end()) {
intersections
= n - it1.second + 1;
}
else {
intersections
= it2.second
- it1.second;
}
ans += intersections;
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// N is the number of vertical lines
// M is the number of line segments
int N = 4;
int M = 8;
int lines[N] = { -5, -3, 2, 3 };
// Format : x1, y1, x2, y1
int segments[M][4]
= { { -2, 5, 5, -6 },
{ -5, -2, -3, -5 },
{ -2, 3, -6, 1 },
{ -1, -3, 4, 2 },
{ 2, 5, 2, 1 },
{ 4, 5, 4, -5 },
{ -2, -4, 5, 3 },
{ 1, 2, -2, 1 } };
map pref = createMap(N, lines);
cout << pointsOfIntersection(
M,
segments,
N, pref)
<< endl;
return 0;
} 8方法 3:为了优化上述方法,我们可以采用一种使用 Map Data 结构的空间高效的方法。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 我们可以制作一个存储到现在出现次数的地图,与第一种方法的不同之处在于我们只插入具有垂直线的坐标。
- 当我们想要搜索从 x1 到 x2 的交叉点数量时,我们可以从地图的 upper_bound(x2-1) 中减去 lower_bound(x1+1) 。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ implementation for the
// above approach.
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to create map that stores
// the number of occurences of the
// vertical lines till now.
map createMap(int n,
int arr[])
{
map mp;
sort(arr, arr + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
mp.insert({ arr[i], i + 1 });
}
return mp;
}
// Function returns the count of
// total intersections
int pointsOfIntersection(int m,
int segments[][4],
int n,
map pref)
{
// ans stores the number
// of intersections
int ans = 0;
// Loop over all the segments
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x1 = segments[i][0];
int x2 = segments[i][2];
if (x1 == x2) {
continue;
}
// For convenience we make x1 as
// x co-ordinate of left point
// and x2 as x co-ordinate of
// right point.
if (x1 > x2) {
swap(x1, x2);
}
auto it1 = *pref.lower_bound(x1 + 1);
auto it2 = *pref.upper_bound(x2 - 1);
int intersections = 0;
// If x co-ordinate of the left point
// is after the last vertical line
// then we dont add anything.
if (pref.lower_bound(x1 + 1)
== pref.end()) {
intersections = 0;
}
// If there is no occurence of any
// vertical line after (x2-1)
// then we can mark the
// number of intersections as
// n - occurrences till x1
// because the total occurrences
// are n and all of them
// will fall before x2.
else if (pref.upper_bound(x2 - 1)
== pref.end()) {
intersections
= n - it1.second + 1;
}
else {
intersections
= it2.second
- it1.second;
}
ans += intersections;
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// N is the number of vertical lines
// M is the number of line segments
int N = 4;
int M = 8;
int lines[N] = { -5, -3, 2, 3 };
// Format : x1, y1, x2, y1
int segments[M][4]
= { { -2, 5, 5, -6 },
{ -5, -2, -3, -5 },
{ -2, 3, -6, 1 },
{ -1, -3, 4, 2 },
{ 2, 5, 2, 1 },
{ 4, 5, 4, -5 },
{ -2, -4, 5, 3 },
{ 1, 2, -2, 1 } };
map pref = createMap(N, lines);
cout << pointsOfIntersection(
M,
segments,
N, pref)
<< endl;
return 0;
}
8