霍夫曼编码是一种无损数据压缩算法。其思想是为输入的字符分配可变长度的代码,分配的代码的长度基于相应字符的频率。最频繁的字符获得最小的代码,最不频繁的字符获得最大的代码。
分配给输入字符的可变长度代码是前缀代码,意味着代码(位序列)的分配方式是分配给一个字符的代码不是分配给任何其他字符的代码的前缀。这就是霍夫曼编码确保在解码生成的比特流时没有歧义的方式。
让我们通过一个反例来理解前缀代码。假设有四个字符a、b、c和d,它们对应的变长代码是00、01、0和1。这种编码会导致歧义,因为分配给c的代码是分配给a和b的代码的前缀。如果压缩比特流是0001,解压后的输出可能是“cccd”或“ccb”或“acd”或“ab”。
请参阅此处了解霍夫曼编码的应用。
霍夫曼编码主要有两个主要部分
- 从输入字符构建霍夫曼树。
- 遍历霍夫曼树并为字符分配代码。
构建霍夫曼树的步骤
输入是一组独特的字符及其出现频率,输出是霍夫曼树。
- 为每个唯一的字符创建一个叶子节点,并构建所有叶子节点的最小堆(最小堆用作优先级队列。频率字段的值用于比较最小堆中的两个节点。最初,最不频繁的字符在根)
- 从最小堆中提取频率最小的两个节点。
- 创建一个新的内部节点,其频率等于两个节点频率之和。将第一个提取的节点作为其左子节点,将另一个提取的节点作为其右子节点。将此节点添加到最小堆。
- 重复步骤#2 和#3,直到堆只包含一个节点。剩下的节点是根节点,树是完整的。
让我们通过一个例子来理解算法:
character Frequency
a 5
b 9
c 12
d 13
e 16
f 45步骤 1.构建一个包含 6 个节点的最小堆,其中每个节点代表具有单个节点的树的根。
步骤 2从最小堆中提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个新的内部节点,频率为 5 + 9 = 14。
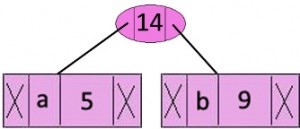
现在最小堆包含 5 个节点,其中 4 个节点是具有单个元素的树的根,一个堆节点是具有 3 个元素的树的根
character Frequency
c 12
d 13
Internal Node 14
e 16
f 45步骤 3:从堆中提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个新的内部节点,频率为 12 + 13 = 25
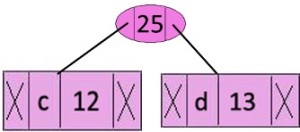
现在最小堆包含 4 个节点,其中 2 个节点是具有单个元素的树的根,两个堆节点是具有多个节点的树的根
character Frequency
Internal Node 14
e 16
Internal Node 25
f 45步骤 4:提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个新的内部节点,频率为 14 + 16 = 30
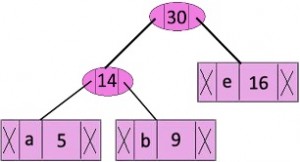
现在最小堆包含 3 个节点。
character Frequency
Internal Node 25
Internal Node 30
f 45 第五步:提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个新的内部节点,频率为 25 + 30 = 55
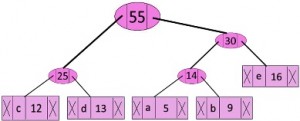
现在最小堆包含 2 个节点。
character Frequency
f 45
Internal Node 55步骤 6:提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个新的内部节点,频率为 45 + 55 = 100
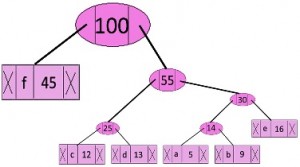
现在最小堆只包含一个节点。
character Frequency
Internal Node 100由于堆只包含一个节点,算法到此为止。
从哈夫曼树打印代码的步骤:
遍历从根开始形成的树。维护一个辅助数组。在移动到左孩子的同时,将 0 写入数组。在移动到右孩子时,将 1 写入数组。遇到叶节点时打印数组。
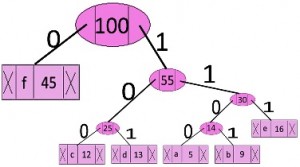
代码如下:
character code-word
f 0
c 100
d 101
a 1100
b 1101
e 111下面是上述方法的实现:
C
// C program for Huffman Coding
#include
#include
// This constant can be avoided by explicitly
// calculating height of Huffman Tree
#define MAX_TREE_HT 100
// A Huffman tree node
struct MinHeapNode {
// One of the input characters
char data;
// Frequency of the character
unsigned freq;
// Left and right child of this node
struct MinHeapNode *left, *right;
};
// A Min Heap: Collection of
// min-heap (or Huffman tree) nodes
struct MinHeap {
// Current size of min heap
unsigned size;
// capacity of min heap
unsigned capacity;
// Array of minheap node pointers
struct MinHeapNode** array;
};
// A utility function allocate a new
// min heap node with given character
// and frequency of the character
struct MinHeapNode* newNode(char data, unsigned freq)
{
struct MinHeapNode* temp = (struct MinHeapNode*)malloc(
sizeof(struct MinHeapNode));
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
temp->data = data;
temp->freq = freq;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to create
// a min heap of given capacity
struct MinHeap* createMinHeap(unsigned capacity)
{
struct MinHeap* minHeap
= (struct MinHeap*)malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeap));
// current size is 0
minHeap->size = 0;
minHeap->capacity = capacity;
minHeap->array = (struct MinHeapNode**)malloc(
minHeap->capacity * sizeof(struct MinHeapNode*));
return minHeap;
}
// A utility function to
// swap two min heap nodes
void swapMinHeapNode(struct MinHeapNode** a,
struct MinHeapNode** b)
{
struct MinHeapNode* t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// The standard minHeapify function.
void minHeapify(struct MinHeap* minHeap, int idx)
{
int smallest = idx;
int left = 2 * idx + 1;
int right = 2 * idx + 2;
if (left < minHeap->size
&& minHeap->array[left]->freq
< minHeap->array[smallest]->freq)
smallest = left;
if (right < minHeap->size
&& minHeap->array[right]->freq
< minHeap->array[smallest]->freq)
smallest = right;
if (smallest != idx) {
swapMinHeapNode(&minHeap->array[smallest],
&minHeap->array[idx]);
minHeapify(minHeap, smallest);
}
}
// A utility function to check
// if size of heap is 1 or not
int isSizeOne(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{
return (minHeap->size == 1);
}
// A standard function to extract
// minimum value node from heap
struct MinHeapNode* extractMin(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{
struct MinHeapNode* temp = minHeap->array[0];
minHeap->array[0] = minHeap->array[minHeap->size - 1];
--minHeap->size;
minHeapify(minHeap, 0);
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert
// a new node to Min Heap
void insertMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap,
struct MinHeapNode* minHeapNode)
{
++minHeap->size;
int i = minHeap->size - 1;
while (i
&& minHeapNode->freq
< minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2]->freq) {
minHeap->array[i] = minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2];
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
minHeap->array[i] = minHeapNode;
}
// A standard function to build min heap
void buildMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{
int n = minHeap->size - 1;
int i;
for (i = (n - 1) / 2; i >= 0; --i)
minHeapify(minHeap, i);
}
// A utility function to print an array of size n
void printArr(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
printf("%d", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Utility function to check if this node is leaf
int isLeaf(struct MinHeapNode* root)
{
return !(root->left) && !(root->right);
}
// Creates a min heap of capacity
// equal to size and inserts all character of
// data[] in min heap. Initially size of
// min heap is equal to capacity
struct MinHeap* createAndBuildMinHeap(char data[],
int freq[], int size)
{
struct MinHeap* minHeap = createMinHeap(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
minHeap->array[i] = newNode(data[i], freq[i]);
minHeap->size = size;
buildMinHeap(minHeap);
return minHeap;
}
// The main function that builds Huffman tree
struct MinHeapNode* buildHuffmanTree(char data[],
int freq[], int size)
{
struct MinHeapNode *left, *right, *top;
// Step 1: Create a min heap of capacity
// equal to size. Initially, there are
// modes equal to size.
struct MinHeap* minHeap
= createAndBuildMinHeap(data, freq, size);
// Iterate while size of heap doesn't become 1
while (!isSizeOne(minHeap)) {
// Step 2: Extract the two minimum
// freq items from min heap
left = extractMin(minHeap);
right = extractMin(minHeap);
// Step 3: Create a new internal
// node with frequency equal to the
// sum of the two nodes frequencies.
// Make the two extracted node as
// left and right children of this new node.
// Add this node to the min heap
// '$' is a special value for internal nodes, not
// used
top = newNode('$', left->freq + right->freq);
top->left = left;
top->right = right;
insertMinHeap(minHeap, top);
}
// Step 4: The remaining node is the
// root node and the tree is complete.
return extractMin(minHeap);
}
// Prints huffman codes from the root of Huffman Tree.
// It uses arr[] to store codes
void printCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, int arr[],
int top)
{
// Assign 0 to left edge and recur
if (root->left) {
arr[top] = 0;
printCodes(root->left, arr, top + 1);
}
// Assign 1 to right edge and recur
if (root->right) {
arr[top] = 1;
printCodes(root->right, arr, top + 1);
}
// If this is a leaf node, then
// it contains one of the input
// characters, print the character
// and its code from arr[]
if (isLeaf(root)) {
printf("%c: ", root->data);
printArr(arr, top);
}
}
// The main function that builds a
// Huffman Tree and print codes by traversing
// the built Huffman Tree
void HuffmanCodes(char data[], int freq[], int size)
{
// Construct Huffman Tree
struct MinHeapNode* root
= buildHuffmanTree(data, freq, size);
// Print Huffman codes using
// the Huffman tree built above
int arr[MAX_TREE_HT], top = 0;
printCodes(root, arr, top);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
char arr[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' };
int freq[] = { 5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
HuffmanCodes(arr, freq, size);
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program for Huffman Coding
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// This constant can be avoided by explicitly
// calculating height of Huffman Tree
#define MAX_TREE_HT 100
// A Huffman tree node
struct MinHeapNode {
// One of the input characters
char data;
// Frequency of the character
unsigned freq;
// Left and right child of this node
struct MinHeapNode *left, *right;
};
// A Min Heap: Collection of
// min-heap (or Huffman tree) nodes
struct MinHeap {
// Current size of min heap
unsigned size;
// capacity of min heap
unsigned capacity;
// Attay of minheap node pointers
struct MinHeapNode** array;
};
// A utility function allocate a new
// min heap node with given character
// and frequency of the character
struct MinHeapNode* newNode(char data, unsigned freq)
{
struct MinHeapNode* temp
= (struct MinHeapNode*)malloc
(sizeof(struct MinHeapNode));
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
temp->data = data;
temp->freq = freq;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to create
// a min heap of given capacity
struct MinHeap* createMinHeap(unsigned capacity)
{
struct MinHeap* minHeap
= (struct MinHeap*)malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeap));
// current size is 0
minHeap->size = 0;
minHeap->capacity = capacity;
minHeap->array
= (struct MinHeapNode**)malloc(minHeap->
capacity * sizeof(struct MinHeapNode*));
return minHeap;
}
// A utility function to
// swap two min heap nodes
void swapMinHeapNode(struct MinHeapNode** a,
struct MinHeapNode** b)
{
struct MinHeapNode* t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// The standard minHeapify function.
void minHeapify(struct MinHeap* minHeap, int idx)
{
int smallest = idx;
int left = 2 * idx + 1;
int right = 2 * idx + 2;
if (left < minHeap->size && minHeap->array[left]->
freq < minHeap->array[smallest]->freq)
smallest = left;
if (right < minHeap->size && minHeap->array[right]->
freq < minHeap->array[smallest]->freq)
smallest = right;
if (smallest != idx) {
swapMinHeapNode(&minHeap->array[smallest],
&minHeap->array[idx]);
minHeapify(minHeap, smallest);
}
}
// A utility function to check
// if size of heap is 1 or not
int isSizeOne(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{
return (minHeap->size == 1);
}
// A standard function to extract
// minimum value node from heap
struct MinHeapNode* extractMin(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{
struct MinHeapNode* temp = minHeap->array[0];
minHeap->array[0]
= minHeap->array[minHeap->size - 1];
--minHeap->size;
minHeapify(minHeap, 0);
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert
// a new node to Min Heap
void insertMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap,
struct MinHeapNode* minHeapNode)
{
++minHeap->size;
int i = minHeap->size - 1;
while (i && minHeapNode->freq < minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2]->freq) {
minHeap->array[i] = minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2];
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
minHeap->array[i] = minHeapNode;
}
// A standard function to build min heap
void buildMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{
int n = minHeap->size - 1;
int i;
for (i = (n - 1) / 2; i >= 0; --i)
minHeapify(minHeap, i);
}
// A utility function to print an array of size n
void printArr(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
cout<< arr[i];
cout<<"\n";
}
// Utility function to check if this node is leaf
int isLeaf(struct MinHeapNode* root)
{
return !(root->left) && !(root->right);
}
// Creates a min heap of capacity
// equal to size and inserts all character of
// data[] in min heap. Initially size of
// min heap is equal to capacity
struct MinHeap* createAndBuildMinHeap(char data[], int freq[], int size)
{
struct MinHeap* minHeap = createMinHeap(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
minHeap->array[i] = newNode(data[i], freq[i]);
minHeap->size = size;
buildMinHeap(minHeap);
return minHeap;
}
// The main function that builds Huffman tree
struct MinHeapNode* buildHuffmanTree(char data[], int freq[], int size)
{
struct MinHeapNode *left, *right, *top;
// Step 1: Create a min heap of capacity
// equal to size. Initially, there are
// modes equal to size.
struct MinHeap* minHeap = createAndBuildMinHeap(data, freq, size);
// Iterate while size of heap doesn't become 1
while (!isSizeOne(minHeap)) {
// Step 2: Extract the two minimum
// freq items from min heap
left = extractMin(minHeap);
right = extractMin(minHeap);
// Step 3: Create a new internal
// node with frequency equal to the
// sum of the two nodes frequencies.
// Make the two extracted node as
// left and right children of this new node.
// Add this node to the min heap
// '$' is a special value for internal nodes, not used
top = newNode('$', left->freq + right->freq);
top->left = left;
top->right = right;
insertMinHeap(minHeap, top);
}
// Step 4: The remaining node is the
// root node and the tree is complete.
return extractMin(minHeap);
}
// Prints huffman codes from the root of Huffman Tree.
// It uses arr[] to store codes
void printCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, int arr[], int top)
{
// Assign 0 to left edge and recur
if (root->left) {
arr[top] = 0;
printCodes(root->left, arr, top + 1);
}
// Assign 1 to right edge and recur
if (root->right) {
arr[top] = 1;
printCodes(root->right, arr, top + 1);
}
// If this is a leaf node, then
// it contains one of the input
// characters, print the character
// and its code from arr[]
if (isLeaf(root)) {
cout<< root->data <<": ";
printArr(arr, top);
}
}
// The main function that builds a
// Huffman Tree and print codes by traversing
// the built Huffman Tree
void HuffmanCodes(char data[], int freq[], int size)
{
// Construct Huffman Tree
struct MinHeapNode* root
= buildHuffmanTree(data, freq, size);
// Print Huffman codes using
// the Huffman tree built above
int arr[MAX_TREE_HT], top = 0;
printCodes(root, arr, top);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
char arr[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' };
int freq[] = { 5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
HuffmanCodes(arr, freq, size);
return 0;
}
C++(STL)// C++ program for Huffman Coding with STL
#include
using namespace std;
// A Huffman tree node
struct MinHeapNode {
// One of the input characters
char data;
// Frequency of the character
unsigned freq;
// Left and right child
MinHeapNode *left, *right;
MinHeapNode(char data, unsigned freq)
{
left = right = NULL;
this->data = data;
this->freq = freq;
}
};
// For comparison of
// two heap nodes (needed in min heap)
struct compare {
bool operator()(MinHeapNode* l, MinHeapNode* r)
{
return (l->freq > r->freq);
}
};
// Prints huffman codes from
// the root of Huffman Tree.
void printCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, string str)
{
if (!root)
return;
if (root->data != '$')
cout << root->data << ": " << str << "\n";
printCodes(root->left, str + "0");
printCodes(root->right, str + "1");
}
// The main function that builds a Huffman Tree and
// print codes by traversing the built Huffman Tree
void HuffmanCodes(char data[], int freq[], int size)
{
struct MinHeapNode *left, *right, *top;
// Create a min heap & inserts all characters of data[]
priority_queue, compare> minHeap;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
minHeap.push(new MinHeapNode(data[i], freq[i]));
// Iterate while size of heap doesn't become 1
while (minHeap.size() != 1) {
// Extract the two minimum
// freq items from min heap
left = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
right = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
// Create a new internal node with
// frequency equal to the sum of the
// two nodes frequencies. Make the
// two extracted node as left and right children
// of this new node. Add this node
// to the min heap '$' is a special value
// for internal nodes, not used
top = new MinHeapNode('$', left->freq + right->freq);
top->left = left;
top->right = right;
minHeap.push(top);
}
// Print Huffman codes using
// the Huffman tree built above
printCodes(minHeap.top(), "");
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
char arr[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' };
int freq[] = { 5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
HuffmanCodes(arr, freq, size);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Goel Java
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Comparator;
// node class is the basic structure
// of each node present in the Huffman - tree.
class HuffmanNode {
int data;
char c;
HuffmanNode left;
HuffmanNode right;
}
// comparator class helps to compare the node
// on the basis of one of its attribute.
// Here we will be compared
// on the basis of data values of the nodes.
class MyComparator implements Comparator {
public int compare(HuffmanNode x, HuffmanNode y)
{
return x.data - y.data;
}
}
public class Huffman {
// recursive function to print the
// huffman-code through the tree traversal.
// Here s is the huffman - code generated.
public static void printCode(HuffmanNode root, String s)
{
// base case; if the left and right are null
// then its a leaf node and we print
// the code s generated by traversing the tree.
if (root.left
== null
&& root.right
== null
&& Character.isLetter(root.c)) {
// c is the character in the node
System.out.println(root.c + ":" + s);
return;
}
// if we go to left then add "0" to the code.
// if we go to the right add"1" to the code.
// recursive calls for left and
// right sub-tree of the generated tree.
printCode(root.left, s + "0");
printCode(root.right, s + "1");
}
// main function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
// number of characters.
int n = 6;
char[] charArray = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' };
int[] charfreq = { 5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45 };
// creating a priority queue q.
// makes a min-priority queue(min-heap).
PriorityQueue q
= new PriorityQueue(n, new MyComparator());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// creating a Huffman node object
// and add it to the priority queue.
HuffmanNode hn = new HuffmanNode();
hn.c = charArray[i];
hn.data = charfreq[i];
hn.left = null;
hn.right = null;
// add functions adds
// the huffman node to the queue.
q.add(hn);
}
// create a root node
HuffmanNode root = null;
// Here we will extract the two minimum value
// from the heap each time until
// its size reduces to 1, extract until
// all the nodes are extracted.
while (q.size() > 1) {
// first min extract.
HuffmanNode x = q.peek();
q.poll();
// second min extarct.
HuffmanNode y = q.peek();
q.poll();
// new node f which is equal
HuffmanNode f = new HuffmanNode();
// to the sum of the frequency of the two nodes
// assigning values to the f node.
f.data = x.data + y.data;
f.c = '-';
// first extracted node as left child.
f.left = x;
// second extracted node as the right child.
f.right = y;
// marking the f node as the root node.
root = f;
// add this node to the priority-queue.
q.add(f);
}
// print the codes by traversing the tree
printCode(root, "");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kunwar Desh Deepak Singh Python3
# A Huffman Tree Node
class node:
def __init__(self, freq, symbol, left=None, right=None):
# frequency of symbol
self.freq = freq
# symbol name (charecter)
self.symbol = symbol
# node left of current node
self.left = left
# node right of current node
self.right = right
# tree direction (0/1)
self.huff = ''
# utility function to print huffman
# codes for all symbols in the newly
# created Huffman tree
def printNodes(node, val=''):
# huffman code for current node
newVal = val + str(node.huff)
# if node is not an edge node
# then traverse inside it
if(node.left):
printNodes(node.left, newVal)
if(node.right):
printNodes(node.right, newVal)
# if node is edge node then
# display its huffman code
if(not node.left and not node.right):
print(f"{node.symbol} -> {newVal}")
# charecters for huffman tree
chars = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']
# frequency of charecters
freq = [ 5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45]
# list containing unused nodes
nodes = []
# converting ccharecters and frequencies
# into huffman tree nodes
for x in range(len(chars)):
nodes.append(node(freq[x], chars[x]))
while len(nodes) > 1:
# sort all the nodes in ascending order
# based on theri frequency
nodes = sorted(nodes, key=lambda x: x.freq)
# pick 2 smallest nodes
left = nodes[0]
right = nodes[1]
# assign directional value to these nodes
left.huff = 0
right.huff = 1
# combine the 2 smallest nodes to create
# new node as their parent
newNode = node(left.freq+right.freq, left.symbol+right.symbol, left, right)
# remove the 2 nodes and add their
# parent as new node among others
nodes.remove(left)
nodes.remove(right)
nodes.append(newNode)
# Huffman Tree is ready!
printNodes(nodes[0])Javascript
输出:
f: 0
c: 100
d: 101
a: 1100
b: 1101
e: 111时间复杂度: O(nlogn) 其中 n 是唯一字符的数量。如果有 n 个节点,extractMin() 被调用 2*(n – 1) 次。 extractMin() 在调用 minHeapify() 时花费 O(logn) 时间。所以,整体复杂度是 O(nlogn)。
如果输入数组已排序,则存在线性时间算法。我们很快将在下一篇文章中讨论。
霍夫曼编码的应用:
- 它们用于传输传真和文本。
- 它们被传统的压缩格式使用,如 PKZIP、GZIP 等。
在有一系列频繁出现的字符的情况下很有用。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。