固体缺陷
固体由许多小晶体组成。然而,由于晶体形成的速度较快或适中,在结晶过程中会出现固体缺陷。缺陷通常被描述为组成颗粒排列的不规则性。缺陷可以是基于不规则排列的点或线缺陷。当晶体中任何点或原子周围的排列出现异常时,理想晶体中就会出现偏差点缺陷。类似地,当晶体中整行晶格点的排列发生变化时,就会出现线缺陷。
实体中的缺陷或缺陷
结晶固体是通过在所有方向上按体积数量的晶胞的有序复制而形成的。由整个晶体具有相同晶格点的单个晶胞组成的离子晶体被称为理想晶体。不管这种理想晶体是否仅存在于绝对零 (0K) 温度下。在任何高于 0 K 的温度下,晶体都有些不完全排列。一世
Any deviation from the perfectly arranged arrangement of constituent particles in a crystal is called a disorder or defect. Hence,
Imperfection in solids refers to any abnormality in the pattern of crystal arrangement in solids. When crystals form, faults develop. It can happen very quickly or at a slower pace. Because particles don’t have enough time to arrange themselves in a regular manner, this happens.
由于某些杂质的存在,晶体中可能会出现额外的缺陷。术语无序或不完美被广泛使用来指代从晶体成分的完美排列状态开始的亲密方式。这些缺陷不仅会改变晶体的特性,还会产生新的特性。
Causes of Imperfections or Defects in a Solid:
- The different types of Impurities are found in the crystal lattice or in a solid.
- Vacancies in the lattice
- Nonstoichiometric proportions of the ions
- Dislocation of a particle in the lattice
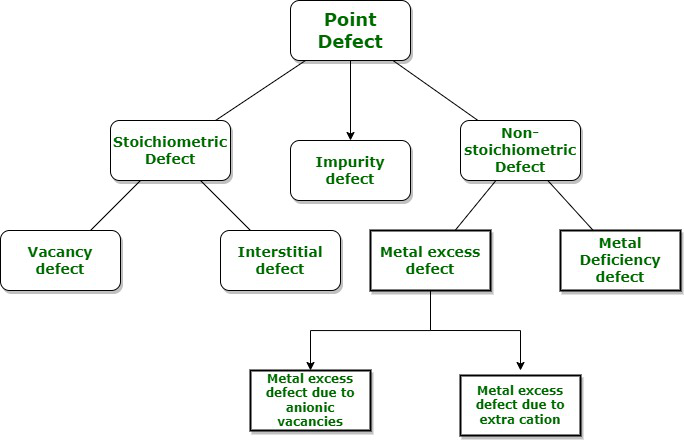
缺陷类型
缺陷分为两类:
- 点缺陷:由于晶体材料中的点或原子周围的原子的理想排列不规则或偏离而产生的缺陷称为点缺陷或原子缺陷。
- 线缺陷:在整排晶格点中由于不规则或偏离理想排列而滚出的缺陷称为线缺陷。
这些不规则性称为晶体缺陷的晶体缺陷。
实体中的点缺陷
当结晶迅速发生时,会出现点缺陷,从而阻止形成完美的晶体结构。然而,应该注意的是,即使在缓慢的结晶过程中,也存在缺陷。点缺陷可分为三类。
可能注意到空位和间隙缺陷由非离子固体显示。另一方面,离子固体必须始终保持电中性。
离子晶体中的点缺陷大概在幕后为:
- 化学计量缺陷:化学计量化合物是指其中正离子和负离子的数量符合其化学式所指示的比率的化合物。为简单起见,我们可以考虑具有相同数量的 A +和 B -离子的 AB 型化合物。这些类型的化合物中的缺陷称为化学计量缺陷。通常,在这些化合物中观察到两种类型的缺陷。
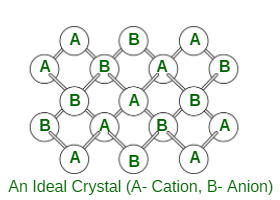
以下是化学计量缺陷的类型
肖特基缺陷:如果某些原子或离子从它们的正常晶格位置丢失,就会出现肖特基缺陷。不合格的晶格位点称为晶格空位或空穴。只要晶体必须是电中性的,就缺少相等数量的阳离子和阴离子。理想的 AB 晶体如上图所示。存在两个孔,一个是由于缺少阳离子,另一个是由于缺少。离子固体中的空位缺陷非常出色。
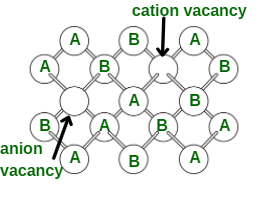
肖特基缺陷
肖特基缺陷分为三种:
- 空位缺陷——当无数晶格位置空缺时,称晶体具有空位缺陷。这种缺陷导致物质密度不足。这种类型的缺陷也可以在加热材料上发展,因此也称为热力学缺陷。

空缺缺陷
- 间隙缺陷-当一些组成粒子(原子或分子)围绕空缺的间隙位置时,晶体被称为具有间隙缺陷。该缺陷略微增加了密度。
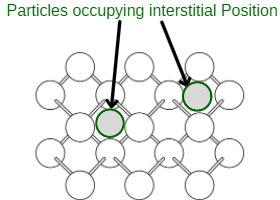
间隙缺陷
导致肖特基缺陷的条件——这种类型的缺陷通常见于具有
- 高配位数
- 大小大致相同的离子。
例如,NaCl、KCl、KBr、CsCl 和 AgBr 离子固体具有肖特基缺陷。已经确定在 NaCl 中,在室温下每立方厘米大约有 10 6 个肖特基对。在 1cm³ 中大约有 10 22 个离子,这意味着在 NaCl 中每 10 16 个离子就会有一个肖特基缺陷。由于晶体中存在大量空位,因此其密度显着降低。
Frenkel 缺陷:当离子从其正常状态消失并占据晶格点之间的间隙位置时,就会发生 Frenkel 缺陷。显示了由于从其正常位置缺少阳离子并占据间隙位置而导致的硬朗的存在。在这种情况下,由于阴离子和阳离子的数量保持不变,晶体也保持电中性。这种缺陷也称为间隙缺陷。它会产生空缺缺陷。它有它原来的位置,在它的新位置有一个间隙缺陷。

弗兰克尔缺陷
导致弗伦克尔缺陷的条件 -这种缺陷通常发生在配位数低的化合物中,阴离子远大于阳离子。
在完美的碱金属卤化物中,这些缺陷并不常见,因为离子由于尺寸大而不能移动到间隙状态。在AgCl、AgBr、AgI、ZnS等卤化银中可以发现缺陷。只要Ag离子和离子的尺寸很小,这些离子就可以移动到间隙位置。
具有肖特基阱和弗伦克尔缺陷的晶体中存在空位或空穴,但前者会降低物质的整体密度,而后者不会。 ,另一种混合类型的缺陷也可能来自两者的结合。
Causes of Schottky and Frenkel Defects
Defects in Schottky and Frank crystals give some interesting results. These are-
- The presence of these defects increases the electrical conductivity of crystals. When an electric field is about the experiment, an adjoining ion moves from its lattice site to occupy a hole. As a result, a new hole is created and another nearby ion moves into it, and so on. This process continues and thus h moves from one end to the other. Thus, it conducts electricity throughout the crystal.
- Due to the impendence of pores in the crystal, its density decreases. It presumably noted that the density decreases only for crystals with Schottky defects.
- The presence of pores also reduces the lattice energy or stabilization of the crystal. The presence of too many pores can cause partial collapse of the lattice.
- In Frenkel defects, the dielectric constant of the crystal is increased by placing it in a pattern of equal charges.
- 杂质缺陷:当晶格空间或间隙位置存在一些外来原子或离子时,就会出现这些缺陷,例如含有少量 SrCl 2的熔融 NaCl 和 CdCl 2和 AgCl 的固溶体。
- 非化学计量晶体中的缺陷:非化学计量缺陷扰乱了固体的化学计量。被不成对电子占据的离子位点称为F 中心(Farbenzenter 或色心)。它们赋予碱金属卤化物晶体颜色。当这些电子从落在晶体上的可见光吸收能量时,这些电子的激发产生了颜色。 Na过量使NaCl晶体变黄,Li过量使LICI呈粉红色,钾过量使KCl晶体变紫。
- 由阴离子空位引起的金属过量缺陷由碱金属卤化物如 NaCl 和 KCl 显示。在这种缺陷中,负离子从其晶格位置丢失,留下一个被电子占据的空穴以保持电中性。
- 由于在间隙位置存在额外的阳离子而导致的金属过量通过加热时的氧化锌显示。加热时,氧化锌(白色)失去氧气并变成黄色。
ZnO + 加热 → Zn² + + O₂ +2e –
示例问题
问题 1. Fe 3 O 4在室温下是铁磁性的,在 850 K 时变成顺磁性的。解释一下。
回答:
Due to the randomization of spins at high temperatures.
问题 2. 说出任何一种同时具有弗伦克尔缺陷和肖特基缺陷的固体。
回答:
Silver bromide, AgBr, has both Frenkel and Schottky defects.
问题 3. 温度对金属和半金属的电导率有什么影响?
Ans. In general, with an increase in temperature, the conductivity of metals decreases, and that of semi-metals increases
问题 4. 什么是光伏电池?
回答:
The process in which electricity is generated by the shining of sunlight on certain substances. Amorphous silicon acts as a exemplary photovoltaic cell.
问题 5. 为什么纯碱金属卤化物中没有发现 Frenkel 缺陷?
回答:
Frenkel defect is not found in alkali metal halides because the ions cannot get into the interstitial.
问题 6. 肖特基缺陷的存在对晶体密度有何影响?
回答:
The overall density of a crystalline material decreases due to the Schottky defect.
问题 7. 用 As 或 Ga 掺杂硅得到的半导体有什么区别?
回答:
The semiconductor produced by silicon doped with As is an n-type semiconductor in which the flow of current is due to electrons while silicon doped with Ga is a p-type semiconductor in which the flow of current is due to positive holes.