n-ary 树中给定节点的子节点数
给定一个节点 x,在给定的 n 叉树中找到 x(如果存在)的子节点数。
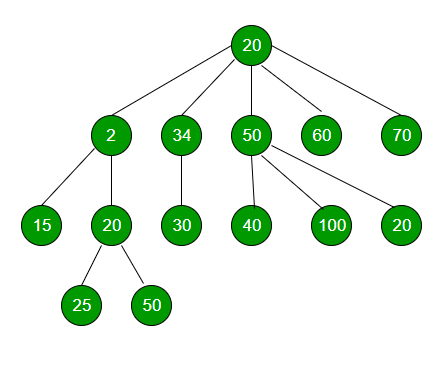
例子 :
Input : x = 50
Output : 3
Explanation : 50 has 3 children having values 40, 100 and 20.方法 :
- 将孩子的数量初始化为 0。
- 对于 n 叉树中的每个节点,检查其值是否等于 x。如果是,则返回孩子的数量。
- 如果 x 的值不等于当前节点,则将当前节点的所有子节点推入队列。
- 不断重复上述步骤,直到队列变空。
下面是上述想法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to find number
// of children of given node
#include
using namespace std;
// Represents a node of an n-ary tree
class Node {
public:
int key;
vector child;
Node(int data)
{
key = data;
}
};
// Function to calculate number
// of children of given node
int numberOfChildren(Node* root, int x)
{
// initialize the numChildren as 0
int numChildren = 0;
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Creating a queue and pushing the root
queue q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int n = q.size();
// If this node has children
while (n > 0) {
// Dequeue an item from queue and
// check if it is equal to x
// If YES, then return number of children
Node* p = q.front();
q.pop();
if (p->key == x) {
numChildren = numChildren + p->child.size();
return numChildren;
}
// Enqueue all children of the dequeued item
for (int i = 0; i < p->child.size(); i++)
q.push(p->child[i]);
n--;
}
}
return numChildren;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// Creating a generic tree
Node* root = new Node(20);
(root->child).push_back(new Node(2));
(root->child).push_back(new Node(34));
(root->child).push_back(new Node(50));
(root->child).push_back(new Node(60));
(root->child).push_back(new Node(70));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(new Node(15));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(new Node(20));
(root->child[1]->child).push_back(new Node(30));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(new Node(40));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(new Node(100));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(new Node(20));
(root->child[0]->child[1]->child).push_back(new Node(25));
(root->child[0]->child[1]->child).push_back(new Node(50));
// Node whose number of
// children is to be calculated
int x = 50;
// Function calling
cout << numberOfChildren(root, x) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find number
// of children of given node
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Represents a node of an n-ary tree
static class Node
{
int key;
Vector child = new Vector<>();
Node(int data)
{
key = data;
}
};
// Function to calculate number
// of children of given node
static int numberOfChildren(Node root, int x)
{
// initialize the numChildren as 0
int numChildren = 0;
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Creating a queue and pushing the root
Queue q = new LinkedList();
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
int n = q.size();
// If this node has children
while (n > 0)
{
// Dequeue an item from queue and
// check if it is equal to x
// If YES, then return number of children
Node p = q.peek();
q.remove();
if (p.key == x)
{
numChildren = numChildren +
p.child.size();
return numChildren;
}
// Enqueue all children of the dequeued item
for (int i = 0; i < p.child.size(); i++)
q.add(p.child.get(i));
n--;
}
}
return numChildren;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a generic tree
Node root = new Node(20);
(root.child).add(new Node(2));
(root.child).add(new Node(34));
(root.child).add(new Node(50));
(root.child).add(new Node(60));
(root.child).add(new Node(70));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(new Node(15));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(new Node(20));
(root.child.get(1).child).add(new Node(30));
(root.child.get(2).child).add(new Node(40));
(root.child.get(2).child).add(new Node(100));
(root.child.get(2).child).add(new Node(20));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(1).child).add(new Node(25));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(1).child).add(new Node(50));
// Node whose number of
// children is to be calculated
int x = 50;
// Function calling
System.out.println(numberOfChildren(root, x));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python3 program to find number
# of children of given node
# Node of a linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data = None):
self.key = data
self.child = []
# Function to calculate number
# of children of given node
def numberOfChildren( root, x):
# initialize the numChildren as 0
numChildren = 0
if (root == None):
return 0
# Creating a queue and appending the root
q = []
q.append(root)
while (len(q) > 0) :
n = len(q)
# If this node has children
while (n > 0):
# Dequeue an item from queue and
# check if it is equal to x
# If YES, then return number of children
p = q[0]
q.pop(0)
if (p.key == x) :
numChildren = numChildren + len(p.child)
return numChildren
i = 0
# Enqueue all children of the dequeued item
while ( i < len(p.child)):
q.append(p.child[i])
i = i + 1
n = n - 1
return numChildren
# Driver program
# Creating a generic tree
root = Node(20)
(root.child).append(Node(2))
(root.child).append(Node(34))
(root.child).append(Node(50))
(root.child).append(Node(60))
(root.child).append(Node(70))
(root.child[0].child).append(Node(15))
(root.child[0].child).append(Node(20))
(root.child[1].child).append(Node(30))
(root.child[2].child).append(Node(40))
(root.child[2].child).append(Node(100))
(root.child[2].child).append(Node(20))
(root.child[0].child[1].child).append(Node(25))
(root.child[0].child[1].child).append(Node(50))
# Node whose number of
# children is to be calculated
x = 50
# Function calling
print( numberOfChildren(root, x) )
# This code is contributed by Arnab KunduC#
// C# program to find number
// of children of given node
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Represents a node of an n-ary tree
public class Node
{
public int key;
public List child = new List();
public Node(int data)
{
key = data;
}
};
// Function to calculate number
// of children of given node
static int numberOfChildren(Node root, int x)
{
// initialize the numChildren as 0
int numChildren = 0;
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Creating a queue and pushing the root
Queue q = new Queue();
q.Enqueue(root);
while (q.Count != 0)
{
int n = q.Count;
// If this node has children
while (n > 0)
{
// Dequeue an item from queue and
// check if it is equal to x
// If YES, then return number of children
Node p = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
if (p.key == x)
{
numChildren = numChildren +
p.child.Count;
return numChildren;
}
// Enqueue all children of the dequeued item
for (int i = 0; i < p.child.Count; i++)
q.Enqueue(p.child[i]);
n--;
}
}
return numChildren;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a generic tree
Node root = new Node(20);
(root.child).Add(new Node(2));
(root.child).Add(new Node(34));
(root.child).Add(new Node(50));
(root.child).Add(new Node(60));
(root.child).Add(new Node(70));
(root.child[0].child).Add(new Node(15));
(root.child[0].child).Add(new Node(20));
(root.child[1].child).Add(new Node(30));
(root.child[2].child).Add(new Node(40));
(root.child[2].child).Add(new Node(100));
(root.child[2].child).Add(new Node(20));
(root.child[0].child[1].child).Add(new Node(25));
(root.child[0].child[1].child).Add(new Node(50));
// Node whose number of
// children is to be calculated
int x = 50;
// Function calling
Console.WriteLine(numberOfChildren(root, x));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
输出:
3时间复杂度: O(N),其中 N 是树中的节点数。
辅助空间: O(N),其中 N 是树中的节点数。
?list=PLqM7alHXFySHCXD7r1J0ky9Zg_GBB1dbk