SARSA 强化学习
先决条件: Q-Learning技术
SARSA 算法是流行的 Q-Learning 算法的轻微变体。对于任何强化学习算法中的学习代理,它的策略可以有两种类型:-
- On Policy:在此,学习代理根据从当前使用的策略派生的当前动作来学习价值函数。
- Off Policy:在这种情况下,学习代理根据从另一个策略派生的动作来学习价值函数。
Q-Learning 技术是一种Off Policy技术,使用贪婪方法来学习 Q 值。另一方面,SARSA 技术是一种On Policy ,它使用当前策略执行的操作来学习 Q 值。
这种差异在每种技术的更新语句的差异中是可见的:-
- Q-学习:
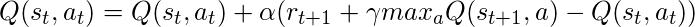
- 沙萨:
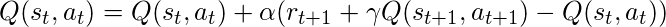
这里,SARSA 的更新方程取决于当前状态、当前动作、获得的奖励、下一个状态和下一个动作。这一观察导致学习技术的命名为 SARSA 代表状态动作奖励状态动作,它象征着元组 (s, a, r, s', a')。
以下Python代码演示了如何使用 OpenAI 的gym 模块加载环境来实现 SARSA 算法。
第 1 步:导入所需的库
Python3
import numpy as np
import gymPython3
#Building the environment
env = gym.make('FrozenLake-v0')Python3
#Defining the different parameters
epsilon = 0.9
total_episodes = 10000
max_steps = 100
alpha = 0.85
gamma = 0.95
#Initializing the Q-matrix
Q = np.zeros((env.observation_space.n, env.action_space.n))Python3
#Function to choose the next action
def choose_action(state):
action=0
if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < epsilon:
action = env.action_space.sample()
else:
action = np.argmax(Q[state, :])
return action
#Function to learn the Q-value
def update(state, state2, reward, action, action2):
predict = Q[state, action]
target = reward + gamma * Q[state2, action2]
Q[state, action] = Q[state, action] + alpha * (target - predict)Python3
#Initializing the reward
reward=0
# Starting the SARSA learning
for episode in range(total_episodes):
t = 0
state1 = env.reset()
action1 = choose_action(state1)
while t < max_steps:
#Visualizing the training
env.render()
#Getting the next state
state2, reward, done, info = env.step(action1)
#Choosing the next action
action2 = choose_action(state2)
#Learning the Q-value
update(state1, state2, reward, action1, action2)
state1 = state2
action1 = action2
#Updating the respective vaLues
t += 1
reward += 1
#If at the end of learning process
if done:
breakPython3
#Evaluating the performance
print ("Performance : ", reward/total_episodes)
#Visualizing the Q-matrix
print(Q)第 2 步:构建环境
在这里,我们将使用预加载到健身房的“FrozenLake-v0”环境。您可以在此处阅读有关环境描述的信息。
Python3
#Building the environment
env = gym.make('FrozenLake-v0')
第三步:初始化不同的参数
Python3
#Defining the different parameters
epsilon = 0.9
total_episodes = 10000
max_steps = 100
alpha = 0.85
gamma = 0.95
#Initializing the Q-matrix
Q = np.zeros((env.observation_space.n, env.action_space.n))
第 4 步:定义要在学习过程中使用的效用函数
Python3
#Function to choose the next action
def choose_action(state):
action=0
if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < epsilon:
action = env.action_space.sample()
else:
action = np.argmax(Q[state, :])
return action
#Function to learn the Q-value
def update(state, state2, reward, action, action2):
predict = Q[state, action]
target = reward + gamma * Q[state2, action2]
Q[state, action] = Q[state, action] + alpha * (target - predict)
第 5 步:训练学习代理
Python3
#Initializing the reward
reward=0
# Starting the SARSA learning
for episode in range(total_episodes):
t = 0
state1 = env.reset()
action1 = choose_action(state1)
while t < max_steps:
#Visualizing the training
env.render()
#Getting the next state
state2, reward, done, info = env.step(action1)
#Choosing the next action
action2 = choose_action(state2)
#Learning the Q-value
update(state1, state2, reward, action1, action2)
state1 = state2
action1 = action2
#Updating the respective vaLues
t += 1
reward += 1
#If at the end of learning process
if done:
break

在上面的输出中,红色标记确定了代理在环境中的当前位置,而括号中给出的方向给出了代理接下来将进行的移动方向。请注意,如果超出范围,代理将停留在其位置。
第 6 步:评估性能
Python3
#Evaluating the performance
print ("Performance : ", reward/total_episodes)
#Visualizing the Q-matrix
print(Q)
