R 编程中的回归及其类型
回归分析是一种统计工具,用于估计两个或多个变量之间的关系。总是有一个响应变量和一个或多个预测变量。回归分析被广泛用于对数据进行相应的拟合,并进一步预测数据以进行预测。它使用因/响应变量和自/预测变量帮助企业和组织了解其产品在市场中的行为。在本文中,让我们借助示例了解 R 编程中不同类型的回归。
R中的回归类型
R编程中广泛使用的回归主要有三种类型。他们是:
- 线性回归
- 多重回归
- 逻辑回归
线性回归
线性回归模型是三种回归类型中广泛使用的模型之一。在线性回归中,估计两个变量之间的关系,即一个响应变量和一个预测变量。线性回归在图上生成一条直线。数学上
where,
- x indicates predictor or independent variable
- y indicates response or dependent variable
- a and b are coefficients
R中的实现
在 R 编程中, lm()函数用于创建线性回归模型。
Syntax: lm(formula)
Parameter:
formula: represents the formula on which data has to be fitted To know about more optional parameters, use below command in console: help(“lm”)
示例:在此示例中,让我们在图表上绘制线性回归线,并使用身高预测基于体重。
R
# R program to illustrate
# Linear Regression
# Height vector
x <- c(153, 169, 140, 186, 128,
136, 178, 163, 152, 133)
# Weight vector
y <- c(64, 81, 58, 91, 47, 57,
75, 72, 62, 49)
# Create a linear regression model
model <- lm(y~x)
# Print regression model
print(model)
# Find the weight of a person
# With height 182
df <- data.frame(x = 182)
res <- predict(model, df)
cat("\nPredicted value of a person
with height = 182")
print(res)
# Output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "linearRegGFG.png")
# Plot
plot(x, y, main = "Height vs Weight
Regression model")
abline(lm(y~x))
# Save the file.
dev.off()R
# R program to illustrate
# Multiple Linear Regression
# Using airquality dataset
input <- airquality[1:50,
c("Ozone", "Wind", "Temp")]
# Create regression model
model <- lm(Ozone~Wind + Temp,
data = input)
# Print the regression model
cat("Regression model:\n")
print(model)
# Output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "multipleRegGFG.png")
# Plot
plot(model)
# Save the file.
dev.off()R
# R program to illustrate
# Logistic Regression
# Using mtcars dataset
# To create the logistic model
model <- glm(formula = vs ~ wt,
family = binomial,
data = mtcars)
# Creating a range of wt values
x <- seq(min(mtcars$wt),
max(mtcars$wt),
0.01)
# Predict using weight
y <- predict(model, list(wt = x),
type = "response")
# Print model
print(model)
# Output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "LogRegGFG.png")
# Plot
plot(mtcars$wt, mtcars$vs, pch = 16,
xlab = "Weight", ylab = "VS")
lines(x, y)
# Saving the file
dev.off()输出:
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) x
-39.7137 0.6847
Predicted value of a person with height = 182
1
84.9098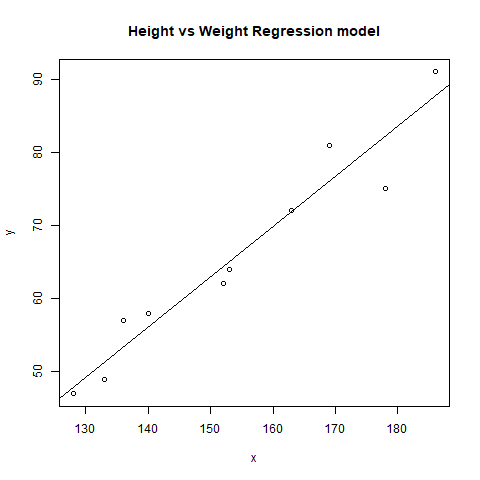
多重回归
多元回归是另一种类型的回归分析技术,它是线性回归模型的扩展,因为它使用多个预测变量来创建模型。数学上,
R中的实现
R 编程中的多元回归使用相同的lm()函数来创建模型。
Syntax: lm(formula, data)
Parameters:
- formula: represents the formula on which data has to be fitted
- data: represents dataframe on which formula has to be applied
示例:让我们创建 R 基础包中存在的空气质量数据集的多元回归模型,并将模型绘制在图表上。
R
# R program to illustrate
# Multiple Linear Regression
# Using airquality dataset
input <- airquality[1:50,
c("Ozone", "Wind", "Temp")]
# Create regression model
model <- lm(Ozone~Wind + Temp,
data = input)
# Print the regression model
cat("Regression model:\n")
print(model)
# Output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "multipleRegGFG.png")
# Plot
plot(model)
# Save the file.
dev.off()
输出:
Regression model:
Call:
lm(formula = Ozone ~ Wind + Temp, data = input)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) Wind Temp
-58.239 -0.739 1.329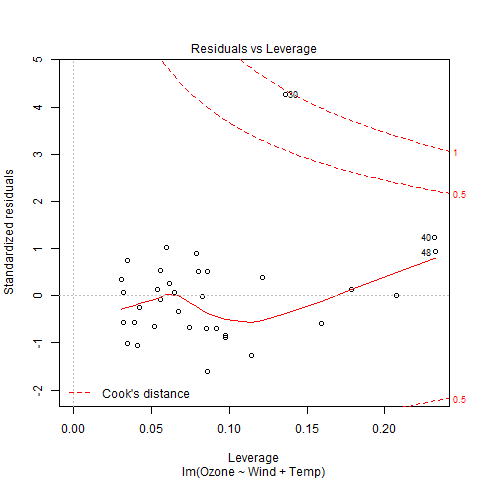
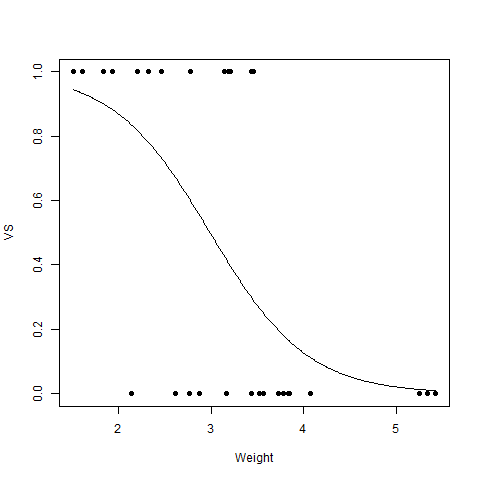
逻辑回归
Logistic Regression 是另一种广泛使用的回归分析技术,它用一个范围来预测值。此外,它用于预测分类数据的值。例如,电子邮件是垃圾邮件还是非垃圾邮件、赢家或输家、男性或女性等。从数学上讲,
where,
- y represents response variable
- z represents equation of independent variables or features
R中的实现
在 R 编程中, glm()函数用于创建逻辑回归模型。
Syntax: glm(formula, data, family)
Parameters:
- formula: represents a formula on the basis of which model has to be fitted
- data: represents dataframe on which formula has to be applied
- family: represents the type of function to be used. “binomial” for logistic regression
例子:
R
# R program to illustrate
# Logistic Regression
# Using mtcars dataset
# To create the logistic model
model <- glm(formula = vs ~ wt,
family = binomial,
data = mtcars)
# Creating a range of wt values
x <- seq(min(mtcars$wt),
max(mtcars$wt),
0.01)
# Predict using weight
y <- predict(model, list(wt = x),
type = "response")
# Print model
print(model)
# Output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "LogRegGFG.png")
# Plot
plot(mtcars$wt, mtcars$vs, pch = 16,
xlab = "Weight", ylab = "VS")
lines(x, y)
# Saving the file
dev.off()
输出:
Call: glm(formula = vs ~ wt, family = binomial, data = mtcars)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) wt
5.715 -1.911
Degrees of Freedom: 31 Total (i.e. Null); 30 Residual
Null Deviance: 43.86
Residual Deviance: 31.37 AIC: 35.37