R 编程中的回归决策树
决策树是机器学习中的一种算法,它以决策为特征,以树状结构的形式表示结果。它是一种常用工具,用于直观地表示算法做出的决策。决策树同时使用分类和回归。当因变量是连续的时使用回归树,而当因变量是分类时使用分类树。例如,确定/预测性别是分类的示例,基于发动机功率预测汽车的里程是回归的示例。在本文中,让我们讨论 R 编程中使用回归的决策树以及 R 编程中的语法和实现。
R中的实现
在 R 编程中, rpart()函数存在于rpart包中。使用rpart()函数,可以在 R 中构建决策树。
Syntax:
rpart(formula, data, method)
Parameters:
formula: indicates the formula based on which model has to be fitted
data: indicates the dataframe
method: indicates the method to create decision tree. “anova” is used for regression and “class” is used as method for classification.
示例 1:
在这个例子中,让我们使用回归决策树预测萼片宽度。
第一步:安装需要的包
# Install the package
install.packages("rpart")
第 2 步:加载包
# Load the package
library(rpart)
第 3 步:拟合回归决策树模型
# Create decision tree using regression
fit <- rpart(Sepal.Width ~ Sepal.Length +
Petal.Length + Petal.Width + Species,
method = "anova", data = iris)
第 4 步:绘制树
# Output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "decTreeGFG.png", width = 600,
height = 600)
# Plot
plot(fit, uniform = TRUE,
main = "Sepal Width Decision
Tree using Regression")
text(fit, use.n = TRUE, cex = .7)
# Saving the file
dev.off()
第 5 步:打印决策树模型
# Print model
print(fit)
第 6 步:预测萼片宽度
# Create test data
df <- data.frame (Species = 'versicolor',
Sepal.Length = 5.1,
Petal.Length = 4.5,
Petal.Width = 1.4)
# Predicting sepal width
# using testing data and model
# method anova is used for regression
cat("Predicted value:\n")
predict(fit, df, method = "anova")
输出:
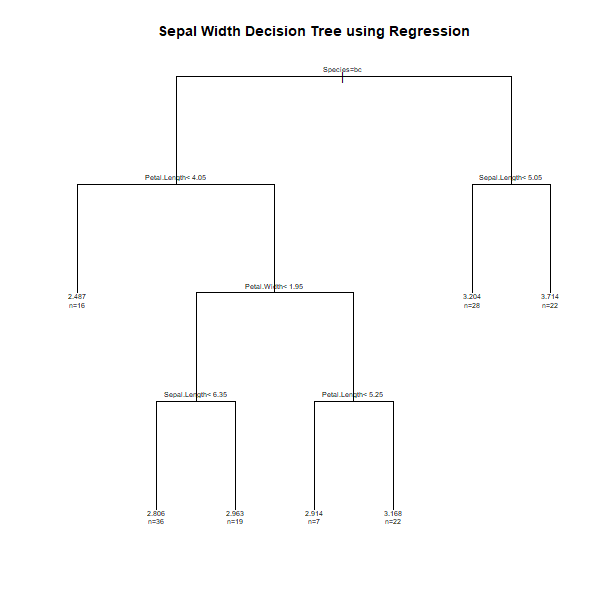
n= 150
node), split, n, deviance, yval
* denotes terminal node
1) root 150 28.3069300 3.057333
2) Species=versicolor, virginica 100 10.9616000 2.872000
4) Petal.Length=4.05 84 7.3480950 2.945238
10) Petal.Width< 1.95 55 3.4920000 2.860000
20) Sepal.Length=6.35 19 0.6242105 2.963158 *
11) Petal.Width>=1.95 29 2.6986210 3.106897
22) Petal.Length=5.25 22 2.0277270 3.168182 *
3) Species=setosa 50 7.0408000 3.428000
6) Sepal.Length=5.05 22 1.7859090 3.713636 *
Predicted value:
1
2.805556
示例 2:
在此示例中,让我们使用决策树进行回归预测 mpg 值。
第一步:安装需要的包
# Install the package
install.packages("rpart")
第 2 步:加载包
# Load the package
library(rpart)
第 3 步:拟合回归决策树模型
# Create decision tree using regression
fit <- rpart(mpg ~ disp + hp + cyl,
method = "anova", data = mtcars )
第 4 步:绘制树
# Output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "decTree2GFG.png", width = 600,
height = 600)
# Plot
plot(fit, uniform = TRUE,
main = "MPG Decision Tree using Regression")
text(fit, use.n = TRUE, cex = .6)
# Saving the file
dev.off()
第 5 步:打印决策树模型
# Print model
print(fit)
第 6 步:使用测试数据集预测 mpg 值
# Create test data
df <- data.frame (disp = 351, hp = 250,
cyl = 8)
# Predicting mpg using testing data and model
cat("Predicted value:\n")
predict(fit, df, method = "anova")
输出:
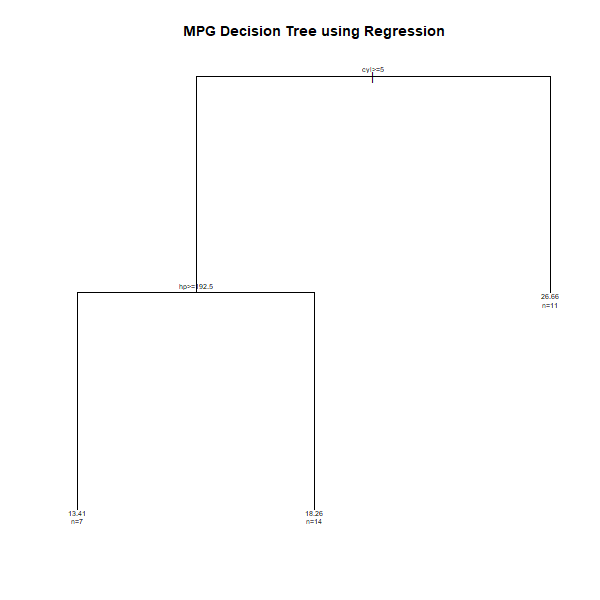
n= 32
node), split, n, deviance, yval
* denotes terminal node
1) root 32 1126.04700 20.09062
2) cyl>=5 21 198.47240 16.64762
4) hp>=192.5 7 28.82857 13.41429 *
5) hp< 192.5 14 59.87214 18.26429 *
3) cyl< 5 11 203.38550 26.66364 *
Predicted value:
1
13.41429
决策树的优势
- 考虑所有可能的决策:决策树考虑所有可能的决策以产生问题的结果。
- 易于使用:借助分类和回归技术,它可以轻松用于任何类型的问题,并进一步创建预测和解决问题。
- 缺失值没有问题:数据集缺失值没有问题,不影响决策树的构建。
决策树的缺点
- 需要更长的时间:决策树需要更长的时间来计算大型数据集。
- 学习少:决策树不是好的学习者。随机森林方法用于更好的学习。