杨氏双缝实验
光学是材料科学的一部分,专注于光的行为和特性,将其与问题的联系以及利用或识别它的仪器的开发结合起来。光学通常描述明显、明亮和红外光的传导。由于光是一种电磁波,不同类型的电磁辐射,例如 X 射线、微波和无线电波显示出比较特性。大多数光学奇迹都可以通过利用传统的电磁光描绘来表示。
无论如何,光的完整电磁描述通常很难实际应用。脚踏实地的光学通常是利用工作模型完成的。其中最广为人知的是数学光学,将光视为各种光束,当它们穿过或从表面反射时,它们会以直线和曲线移动。实际光学是一种更全面的光模型,它包含了波的影响,例如数学光学中无法表示的衍射和障碍。总的来说,基于光束的光模型首先发展起来,然后是光的波动模型。 19 世纪电磁假说的进展促使人们发现光波确实是电磁辐射。
杨氏双缝实验
Young’s double-slit experiment employs two coherent light sources separated by a modest distance, generally a few orders of magnitude larger than the wavelength of light.
杨的双缝实验有助于理解光波理论。狭缝与屏幕或光电探测器相隔很大距离“D”。 Young 最初的双缝实验采用来自单一光源的衍射光,然后通过两个额外的狭缝传输作为相干光源。在今天的研究中,激光经常被用作相干光源。

每个源都可以被认为是一个相干光波源。波行进长度为 l1 和 l2,以在屏幕上距中心距离为“y”的任何位置产生 l 的路径差。在源处,该点大致对角 (由于距离 D 很大,源处对角的差异很小)。

杨氏双缝实验推导
考虑一个远离两个狭缝 s 1和 s 2的单色光源“S”。 S与s 1和s 2在同一平面上。因为 s 1和 s 2都是从 S 中提取的,所以它们充当了两个一致的来源。
光穿过这些狭缝并落在屏幕上,该屏幕位于距孔径 s 1和 s 2距离“D”处。两个狭缝之间的距离用字母“d”表示。
如果 s 1打开而 s 2关闭,则 s 1对面的屏幕变暗,仅 s 2对面的屏幕亮起。只有当狭缝s 1和s 2都打开时,才能形成干涉图案。
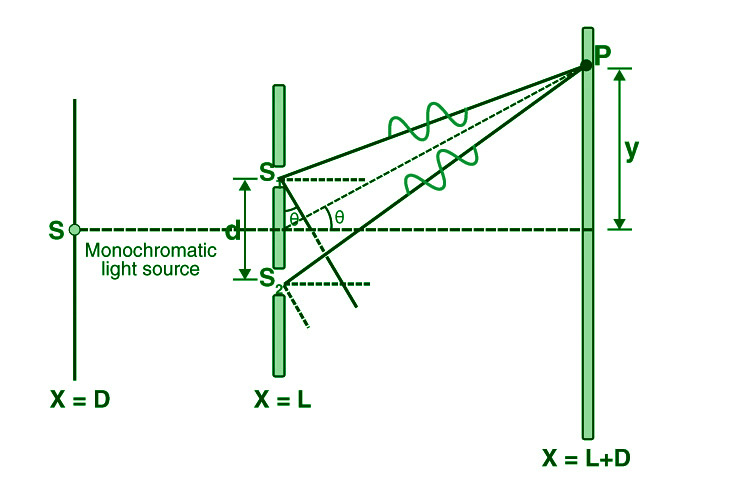
在切割分区 (d) 和屏幕距离 (D) 保持不变的点,为了到达 P,来自 s 1和 s 2的光波应该传播不同的距离。这表明来自 s 1和 s 2的两个光波在 Young 的双重切割测试中存在方式对比。
Approximations in Young’s twofold cut analysis-
Guess 1: D > d
Since D > d, the two light beams are thought to be equal.
Guess 2: d/λ >> 1
Often, d is a small amount of a millimeter and λ is a negligible portion of a micrometer for noticeable light.
在这些条件下 θ 很小,因此,我们可以利用估计,
sin θ = tan θ ≈ θ = λ/d
∴路径差,
Δz = λ/d
这是在屏幕上某一点相遇的两个波之间的路径差。正因为杨双切调查的这种路径差异,银幕上的焦点有的精彩,有的焦点平淡。
杨氏双缝实验中条纹的位置
- 亮边的位置
为了在 P 处形成最大强度或明亮的条纹
路径差, Δz = nλ (n = 0, ±1, ±2, ...)
IE
xd/D = nλ
要么
x = nλD/d
第 n 个亮条纹到中心的距离为
x n = nλD/d
同理,第( n -1)条亮条纹到中心的距离为
x (n-1) = (n -1)λD/d
条纹宽度, β = x n – x (n-1) = nλD/d – (n -1)λD/d = λD/d
(n = 0、±1、±2、……)
- 黑边的位置
为了在 P 处形成最小强度或暗条纹,
路径差, Δz = (2n + 1) (λ/2) (n = 0, ±1, ±2, ...)
IE
x = (2n +1)λD/2d
第 n 个暗条纹到中心的距离为
x n = (2n+1)λD/2d
同理,第( n -1)条亮条纹到中心的距离为
x (n-1) = (2(n-1) +1)λD/2d
条纹宽度, β = x n – x (n-1) = (2n + 1) λD/2d – (2(n -1) + 1)λD/2d = λD/d
(n = 0、±1、±2、……)
边缘宽度
The fringe width is the distance between two consecutive bright (or dark) fringes.
β = λD/d
当杨氏双缝实验设备浸入折射率为(μ)的液体中时,光的波长和条纹宽度均下降“倍”。
β 1 = β/μ
当使用白光代替单色光时,屏幕上会出现彩色条纹,红色条纹大于紫色条纹。
干涉条纹的最大阶数
在屏幕上,第 n阶最大值的位置是,
γ = nλD/d
其中 n=0, ±1, ±2, …
但是,因为会违反第二个近似值,所以“n”值不能取无限高的值。即 θ 很小(或)y << D。
⇒ γ/D = nλ/d <<1
因此,可以使用上述干扰最大值公式n<< d/λ。当“n”的值等于 d/λ 的值时,路径差不再可以计算为 dγ/D。
因此对于最大值,路径差 = nλ
⇒ dsinθ = nλ
要么
n = dsinθ/λ
和
n最大值= d/λ
上面表示的是框函数或最大整数函数。类似地,干扰最小值的最高阶由下式给出,
n min =[d/λ+1/2]
YDSE中干涉条纹的形状
两个狭缝之间的路径差异由 YDSE 图表示。
s 2 p−s 1 p≈dsinθ (常数)
前面的方程描述了一条双曲线,它有两个焦点,用字母 s 1和 s 2表示。

当我们在轴 s 1 s 2上旋转一条双曲线时,我们会在屏幕上获得一个干涉图案,它是一段双曲线。边缘是双曲线的,屏幕的直线中间部分位于 yz 平面中。
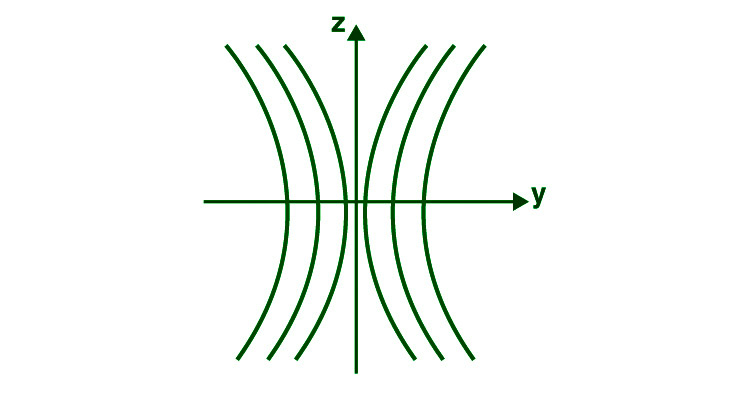
YDSE 中的条纹强度
两个相干源 s1 和 s2 在位置 p 处得到的强度由下式给出
I = I 1 + I 2 + 2 √(I 1 . I 2 ) cos φ
假设,I 1 = I 2 = I 0 (因为,d<< I = I 0 + I 0 + 2 √(I 0 .I 0 ) cos φ = 2I 0 + 2 (I 0 ) cos φ = 2I 0 (1 + cos φ) = 4I 0 cos 2 (φ/2) 路径差必须是波长的整数倍,才能发生相长干涉。结果,如果明亮的边缘位于“y”, nλ = yd/D 其中 n = ±0,1,2,3….. 中心明亮边缘由第 0 边缘表示。类似地,在 Young 的双缝实验中,可以通过将路径差设置为: Δl = (2n+1)λ/2 这简化为, (2n+1)λ/2 = yd/D 要么 y = (2n+1)λD/2d 杨的双缝实验是科学的一个突破点,因为它毫无疑问地证明了光的行为就像波一样。后来,用电子重复了双缝实验,令所有人惊讶的是,产生的图案几乎与用光看到的相同。这将永远改变我们对物质和粒子的看法,要求我们相信物质就像光一样,就像波一样。 问题1:杨氏双缝实验中,最小值与峰值的亮度比为9:25。计算两个狭缝宽度的比率。 回答: Imax/Imin = (a1+a2)2/(a1-a2)2 = 9/25 Solving, a1/a2 = 4/1 Therefore, Ratio of slit width , w1/w2 = a12/a22=16. 问题2:双缝实验中的缝间距为3mm,缝距屏幕2m。在屏幕上,可以观察到两种干涉图案,一种是由波长为 480 nm 的光引起的,另一种是由波长为 600 nm 的光引起的。屏幕上两个干涉图案的五阶亮边之间的距离是多少? 回答: Separation is given by, y= nλD/d where, d = 3 mm = 3 × 10 −3 m D = 2 m λ1 = 480 nm = 480×10 −9 m λ2 = 600 nm = 600×10 −9 m n1=n2=5 So, y1= nλ1D/d y1= 5×480×10 −9×2 / 3×10 −3 y1=1.6×10−3m Also, y2= nλ2D /d y2= 5×600×10−9×2 / 3×10−3 y2=2×10−3m As , y2 > y 1 y 2 − y1 = 2×10 −3−1.6×10 −3 = 4×10 −4 m Therefore the separation on the screen between the fifth order bright fringes of the two interference patterns is 4×10−4 m. 问题3:杨氏实验中两条狭缝的宽度为1:25。干涉图样的峰与最小值的强度比,I max /I min为 回答: Intensity is proportional to width of the slit. thus, I1/I2 = 1/25 or a1/a2 = 1/5 Imax/Imin = (a1+a2)2/(a1-a2)2 = (a1+5a1)2/(a1-5a1)2 = 36/16 = 9/4 问题4:舞台上振动的两个清醒点源S 1和S 2辐射出频率为λ的光。源之间的划分为 2λ。考虑一条穿过 S 2并与线 S 1 S 2相对的线。与至少发生功率的 S 2的最小分离是什么? 回答: For minimum intensity of light, path difference must be equal to path difference for dark e.g Δx=λ/2,3λ/2,5λ/2 Consider Δx=(2λ−λ/2)=3λ/2 Now, path difference=S1P−S2P Δx= √(4λ2+x2)−x 3λ/2+x= √4λ 2+x 2 Taking square on both sides, 9λ2/4+x 2+3λx=4λ 2+x 2 3λx=4λ2−9λ2/4 x=7λ/12 The smallest distance from S2 where a minimum of intensity occurs is 7λ/12 问题 5:玻璃镜片上镀有一层折射率为 1.50 的薄层。玻璃的折射率为 1.60。可以极强反射 546 nm 光(相长薄膜干涉)的最薄薄膜涂层是什么? 回答: Light is entering in a medium of higher refractive index (n2=1.60) from a medium of lower index (n1=1.50), therefore net path difference in the reflected rays from the two interfaces will be equal to 2t (where t is thickness of thin film) , because when light goes from air to thin film path shift in reflected ray =λ’/2, when light goes from thin film to glass path shift in reflected ray =λ’/2+2t for constructive interference, 2t=mλ’ or 2t=mλ/n1 where λ’= wavelength in thin film , λ=546nm(given) wavelength in vacuum , for thinnest coating , m=0(minimum) , therefore, tmin = λ/2n1 = 546/(2×1.50) =182nm 问题 6:对于宽度为“a”的单个狭缝,波长为 e 的单色光的干涉图案的初始最小值出现在角度 λ/a 处。我们发现在相同角度 λ/a 处相隔距离“a”的两个薄狭缝的最大值。解释。 回答: Width of the slit is a. The path difference between two secondary wavelets is given by, Nλ=asinθ Since, θ is very small, sinθ=θ So, for the first order diffraction n=1, the angle is λ/a Now, we know that θ must be very small θ=0 (nearly) because of which the diffraction pattern is minimum. Now for interference case, for two interfering waves of intensity l1 and l2 we must have two slits separated by a distance. We have the resultant intensity, l=l1+l−2+ 2 √l1l 2cosθ Since, θ=0 (nearly) corresponding to angle λ/a, so cosθ=1 (nearly) So, l=l1+l2 +2 √ l1l 2cosθ l=l1+l2+2 √ l1l2cos0 l=l1+l2+2 √ l1l2 We see the resultant intensity is sum of the two intensities, so there is a maxima corresponding to the angle λ/a This is why at the same angle λ/a we get a maximum for two narrow slits separated by a distance a. 问题 7:由两个相干光源产生的干涉图中的最高和最低强度的比率为 9:1。使用的灯的亮度是多少? 回答: Imax /Imin = (a1+a2)2 / (a1-a2)2 9/1 = (a1+a2)2 / (a1-a2)2 a1/a2 = 2/1 a12 / a22 = l1 / l2 = 4/1 建设性和破坏性干扰
示例问题