卢瑟福的 Alpha 散射实验
JJ Thomson 的李子布丁模型无法解释元素原子结构的某些实验结果。仍然没有明确的模型来定义原子,因此在 1909 年,英国科学家欧内斯特·卢瑟福进行了一项实验,并在此基础上观察并提出了元素的原子结构和卢瑟福原子模型。
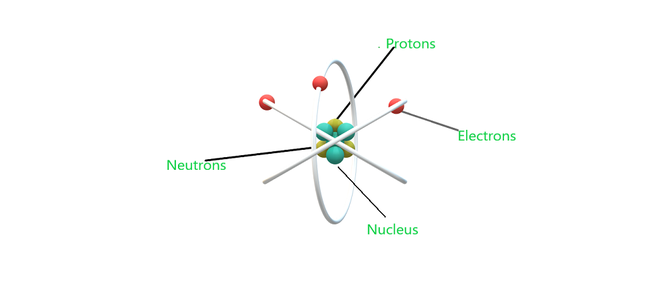
原子模型
原子的基本成分
原子由电子、质子和中子组成,中子是构成原子结构的基本粒子或亚原子粒子。让我们理解每个术语。
- 电子: 1897 年,JJ Thomson 发现带负电的粒子朝向阳极,这些射线是在阴极射线实验中由阴极发射的。然后这些带负电的粒子被提出为电子。
- 质子: 1886 年,欧内斯特·戈德斯坦 (Ernest Goldstein) 发现阳极在同一管中发射出具有不同条件的带正电粒子,称为运河射线或质子。
- 中子: J. Chadwick 发现了一种不带电荷且质量与所有原子核中的质子相当的亚原子粒子。这些带中性电荷的粒子被称为中子。
Isotopes are the elements that have the same atomic number but different mass. e.g. Isotopes of the Hydrogen atoms are Protium (1H1), Deuterium (2H1) and Tritium(3H1). Isotopes of the Carbon atoms are 12C6, 13C6, 14C6.
Isobars are the elements that have different atomic number but have same mass number. e.g. 19K40, 18Ar40, 20Ca40, here all the elements having same mass number hence the are isobars.
卢瑟福的 Alpha 散射实验
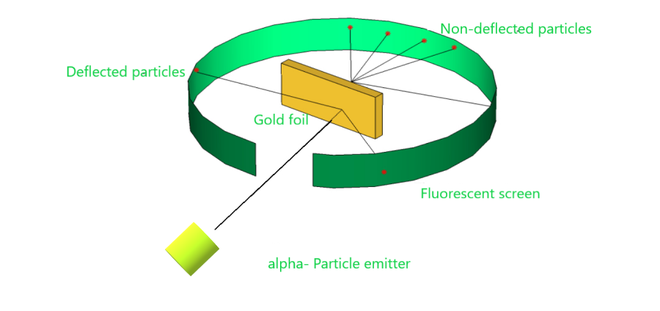
卢瑟福实验的建立
他进行了一项实验,将 α 粒子轰击成薄金片,然后注意到它们与金箔的相互作用以及这些粒子所遵循的轨迹或路径。
In the experiment, Rutherford passes very high streams of alpha-particles from a radioactive source i.e. alpha-particle emitter, at a thin sheet of100 nm thickness of gold. In order to examine the deflection produced by the alpha particles, he placed a screen of fluorescent zinc sulphide around the thin gold foil. Rutherford made certain observations that oppose Thomson’s atomic model.
卢瑟福的阿尔法散射实验的观察
卢瑟福的 Alpha 散射实验的观察结果是:
- 首先,他观察到大部分被轰击到金片上的 α 粒子在没有任何偏转的情况下通过了箔片,因此它表明大部分空间是空的。
- 其中,一些α粒子在金片中偏转了很小的角度,因此表明原子中的正电荷分布不均匀。正电荷集中在原子中非常小的体积中。
- 极少的α-粒子(1-2%) 被偏转回来,即只有极少量的α-粒子具有接近180°的偏转角。这表明带正电粒子所占的体积与原子的总体积相比非常小。
卢瑟福原子模型
卢瑟福在他的实验的基础上提出了元素的原子结构。根据卢瑟福的原子模型:
- 带正电的粒子集中在一个极小的体积中,原子的大部分质量也在那个体积中。他称之为原子核。
- 卢瑟福提出原子核周围有带负电的电子。围绕原子核的电子以非常高速的圆形路径围绕它旋转。他为这些圆形路径命名了轨道。
- 原子核是带正电的粒子和带负电的电子的密集集中质量,通过称为静电吸引力的强大吸引力保持在一起。
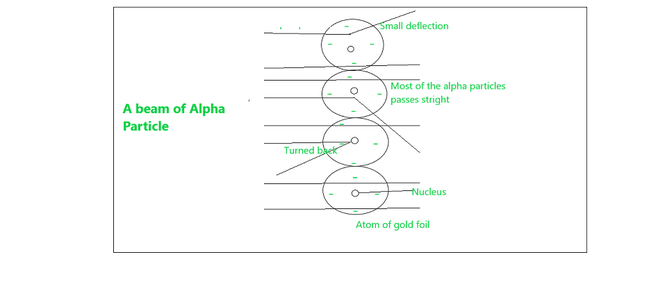
卢瑟福模型的观察
卢瑟福原子模型的局限性
卢瑟福原子模型无法解释某些事情。
- 根据麦克斯韦的说法,围绕原子核旋转的电子应该会发射电磁辐射,因为加速的带电粒子会发射电磁辐射。但是卢瑟福模型说,电子围绕原子核以固定的路径旋转,称为轨道。辐射会从导致轨道缩小的运动中携带能量。最终电子会在原子核内坍缩。
- 根据卢瑟福模型,计算表明电子会在不到 10 -8秒的时间内在原子核中坍缩。因此卢瑟福模型与麦克斯韦理论产生了高度矛盾,卢瑟福后来无法解释原子的稳定性。
- 卢瑟福也没有将轨道中的电子排列描述为他的模型的其他缺点之一。
尽管看到早期的原子模型不准确并且无法解释某些实验结果,但它们是量子力学世界未来发展的基础。
示例问题
问题 1: 命名只有一个电子、一个质子和没有中子的原子。
回答:
It is true for hydrogen atom 1H1.
The atomic number of Hydrogen = No. of Proton = 1
The mass number of hydrogen = 1
No. of neutrons = 0
Therefore hydrogen atom has one electron, one proton and no neutron.
问题 2:定义原子的基态这个术语?
回答:
It is the state of an atom where all the electrons in the atom are in their lowest energy state or levels is called the ground state.
问题 3:表示包含 15 个电子和 16 个中子的元素“X”。
回答:
Atomic number of element = no. of electron = 15
Mass number of element = no. of electrons + no. of neutrons
= 15 + 16
= 31
The correct representation of element X is 31X15.
问题 4:命名粒子并给出它在不带电荷且质量几乎等于质子的原子中的位置。
回答:
The particle which has no charge and has a mass nearly equal to that of a proton is a neutron and it is present in the nucleus of the atom.
问题5:一个原子既具有电子属性负电荷,又具有质子属性正电荷,但为什么没有电荷?
回答:
The positive and negative charges of protons and electrons are equal in magnitude, they cancel the effect of each other. So, the atom as a whole is electrically neutral.
问题6:钠原子(Na)的化合价是多少?
回答:
The atomic number of sodium = 11
electronic configuration (2, 8, 1).
by losing one electron it gains stability hence its valency is 1.
问题 7:以下对显示了哪些属性?
209 X 84和210 X 84
回答:
The atomic number of X is the same hence the pair shows an isotopic property.
So, 209X84 and 210X84 are isotopes.