滚动运动
将扩展体视为刚体,您可以用它们解决很多问题。刚体是具有精确定义且不变的形状的刚体。像这样的物体中所有粒子对之间的距离保持不变。因为实体在力的影响下会弯曲,所以这个刚体的定义表明没有实体是真正刚体的。然而,在许多情况下,变形是微不足道的。另一方面,我们可以忽略这样一个事实,即轮子、顶部、钢梁、分子和行星等物体在各种环境中弯曲(扭曲变形)、弯曲或振动,并将它们视为固体。
滚动运动是日常生活中最普遍的运动之一。汽车、公共汽车、火车、飞机、自行车、水牛车等交通工具中使用的所有轮子都有滚动运动,还有很多东西都像手推车一样附有轮子。为清楚起见,让我们以圆盘为例开始,但结果适用于在水平表面上滚动的任何滚动体。假设盘在滚动时没有滑动。这意味着与平坦表面接触的圆盘底部在任何给定时间都静止在表面上。
什么是滚动运动?
滚动运动包含两种运动,或者是平移和旋转两种运动的组合。物体的平移运动是质心的运动。
在身体的滚动运动中,接触的表面会发生轻微的变形,这种变形是暂时的,即当两个身体的区域相互接触时,会导致身体的暂时变形。这种现象具有称为摩擦的冲击效应,它是与抵抗运动的表面平行的接触力的分量。
(1) 平移运动
平移运动是一种运动,其中身体的所有部分在相同的时间内移动相同的距离。平移运动有两种形式:直线和曲线。
- 当进行平移运动的物体沿直线移动时,就称运动为直线运动。例如,在笔直的道路上行驶的汽车,在笔直的轨道上行驶的火车。
- 曲线运动描述了物体在平移运动中沿曲线路径移动的运动。例如,转动汽车。
(2) 旋转运动
物体围绕空间中的固定点在圆形路径中的运动,也是不变形或改变形状的物体的运动,其中所有粒子围绕轴以共同的角速度做圆周运动。例如地球绕自身轴的运动,车轮、齿轮、电机等的运动。
滚动运动的表达式

车轮在水平面上的滚动运动(不打滑)。
设车轮质心的速度为 v cm ,即它的平移速度。因为滚轮的质心在其几何中心 C,所以 v cm是 C 的速度。它平行于平面。轮子沿其对称轴旋转,该轴穿过 C 的中心。因此,圆盘上每个点的速度,例如 P 0和 P 1或 P 2 ,由两部分组成,即平移速度 v cm和线速度 v r由于旋转。
- v r 的大小为 v r = ωr ,其中 r 是点与轴之间的距离,ω 是车轮绕轴旋转的角速度。关于C,速度v r垂直于给定点wrt C 的半径矢量。在这种情况下,v r垂直于CP 2 。
- 很容易证明 v 2垂直于线 P 0 P 2 。因此,瞬时旋转轴定义为通过 P 0并平行于 ω 的线。
- 由于旋转,线速度 v r在点 P 0处与平移速度 v cm正好相反。此外,在这种情况下,v r的大小是 Rω,其中 R 是车轮的半径。
- P 0瞬时静止的条件需要v cm = Rω 。因此,对于车轮而言,滚动不打滑的条件是v cm = Rω 。
- 这也意味着车轮顶部的点 P 1的速度 v 1为v cm + R或2 v cm并且平行于水平面。
滚动运动的动能
滚动体的动能可分为平移动能和旋转动能两种。粒子系统的动能(K)可分为质心运动(平移)的动能(MV 2 /2)和围绕系统质心的旋转运动的动能(K' )。所以,
![]()
滚动体质心的动能,即平移动能,为m(v cm ) 2 /2,其中m为体质量, v cm为质心速度。
滚动体绕其质心K'的运动是物体的旋转动能K' = Iω 2 /2 ,其中I是关于合适轴的转动惯量,该轴是滚动体的对称轴。因此,滚动体的动能由下式给出
![]()
代入I = mk 2其中 k 是快速运动物体的相应半径, ω=v cm /R其中 R 是圆形运动物体的半径。

刚体的运动类型
让我们看一些刚体运动的例子。让我们从一个矩形块开始,它沿着斜面滑动而不侧向移动。块被视为刚体。它在平面上的行进使得所有身体的粒子都在同步移动,即它们在任何时候都具有相同的速度。在这个场景中,刚体处于纯平移运动中。

块沿斜面的平移(滑动)运动。 (块的任何点,如 P 1或 P 2在任何时刻都以相同的速度移动。)
- 考虑一个坚固的金属或木制圆柱体如何从同一个倾斜平面上滚下来。圆柱体从斜面的顶部移动到底部,给人以平移运动的印象。然而,正如所见,它的所有粒子在任何给定时间都不会以相同的速度行进。结果,身体没有以真正的平移运动移动。它以平移和其他运动的组合运动。
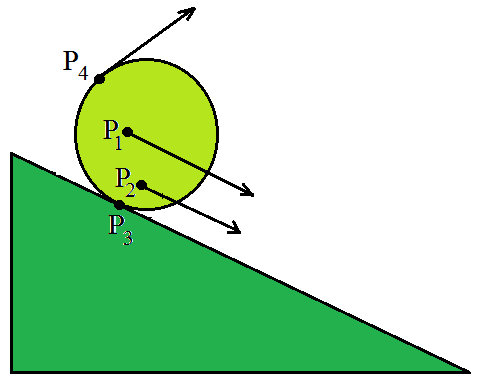
圆柱体的滚动运动。它不是纯粹的狂喜平移运动。点 P 1 , P 2 , P 3 , 和 P 4在任何时刻都有不同的速度(如箭头所示)。事实上,如果圆柱体在没有打滑的情况下滚动,接触点 P3 的速度在任何时刻都为零。
- 沿直线固定刚体是防止其平移运动的最常用方法。对于这样一个刚硬的物体,旋转是唯一可行的运动。旋转轴是身体围绕其旋转的直线或固定轴。比如吊扇、陶轮、集市上的巨轮等等。当一个刚体围绕一个固定轴旋转时,它的每个粒子都在一个圆中移动,该圆存在于一个垂直于轴的平面中,并且它的中心在轴上。但是,在极少数旋转的情况下,轴可能不是固定的。原地陀螺就是这种旋转的一个很好的例子。通过它与地面的接触点,这种旋转陀螺的轴线围绕垂直方向摆动,扫出一个圆锥体。

围绕固定轴旋转吊扇。
- 如果一个刚体没有以任何方式旋转或连接,它的运动要么是纯平移,要么是平移和旋转的组合。以某种方式枢转或固定的刚体的运动称为旋转。旋转可以是固定的,例如使用吊扇,也可以是移动的,例如使用摆动台扇。

一个陀螺
示例问题
问题 1:三个物体,一个圆环、一个实心圆柱体和一个实心球体,沿着同一个斜面滚动而不会打滑。他们从休息开始。物体的半径是相同的。哪个物体以最大速度到达地面?
解决方案:
According to the conservation of energy of the rolling body, i.e. there is no loss of energy due to friction. . The potential energy lost by the body in rolling down the inclined plane is P.E= mgh, therefore, be equal to kinetic energy gained. The bodies start from rest the kinetic energy gained is equal to the final kinetic energy of the bodies.
The expression for the kinetic energy is
![]()
where v is the final velocity of the Centre of mass of the body.

Equate K and mgh,
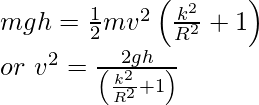
Here, velocity is independent of the mass of the rolling body,
For a ring, k2= R2, therefore the expression can be written as
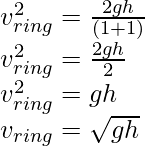
For a solid cylinder k2= R2/2 , therefore,

Now for a solid sphere k2= 2R2/5 , therefore,
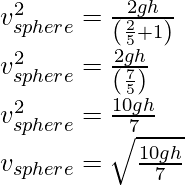
The results show that the sphere has the greatest and the ring has the least velocity of the centre of mass at the bottom of the inclined plane.
问题 2:求球体关于球体切线的转动惯量,给定球体关于其任何直径的转动惯量为 2 MR2/5,其中 M 是球体的质量,R 是球体的半径。 (b) 给定质量为 M 且半径为 R 的圆盘对任何直径到 1 的转动惯量为 1/4 MR2,求绕垂直于圆盘的轴通过其边缘上的一点的转动惯量。
解决方案:
(a) Moment of inertia of sphere about any diameter = 2/5 MR2
Applying theorem of parallel axes,
Moment of inertia of sphere about a tangent to the sphere = 2/5 MR2 +M(R)2
=7/5 MR2
(b) Given,
The expression for the moment of inertia of the disc about any of its diameters can be written as
L= 1/4 MR2
(i) Using theorem of perpendicular axes, the moment of inertia of the disc about an axis passing through its centre and normal to the disc can be written as
I= 2 x 1/4 MR2
I = 1/2 MR2.
(ii) Using theorem axes, moment of inertia of the disc passing through a point on its edge and normal to the dies can be written as
I = 1/2 MR2+ MR2
I = 3/2 MR2.
问题 3:对空心圆柱体和实心球体施加相同大小的扭矩,两者具有相同的质量和半径。圆柱可以绕其标准对称轴自由旋转,而球体可以绕通过其中心的轴自由旋转。在给定时间后,两者中哪一个将获得更大的角速度?
解决方案:
Let the radius of the hollow cylinder, and the solid sphere be R and the mass M .
The moments of inertia of the hollow cylinder about the respective axes is I1 = MR2
And the moments of inertia of the solid sphere about the respective axes I2 = (2/5) MR2
Let the magnitude of the torque applied to the cylinder and the sphere is τ , Which produce angular accelerations α1 and α2.
Then, the magnitude of the torque can be expressed as
τ = I1 α1 = I2 α2
The sphere is larger angular acceleration. Therefore, the sphere will acquire larger angular speed after a given time.
问题 5:如图所示,质量为 m、半径为 R 的环上附有三个粒子。环中心的速度为 v 0 。如果系统的动能是 xmv 0 2 。查找 x(不存在滑倒)
解决方案:
The expression for the rolling motion when slip is absent is,
![]()
Now the speed of the 2m particle placed at left side is
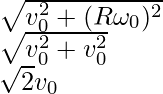
The speed of the m particle placed at right side is

The speed of the m particle placed at top is
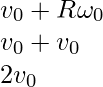
The kinetic energy placed at left , right and top is
Kinetic energy of the ring is
K.E = rotational kinetic energy + translational kinetic energy.
![]()
Substitute I = mR2 and ω = v0/R in the above equation,

The total kinetic energy is

Therefore, the value of x is 6.