给定一棵树,以及所有节点的权重,任务是计算权重为Perfect number的节点的数量。
A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors.
例子:
Input:
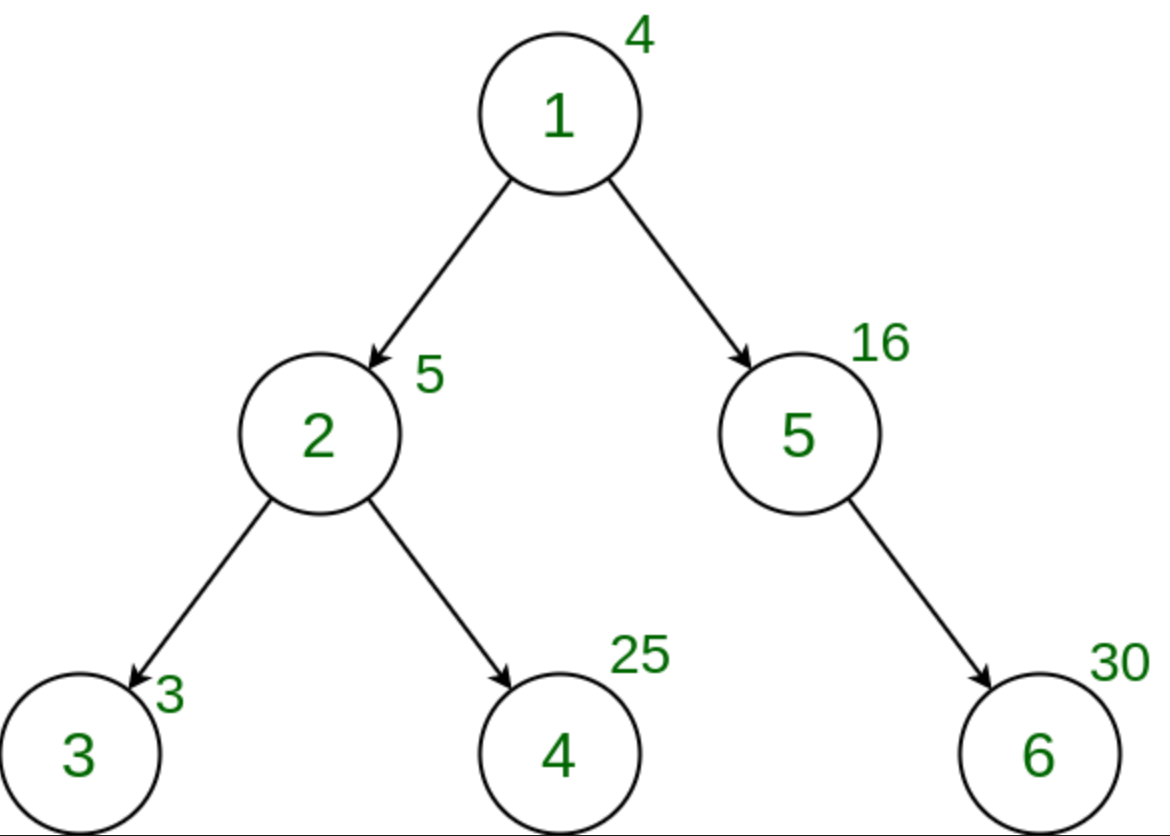
Output: 0
Explanation:
There is no node with a weight that is a perfect number.
方法:
为了解决此问题,我们在树上执行深度优先搜索(DFS)遍历,并针对每个节点检查其权重是否为“完美数”。每当获得这样的权重时,我们就不断增加计数器。整个树遍历完成后该计数器的最终值就是答案。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to Count the nodes in the
// given tree whose weight is a Perfect Number
#include
using namespace std;
int ans = 0;
vector graph[100];
vector weight(100);
// Function that returns true if n is perfect
bool isPerfect(long long int n)
{
// Variable to store sum of divisors
long long int sum = 1;
// Find all divisors and add them
for (long long int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
if (i * i != n)
sum = sum + i + n / i;
else
sum = sum + i;
}
}
// Check if sum of divisors is equal to
// n, then n is a perfect number
if (sum == n && n != 1)
return true;
return false;
}
// Function to perform dfs
void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If weight of the current node
// is a perfect number
if (isPerfect(weight[node]))
ans += 1;
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(4);
graph[1].push_back(5);
dfs(1, 1);
cout << ans;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to Count the nodes in the
// given tree whose weight is a Perfect Number
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int ans = 0;
static Vector []graph = new Vector[100];
static int []weight = new int[100];
// Function that returns true if n is perfect
static boolean isPerfect(int n)
{
// Variable to store sum of divisors
int sum = 1;
// Find all divisors and add them
for (int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
if (i * i != n)
sum = sum + i + n / i;
else
sum = sum + i;
}
}
// Check if sum of divisors is equal to
// n, then n is a perfect number
if (sum == n && n != 1)
return true;
return false;
}
// Function to perform dfs
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If weight of the current node
// is a perfect number
if (isPerfect(weight[node]))
ans += 1;
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++)
graph[i] = new Vector();
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].add(2);
graph[2].add(3);
graph[2].add(4);
graph[1].add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
System.out.print(ans);
}
}
// This code contributed by Princi Singh Python3
# Python3 implementation to
# Count the Nodes in the given
# tree whose weight is a Perfect
# Number
graph = [[] for i in range(100)]
weight = [0] * 100
ans = 0
# Function that returns
# True if n is perfect
def isPerfect(n):
# Variable to store
# sum of divisors
sum = 1;
# Find all divisors
# and add them
i = 2;
while(i * i < n):
if (n % i == 0):
if (i * i != n):
sum = sum + i + n / i;
else:
sum = sum + i;
i += 1;
# Check if sum of divisors
# is equal to n, then n is
# a perfect number
if (sum == n and n != 1):
return True;
return False;
# Function to perform dfs
def dfs(Node, parent):
# If weight of the current
# Node is a perfect number
global ans;
if (isPerfect(weight[Node])):
ans += 1;
for to in graph[Node]:
if (to == parent):
continue;
dfs(to, Node);
# Driver code
# Weights of the Node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
# Edges of the tree
graph[1].append(2);
graph[2].append(3);
graph[2].append(4);
graph[1].append(5);
dfs(1, 1);
print(ans);
# This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarC#
// C# implementation to count the
// nodes in the given tree whose
// weight is a Perfect Number
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int ans = 0;
static List []graph = new List[100];
static int []weight = new int[100];
// Function that returns true
// if n is perfect
static bool isPerfect(int n)
{
// Variable to store sum of
// divisors
int sum = 1;
// Find all divisors and add them
for(int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++)
{
if (n % i == 0)
{
if (i * i != n)
sum = sum + i + n / i;
else
sum = sum + i;
}
}
// Check if sum of divisors is equal
// to n, then n is a perfect number
if (sum == n && n != 1)
return true;
return false;
}
// Function to perform dfs
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If weight of the current node
// is a perfect number
if (isPerfect(weight[node]))
ans += 1;
foreach(int to in graph[node])
{
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < graph.Length; i++)
graph[i] = new List();
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(3);
graph[2].Add(4);
graph[1].Add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey 输出:
1
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度:O(N * logV),其中V是树中节点的最大权重
在DFS中,树的每个节点都处理一次,因此,如果树中总共有N个节点,则由于dfs而导致的复杂度为O(N)。另外,在处理每个节点时,为了检查节点值是否为完美数,将调用isPerfect(V)函数(其中V为节点的权重),该函数的复杂度为O(logV) ,因此对于每个节点,都会增加O(logV)的复杂度。因此,时间复杂度为O(N * logV)。
辅助空间:O(1)。
不需要任何额外的空间,因此空间复杂度是恒定的。