Python中的向量化
我们知道大多数应用程序必须处理大量数据集。因此,非计算最优函数可能会成为算法中的巨大瓶颈,并可能导致模型需要很长时间才能运行。为了确保代码的计算效率,我们将使用向量化。
执行任何算法的时间复杂度对于决定应用程序是否可靠至关重要。当涉及到输出的实时应用时,在尽可能多的最佳时间内运行一个大型算法是非常重要的。为此, Python具有一些标准数学函数,可用于对整个数据数组进行快速运算,而无需编写循环。包含此类函数的此类库之一是numpy 。让我们看看在矢量化的情况下如何使用这个标准函数。
什么是矢量化?
矢量化用于在不使用循环的情况下加速Python代码。使用这样的函数可以帮助有效地最小化代码的运行时间。正在对向量执行各种操作,例如向量的点积,也称为标量积,因为它产生单个输出,外积导致维度等于向量长度 X 长度的方阵,元素乘法乘积矩阵的相同索引和维度的元素保持不变。
我们将通过计算处理时间来了解经典方法如何比使用某些标准函数更耗时。
outer(a, b): Compute the outer product of two vectors.
multiply(a, b): Matrix product of two arrays.
dot(a, b): Dot product of two arrays.
zeros((n, m)): Return a matrix of given shape and type, filled with zeros.
process_time(): Return the value (in fractional seconds) of the sum of the system and user CPU time of the current process. It does not include time elapsed during sleep.
点积:
点积是一种代数运算,其中两个相等长度的向量相乘以产生一个数字。点积通常称为内积。这个产品产生一个标量数。让我们考虑两个相同长度的矩阵a和b ,点积是通过对第一个矩阵进行转置,然后是a' (a的转置)和b的数学矩阵乘法来完成的,如下图所示。
点积的图示—— 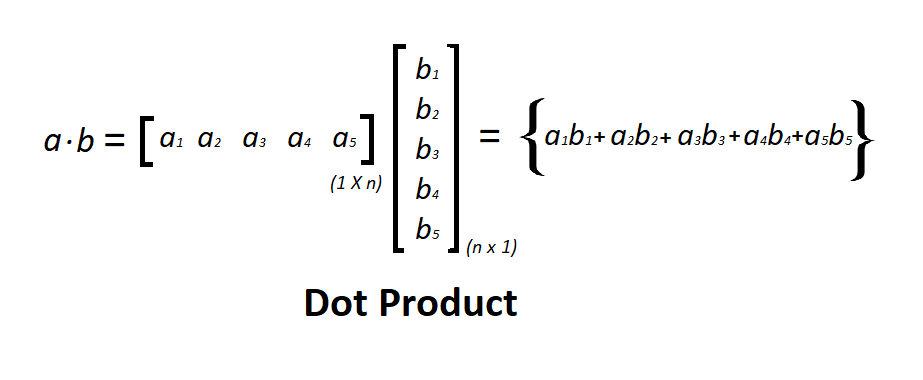
下面是Python代码:
# Dot product
import time
import numpy
import array
# 8 bytes size int
a = array.array('q')
for i in range(100000):
a.append(i);
b = array.array('q')
for i in range(100000, 200000):
b.append(i)
# classic dot product of vectors implementation
tic = time.process_time()
dot = 0.0;
for i in range(len(a)):
dot += a[i] * b[i]
toc = time.process_time()
print("dot_product = "+ str(dot));
print("Computation time = " + str(1000*(toc - tic )) + "ms")
n_tic = time.process_time()
n_dot_product = numpy.dot(a, b)
n_toc = time.process_time()
print("\nn_dot_product = "+str(n_dot_product))
print("Computation time = "+str(1000*(n_toc - n_tic ))+"ms")
输出:
dot_product = 833323333350000.0
Computation time = 35.59449199999999ms
n_dot_product = 833323333350000
Computation time = 0.1559900000000225ms
外层产品:
两个坐标向量的张量积称为外积。让我们考虑维度为nx 1和mx 1的两个向量a和b ,然后向量的外积产生nxm的矩形矩阵。如果两个向量具有相同的维度,则结果矩阵将是如图所示的方阵。
外部产品的图示 - 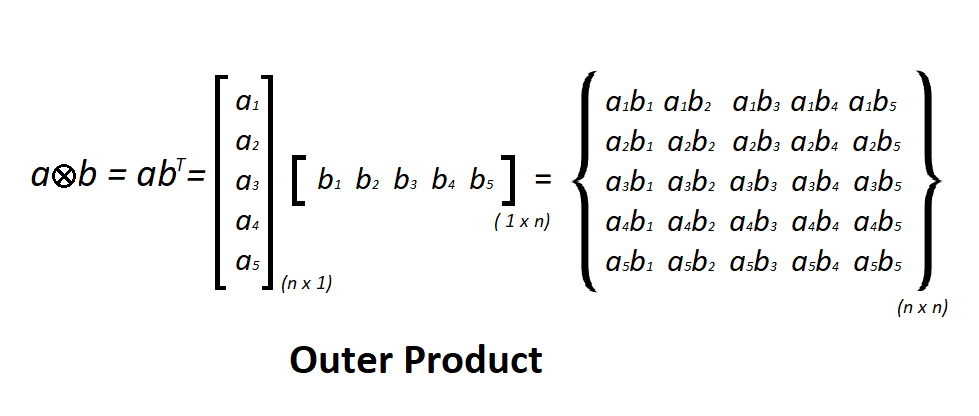
下面是Python代码:
# Outer product
import time
import numpy
import array
a = array.array('i')
for i in range(200):
a.append(i);
b = array.array('i')
for i in range(200, 400):
b.append(i)
# classic outer product of vectors implementation
tic = time.process_time()
outer_product = numpy.zeros((200, 200))
for i in range(len(a)):
for j in range(len(b)):
outer_product[i][j]= a[i]*b[j]
toc = time.process_time()
print("outer_product = "+ str(outer_product));
print("Computation time = "+str(1000*(toc - tic ))+"ms")
n_tic = time.process_time()
outer_product = numpy.outer(a, b)
n_toc = time.process_time()
print("outer_product = "+str(outer_product));
print("\nComputation time = "+str(1000*(n_toc - n_tic ))+"ms")
输出:
outer_product = [[ 0. 0. 0. ..., 0. 0. 0.]
[ 200. 201. 202. ..., 397. 398. 399.]
[ 400. 402. 404. ..., 794. 796. 798.]
...,
[ 39400. 39597. 39794. ..., 78209. 78406. 78603.]
[ 39600. 39798. 39996. ..., 78606. 78804. 79002.]
[ 39800. 39999. 40198. ..., 79003. 79202. 79401.]]
Computation time = 39.821617ms
outer_product = [[ 0 0 0 ..., 0 0 0]
[ 200 201 202 ..., 397 398 399]
[ 400 402 404 ..., 794 796 798]
...,
[39400 39597 39794 ..., 78209 78406 78603]
[39600 39798 39996 ..., 78606 78804 79002]
[39800 39999 40198 ..., 79003 79202 79401]]
Computation time = 0.2809480000000031ms
元素明智的产品:
两个矩阵的元素乘法是代数运算,其中第一个矩阵的每个元素都乘以后面矩阵中的相应元素。矩阵的维度应该相同。
考虑两个矩阵a和b , a 中元素的索引是i和j然后a(i , j) 分别与 b(i, j)相乘,如下图所示。
Element wise 产品的图示 - 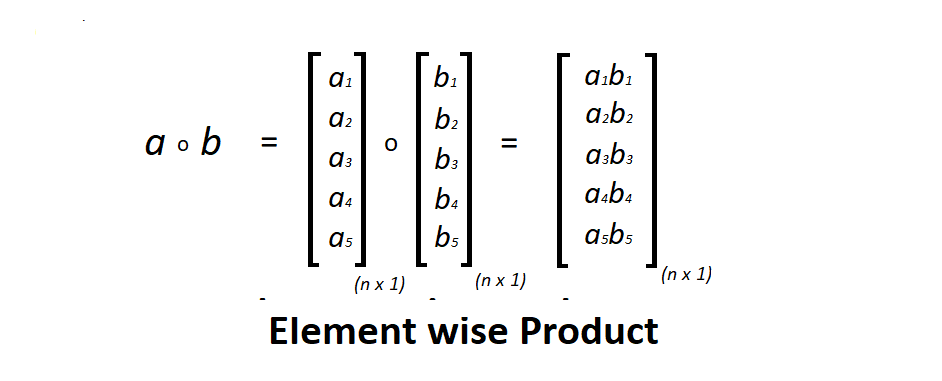
下面是Python代码:
# Element-wise multiplication
import time
import numpy
import array
a = array.array('i')
for i in range(50000):
a.append(i);
b = array.array('i')
for i in range(50000, 100000):
b.append(i)
# classic element wise product of vectors implementation
vector = numpy.zeros((50000))
tic = time.process_time()
for i in range(len(a)):
vector[i]= a[i]*b[i]
toc = time.process_time()
print("Element wise Product = "+ str(vector));
print("\nComputation time = "+str(1000*(toc - tic ))+"ms")
n_tic = time.process_time()
vector = numpy.multiply(a, b)
n_toc = time.process_time()
print("Element wise Product = "+str(vector));
print("\nComputation time = "+str(1000*(n_toc - n_tic ))+"ms")
输出:
Element wise Product = [ 0.00000000e+00 5.00010000e+04 1.00004000e+05 ..., 4.99955001e+09
4.99970000e+09 4.99985000e+09]
Computation time = 23.516678000000013ms
Element wise Product = [ 0 50001 100004 ..., 704582713 704732708 704882705]
Computation time = 0.2250640000000248ms