给定大小为8 x 8的棋盘和Mirandote的当前位置。该国际象棋游戏的所有规则都相同,但是对骑士进行了修改,我们称新骑士为“ Mirandote”。 Mirandote的移动由蓝色表示,在下图中,其当前位置由红色表示:
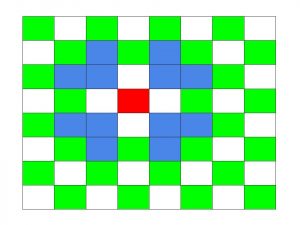
任务是找出棋盘上存在多少个可能的位置,Mirandote可以精确地在S步中达到这些位置。
例子:
Input: row = 4, col = 4, steps = 1
Output: 12
All the 12 moves denoted by the following image by blue color :
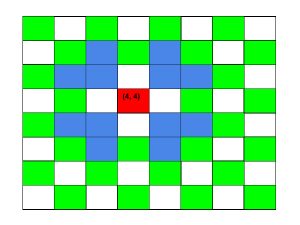
Input: row = 4, col = 4, steps = 2
Output: 55
解决方案:
我们可以观察到,相对于当前位置的所有可能位置都可以以行和列的形式编写。下图说明了这个问题:
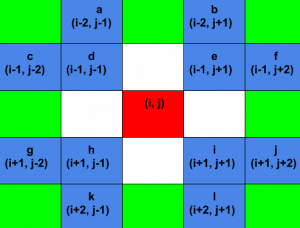
我们可以为每个可能的位置递归调用一个函数,并计算所有可能的位置。
以下是找到职位所需的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// possible positions
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the positions
void findSteps(int current_row, int current_column,
int curr, int board_size, int steps,
int* visited)
{
// Bound checking
if (current_row >= board_size || current_row < 0
|| current_column >= board_size || current_column < 0
|| curr > steps) {
return;
}
// If steps is equal to current steps,
// that means current position is reached by Mirandote
if (curr == steps) {
*((visited + (current_row)*board_size) + current_column) = 1;
return;
}
// Recursive calls for each possible position.
// Position of a, b, c, ..., l given in above image.
/* a = */ findSteps(current_row - 2, current_column - 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* b = */ findSteps(current_row - 2, current_column + 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* c = */ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column - 2,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* d = */ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column - 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* e = */ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column + 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* f = */ findSteps(current_row - 1, current_column + 2,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* g = */ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column - 2,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* h = */ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column - 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* i = */ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column + 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* j = */ findSteps(current_row + 1, current_column + 2,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* k = */ findSteps(current_row + 2, current_column - 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
/* l = */ findSteps(current_row + 2, current_column + 1,
curr + 1, board_size, steps, visited);
return;
}
int countSteps(int current_row, int current_column,
int board_size, int steps)
{
// Visited array
int visited[board_size][board_size];
// Initialize visited array to zero
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board_size; j++) {
visited[i][j] = 0;
}
}
int answer = 0;
// Function call where initial step count is 0
findSteps(current_row, current_column, 0,
board_size, steps, (int*)visited);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board_size; j++) {
// If value of element is 1, that implies,
// the position can be reached by Mirandote.
if (visited[i][j] == 1) {
answer++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int board_size = 8, steps = 1;
int current_row = 4, current_column = 4;
cout << countSteps(current_row, current_column,
board_size, steps);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to find the
// possible positions
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int [][] visited = new int [500][500];
// Function to find the positions
static void findSteps(int current_row,
int current_column,
int curr, int board_size,
int steps)
{
// Bound checking
if (current_row >= board_size ||
current_row < 0 ||
current_column >= board_size ||
current_column < 0 || curr > steps)
{
return;
}
// If steps is equal to current steps,
// that means current position is
// reached by Mirandote
if (curr == steps)
{
visited[current_row][current_column] = 1;
return;
}
// Recursive calls for each possible position.
// Position of a, b, c, ..., l given in
// above image.
/* a = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* b = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* c = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* d = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* e = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* f = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* g = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* h = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* i = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* j = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* k = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* l = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
}
static int countSteps(int current_row,
int current_column,
int board_size, int steps)
{
// Initialize visited array to zero
for(int i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
visited[i][j] = 0;
}
}
int answer = 0;
// Function call where initial step count is 0
findSteps(current_row, current_column, 0,
board_size,steps);
for(int i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
// If value of element is 1, that implies,
// the position can be reached by Mirandote.
if (visited[i][j] == 1)
{
answer++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int board_size = 8, steps = 1;
int current_row = 4, current_column = 4;
System.out.print(countSteps(current_row,
current_column,
board_size, steps));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_CipherC#
// C# implementation to find the
// possible positions
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG{
static int [,] visited = new int[500, 500];
// Function to find the positions
static void findSteps(int current_row,
int current_column,
int curr, int board_size,
int steps)
{
// Bound checking
if (current_row >= board_size ||
current_row < 0 ||
current_column >= board_size ||
current_column < 0 || curr > steps)
{
return;
}
// If steps is equal to current steps,
// that means current position is
// reached by Mirandote
if (curr == steps)
{
visited[current_row, current_column] = 1;
return;
}
// Recursive calls for each possible position.
// Position of a, b, c, ..., l given in above image.
/* a = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* b = */ findSteps(current_row - 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* c = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* d = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* e = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* f = */ findSteps(current_row - 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* g = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* h = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* i = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* j = */ findSteps(current_row + 1,
current_column + 2,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* k = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column - 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
/* l = */ findSteps(current_row + 2,
current_column + 1,
curr + 1,
board_size, steps);
}
static int countSteps(int current_row,
int current_column,
int board_size, int steps)
{
// Initialize visited array to zero
for(int i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
visited[i, j] = 0;
}
}
int answer = 0;
// Function call where initial step count is 0
findSteps(current_row, current_column, 0,
board_size,steps);
for(int i = 0; i < board_size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < board_size; j++)
{
// If value of element is 1,
// that implies, the position
// can be reached by Mirandote.
if (visited[i, j] == 1)
{
answer++;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int board_size = 8, steps = 1;
int current_row = 4, current_column = 4;
Console.WriteLine(countSteps(current_row,
current_column,
board_size, steps));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher输出:
12
上述算法的时间复杂度为O(12 S ),其中S为步数。