对于给定的微分方程![]() 有初始条件
有初始条件![]()
使用Predictor-Corrector方法找到近似解。
预测器校正方法:
预测器-校正器方法也称为Modified-Euler方法。
在欧拉方法中,在一个点处绘制切线,并针对给定的步长计算斜率。因此,该方法最适合线性函数,但在其他情况下,仍然存在截断误差。为了解决这个问题,引入了改进的欧拉方法。在此方法中,不是点,而是间隔上的斜率的算术平均值![]() 用来。
用来。
因此,在Predictor-Corrector方法中,每个步骤的预测值![]() 首先使用欧拉方法计算,然后在点处计算斜率
首先使用欧拉方法计算,然后在点处计算斜率![]() 和
和![]() 计算并把这些斜率的算术平均值加到
计算并把这些斜率的算术平均值加到![]() 计算校正值
计算校正值![]() 。
。
所以,
这里h是每个增量的步长
因为,在这种方法中,由于使用了平均斜率,所以误差显着降低。同样,我们可以重复校正过程以收敛。因此,在每一步,我们都通过提高y的值来减少误差。
例子:
Input : eq = ![]() , y(0) = 0.5, step size(h) = 0.2
, y(0) = 0.5, step size(h) = 0.2
To find: y(1)
Output: y(1) = 2.18147
Explanation: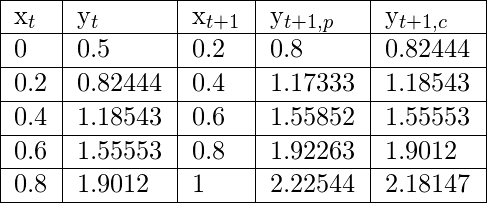
The final value of y at x = 1 is y=2.18147
实现:这里我们考虑微分方程: ![]()
C++
// C++ code for solving the differential equation
// using Predictor-Corrector or Modified-Euler method
// with the given conditions, y(0) = 0.5, step size(h) = 0.2
// to find y(1)
#include
using namespace std;
// consider the differential equation
// for a given x and y, return v
double f(double x, double y)
{
double v = y - 2 * x * x + 1;
return v;
}
// predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
// and step size h using Euler method
double predict(double x, double y, double h)
{
// value of next y(predicted) is returned
double y1p = y + h * f(x, y);
return y1p;
}
// corrects the predicted value
// using Modified Euler method
double correct(double x, double y,
double x1, double y1,
double h)
{
// (x, y) are of previous step
// and x1 is the increased x for next step
// and y1 is predicted y for next step
double e = 0.00001;
double y1c = y1;
do {
y1 = y1c;
y1c = y + 0.5 * h * (f(x, y) + f(x1, y1));
} while (fabs(y1c - y1) > e);
// every iteration is correcting the value
// of y using average slope
return y1c;
}
void printFinalValues(double x, double xn,
double y, double h)
{
while (x < xn) {
double x1 = x + h;
double y1p = predict(x, y, h);
double y1c = correct(x, y, x1, y1p, h);
x = x1;
y = y1c;
}
// at every iteration first the value
// of for next step is first predicted
// and then corrected.
cout << "The final value of y at x = "
<< x << " is : " << y << endl;
}
int main()
{
// here x and y are the initial
// given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
double x = 0, y = 0.5;
// final value of x for which y is needed
double xn = 1;
// step size
double h = 0.2;
printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h);
return 0;
} Java
// Java code for solving the differential
// equation using Predictor-Corrector
// or Modified-Euler method with the
// given conditions, y(0) = 0.5, step
// size(h) = 0.2 to find y(1)
import java.text.*;
class GFG
{
// consider the differential equation
// for a given x and y, return v
static double f(double x, double y)
{
double v = y - 2 * x * x + 1;
return v;
}
// predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
// and step size h using Euler method
static double predict(double x, double y, double h)
{
// value of next y(predicted) is returned
double y1p = y + h * f(x, y);
return y1p;
}
// corrects the predicted value
// using Modified Euler method
static double correct(double x, double y,
double x1, double y1,
double h)
{
// (x, y) are of previous step
// and x1 is the increased x for next step
// and y1 is predicted y for next step
double e = 0.00001;
double y1c = y1;
do
{
y1 = y1c;
y1c = y + 0.5 * h * (f(x, y) + f(x1, y1));
}
while (Math.abs(y1c - y1) > e);
// every iteration is correcting the value
// of y using average slope
return y1c;
}
static void printFinalValues(double x, double xn,
double y, double h)
{
while (x < xn)
{
double x1 = x + h;
double y1p = predict(x, y, h);
double y1c = correct(x, y, x1, y1p, h);
x = x1;
y = y1c;
}
// at every iteration first the value
// of for next step is first predicted
// and then corrected.
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.#####");
System.out.println("The final value of y at x = "+
x + " is : "+df.format(y));
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// here x and y are the initial
// given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
double x = 0, y = 0.5;
// final value of x for which y is needed
double xn = 1;
// step size
double h = 0.2;
printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h);
}
}
// This code is contributed by mitsPython3
# Python3 code for solving the differential equation
# using Predictor-Corrector or Modified-Euler method
# with the given conditions, y(0) = 0.5, step size(h) = 0.2
# to find y(1)
# consider the differential equation
# for a given x and y, return v
def f(x, y):
v = y - 2 * x * x + 1;
return v;
# predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
# and step size h using Euler method
def predict(x, y, h):
# value of next y(predicted) is returned
y1p = y + h * f(x, y);
return y1p;
# corrects the predicted value
# using Modified Euler method
def correct(x, y, x1, y1, h):
# (x, y) are of previous step
# and x1 is the increased x for next step
# and y1 is predicted y for next step
e = 0.00001;
y1c = y1;
while (abs(y1c - y1) > e + 1):
y1 = y1c;
y1c = y + 0.5 * h * (f(x, y) + f(x1, y1));
# every iteration is correcting the value
# of y using average slope
return y1c;
def printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h):
while (x < xn):
x1 = x + h;
y1p = predict(x, y, h);
y1c = correct(x, y, x1, y1p, h);
x = x1;
y = y1c;
# at every iteration first the value
# of for next step is first predicted
# and then corrected.
print("The final value of y at x =",
int(x), "is :", y);
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# here x and y are the initial
# given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
x = 0; y = 0.5;
# final value of x for which y is needed
xn = 1;
# step size
h = 0.2;
printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h);
# This code is contributed by Rajput-JiC#
// C# code for solving the differential
// equation using Predictor-Corrector
// or Modified-Euler method with the
// given conditions, y(0) = 0.5, step
// size(h) = 0.2 to find y(1)
using System;
class GFG
{
// consider the differential equation
// for a given x and y, return v
static double f(double x, double y)
{
double v = y - 2 * x * x + 1;
return v;
}
// predicts the next value for a given (x, y)
// and step size h using Euler method
static double predict(double x, double y, double h)
{
// value of next y(predicted) is returned
double y1p = y + h * f(x, y);
return y1p;
}
// corrects the predicted value
// using Modified Euler method
static double correct(double x, double y,
double x1, double y1,
double h)
{
// (x, y) are of previous step
// and x1 is the increased x for next step
// and y1 is predicted y for next step
double e = 0.00001;
double y1c = y1;
do
{
y1 = y1c;
y1c = y + 0.5 * h * (f(x, y) + f(x1, y1));
}
while (Math.Abs(y1c - y1) > e);
// every iteration is correcting the value
// of y using average slope
return y1c;
}
static void printFinalValues(double x, double xn,
double y, double h)
{
while (x < xn)
{
double x1 = x + h;
double y1p = predict(x, y, h);
double y1c = correct(x, y, x1, y1p, h);
x = x1;
y = y1c;
}
// at every iteration first the value
// of for next step is first predicted
// and then corrected.
Console.WriteLine("The final value of y at x = "+
x + " is : " + Math.Round(y, 5));
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// here x and y are the initial
// given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
double x = 0, y = 0.5;
// final value of x for which y is needed
double xn = 1;
// step size
double h = 0.2;
printFinalValues(x, xn, y, h);
}
}
// This code is contributed by mitsPHP
$e);
// every iteration is correcting the
// value of y using average slope
return $y1c;
}
function printFinalValues($x, $xn, $y, $h)
{
while ($x < $xn)
{
$x1 = $x + $h;
$y1p = predict($x, $y, $h);
$y1c = correct($x, $y, $x1, $y1p, $h);
$x = $x1;
$y = $y1c;
}
// at every iteration first the value
// of for next step is first predicted
// and then corrected.
echo "The final value of y at x = " . $x .
" is : " . round($y, 5) . "\n";
}
// here x and y are the initial
// given condition, so x=0 and y=0.5
$x = 0;
$y = 0.5;
// final value of x for which y is needed
$xn = 1;
// step size
$h = 0.2;
printFinalValues($x, $xn, $y, $h);
// This code is contributed by mits
?>输出:
The final value of y at x = 1 is : 2.18147