给出以下输入:
- 一个普通的微分方程,以x和y的形式定义dy / dx的值。
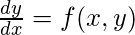
- y的初始值,即y(0) 。
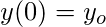
任务是在给定的点x上找到未知函数y的值,即y(x) 。
例子:
Input: x0 = 0, y = 3.0, x = 5.0, h = 0.2
Output: y(x) = 3.410426
Input: x0 = 0, y = 1, x = 3, h = 0.3
Output: y(x) = 1.669395
方法:
吉尔(Gill)方法用于查找给定x的y的近似值。下面是用来从以前的值是否计算下一个值y n + 1个公式。
所以:
yn+1 = value of y at (x = n + 1)
yn = value of y at (x = n)
where
0 ≤ n ≤ (x - x0)/h
h is step height
xn+1 = x0 + h
计算y(n + 1)值的基本公式:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
该公式基本上使用当前y n计算下一个值y n + 1 :
- K 1是基于间隔开始时的斜率的增量,使用y 。
- K 2是基于斜率的增量,使用
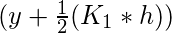
- K 3是基于斜率的增量,使用
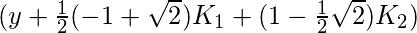
- K 4是基于斜率的增量,使用
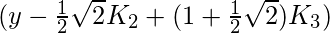
该方法是四阶方法,意味着局部截断误差约为O(h 5 ) 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement Gill's method
#include
using namespace std;
// A sample differential equation
// "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
float dydx(float x, float y)
{
return (x - y) / 2;
}
// Finds value of y for a given x
// using step size h and initial
// value y0 at x0
float Gill(float x0, float y0,
float x, float h)
{
// Count number of iterations
// using step size or height h
int n = (int)((x - x0) / h);
// Value of K_i
float k1, k2, k3, k4;
// Initial value of y(0)
float y = y0;
// Iterate for number of iteration
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Apply Gill's Formulas to
// find next value of y
// Value of K1
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y);
// Value of K2
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * k1);
// Value of K3
k3 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * (-1 + sqrt(2)) * k1
+ k2 * (1 - 0.5 * sqrt(2)));
// Value of K4
k4 = h * dydx(x0 + h,
y - (0.5 * sqrt(2)) * k2
+ k3 * (1 + 0.5 * sqrt(2)));
// Find the next value of y(n+1)
// using y(n) and values of K in
// the above steps
y = y + (1.0 / 6) * (k1 + (2 - sqrt(2)) * k2
+ (2 + sqrt(2)) * k3 + k4);
// Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h;
}
// Return the final value of dy/dx
return y;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
float x0 = 0, y = 3.0,
x = 5.0, h = 0.2;
printf("y(x) = %.6f",
Gill(x0, y, x, h));
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement Gill's method
class GFG{
// A sample differential equation
// "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
static double dydx(double x, double y)
{
return (x - y) / 2;
}
// Finds value of y for a given x
// using step size h and initial
// value y0 at x0
static double Gill(double x0, double y0,
double x, double h)
{
// Count number of iterations
// using step size or height h
int n = (int)((x - x0) / h);
// Value of K_i
double k1, k2, k3, k4;
// Initial value of y(0)
double y = y0;
// Iterate for number of iteration
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Apply Gill's Formulas to
// find next value of y
// Value of K1
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y);
// Value of K2
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * k1);
// Value of K3
k3 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * (-1 + Math.sqrt(2)) *
k1 + k2 * (1 - 0.5 * Math.sqrt(2)));
// Value of K4
k4 = h * dydx(x0 + h,
y - (0.5 * Math.sqrt(2)) *
k2 + k3 * (1 + 0.5 * Math.sqrt(2)));
// Find the next value of y(n+1)
// using y(n) and values of K in
// the above steps
y = y + (1.0 / 6) * (k1 + (2 - Math.sqrt(2)) *
k2 + (2 + Math.sqrt(2)) *
k3 + k4);
// Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h;
}
// Return the final value of dy/dx
return y;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x0 = 0, y = 3.0,
x = 5.0, h = 0.2;
System.out.printf("y(x) = %.6f", Gill(x0, y, x, h));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit KatiyarPython3
# Python3 program to implement Gill's method
from math import sqrt
# A sample differential equation
# "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
def dydx(x, y):
return (x - y) / 2
# Finds value of y for a given x
# using step size h and initial
# value y0 at x0
def Gill(x0, y0, x, h):
# Count number of iterations
# using step size or height h
n = ((x - x0) / h)
# Initial value of y(0)
y = y0
# Iterate for number of iteration
for i in range(1, int(n + 1), 1):
# Apply Gill's Formulas to
# find next value of y
# Value of K1
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y)
# Value of K2
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * k1)
# Value of K3
k3 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * (-1 + sqrt(2)) *
k1 + k2 * (1 - 0.5 * sqrt(2)))
# Value of K4
k4 = h * dydx(x0 + h, y - (0.5 * sqrt(2)) *
k2 + k3 * (1 + 0.5 * sqrt(2)))
# Find the next value of y(n+1)
# using y(n) and values of K in
# the above steps
y = y + (1 / 6) * (k1 + (2 - sqrt(2)) *
k2 + (2 + sqrt(2)) *
k3 + k4)
# Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h
# Return the final value of dy/dx
return y
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
x0 = 0
y = 3.0
x = 5.0
h = 0.2
print("y(x) =", round(Gill(x0, y, x, h), 6))
# This code is contributed by Surendra_GangwarC#
// C# program to implement Gill's method
using System;
class GFG{
// A sample differential equation
// "dy/dx = (x - y)/2"
static double dydx(double x, double y)
{
return (x - y) / 2;
}
// Finds value of y for a given x
// using step size h and initial
// value y0 at x0
static double Gill(double x0, double y0,
double x, double h)
{
// Count number of iterations
// using step size or height h
int n = (int)((x - x0) / h);
// Value of K_i
double k1, k2, k3, k4;
// Initial value of y(0)
double y = y0;
// Iterate for number of iteration
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Apply Gill's Formulas to
// find next value of y
// Value of K1
k1 = h * dydx(x0, y);
// Value of K2
k2 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * k1);
// Value of K3
k3 = h * dydx(x0 + 0.5 * h,
y + 0.5 * (-1 + Math.Sqrt(2)) *
k1 + k2 * (1 - 0.5 * Math.Sqrt(2)));
// Value of K4
k4 = h * dydx(x0 + h,
y - (0.5 * Math.Sqrt(2)) *
k2 + k3 * (1 + 0.5 * Math.Sqrt(2)));
// Find the next value of y(n+1)
// using y(n) and values of K in
// the above steps
y = y + (1.0 / 6) * (k1 + (2 - Math.Sqrt(2)) *
k2 + (2 + Math.Sqrt(2)) *
k3 + k4);
// Update next value of x
x0 = x0 + h;
}
// Return the final value of dy/dx
return y;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
double x0 = 0, y = 3.0,
x = 5.0, h = 0.2;
Console.Write("y(x) = {0:F6}", Gill(x0, y, x, h));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar输出:
y(x) = 3.410426