给定三个整数N , A和B ,任务是计算准确掷N次骰子时获得的数字总和介于A和B之间的概率。
例子:
Input: N = 1, A = 2, B = 3
Output: 0.333333
Explanation: Ways to obtained the sum 2 by N ( = 1) throws of a dice is 1 {2}. Therefore, required probability = 1/6 = 0.33333
Input: N = 2, A = 3, B = 4
Output: 0.138889
递归方法:按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 计算A和B之间所有数字的概率并将其相加以获得答案。
- 调用函数find(N,sum)来计算从a到b的每个数字的概率,其中a和b之间的数字将作为sum传递。
- 基本情况是:
- 如果总和大于6 * N或小于N ,则返回0,因为不可能有大于N * 6或小于N的和。
- 如果N等于1并且总和在1到6之间,则返回1/6。
- 由于在每个状态中,单骰子中可能会出现1到6中的任何数字,因此应该对1≤i≤6的(求和到该状态的总和– i)进行递归调用。
- 返回结果概率。
- 基本情况是:
Recursion call:![]()
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate the
// probability for the given
// sum to be equal to sum in
// N throws of dice
long double find(int N, int sum)
{
// Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
long double s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
s = s + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return s;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
long double probability = 0.0;
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
// Print the answer
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << probability;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate the
// probability for the given
// sum to be equal to sum in
// N throws of dice
static double find(int N, int sum)
{
// Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
{
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
double s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
s = s + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return s;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
double probability = 0.0;
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
// Print the answer
System.out.format("%.6f", probability);
}
}
// This code is contributed by code_hunt.Python3
# Python 2 program for above approach
# Function to calculate the
# probability for the given
# sum to be equal to sum in
# N throws of dice
def find(N, sum):
# Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N or sum < N):
return 0
if (N == 1):
if (sum >= 1 and sum <= 6):
return 1.0 / 6
else:
return 0
s = 0
for i in range(1, 7):
s = s + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6
return s
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 4
a = 13
b = 17
probability = 0.0
for sum in range(a, b + 1):
probability = probability + find(N, sum)
# Print the answer
print(round(probability, 6))
# This code is contributed by chitranayal.C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate the
// probability for the given
// sum to be equal to sum in
// N throws of dice
static double find(int N, int sum)
{
// Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
{
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
double s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
s = s + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return s;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
double probability = 0.0;
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
// Print the answer
Console.WriteLine(Math.Round(probability,6));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07C++
// C++ program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
float dp[105][605];
// Function to calculate the
// probability for the given
// sum to be equal to sum in
// N throws of dice
float find(int N, int sum)
{
if (dp[N][sum])
return dp[N][sum];
// Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum]
+ find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = 0.0;
// Calculate probability of all
// sums from a to b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
// Print the answer
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << probability;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for above approach
class GFG
{
static float[][] dp = new float[105][605];
// Function to calculate the
// probability for the given
// sum to be equal to sum in
// N throws of dice
static float find(int N, int sum)
{
if (N < 0 | sum < 0)
return 0;
if (dp[N][sum] > 0)
return dp[N][sum];
// Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return (float) (1.0 / 6);
else
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum] + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = 0.0f;
// Calculate probability of all
// sums from a to b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
// Print the answer
System.out.printf("%.6f", probability);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajputPython3
# Python program for above approach
dp = [[0 for i in range(605)] for j in range(105)];
# Function to calculate the
# probability for the given
# sum to be equal to sum in
# N throws of dice
def find(N, sum):
if (N < 0 | sum < 0):
return 0;
if (dp[N][sum] > 0):
return dp[N][sum];
# Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N or sum < N):
return 0;
if (N == 1):
if (sum >= 1 and sum <= 6):
return (float)(1.0 / 6);
else:
return 0;
for i in range(1,7):
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum] + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 4; a = 13; b = 17;
probability = 0.0
f = 0;
# Calculate probability of all
# sums from a to b
for sum in range(a,b+1):
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
# Prthe answer
print("%.6f"% probability);
# This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarC#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
static float[,] dp = new float[105, 605];
// Function to calculate the
// probability for the given
// sum to be equal to sum in
// N throws of dice
static float find(int N, int sum)
{
if (N < 0 | sum < 0)
return 0;
if (dp[N, sum] > 0)
return dp[N, sum];
// Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return (float) (1.0 / 6);
else
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N, sum] = dp[N, sum] + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N, sum];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = 0.0f;
// Calculate probability of all
// sums from a to b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
// Print the answer
Console.Write("{0:F6}", probability);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarC++
// C++ program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
float dp[105][605];
// Function to calculate probability
// that the sum of numbers on N throws
// of dice lies between A and B
float find(int N, int a, int b)
{
float probability = 0.0;
// Base case
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1][i] = 1.0 / 6;
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++) {
for (int k = 1; k <= 6; k++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j]
+ dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
// Add the probability for all
// the numbers between a and b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N][sum];
return probability;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = find(N, a, b);
// Print the answer
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << probability;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static float [][]dp = new float[105][605];
// Function to calculate probability
// that the sum of numbers on N throws
// of dice lies between A and B
static float find(int N, int a, int b)
{
float probability = 0.0f;
// Base case
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1][i] = (float) (1.0 / 6);
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= 6 && k <= j; k++)
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j]
+ dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
// Add the probability for all
// the numbers between a and b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N][sum];
return probability;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = find(N, a, b);
// Print the answer
System.out.printf("%.6f",probability);
}
}
// This codeis contributed by shikhasingrajputPython3
# Python3 program for above approach
dp = [[0 for i in range(605)] for j in range(105)]
# Function to calculate probability
# that the sum of numbers on N throws
# of dice lies between A and B
def find(N, a, b) :
probability = 0.0
# Base case
for i in range(1, 7) :
dp[1][i] = 1.0 / 6
for i in range(2, N + 1) :
for j in range(i, (6*i) + 1) :
for k in range(1, 7) :
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] + dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6
# Add the probability for all
# the numbers between a and b
for Sum in range(a, b + 1) :
probability = probability + dp[N][Sum]
return probability
N, a, b = 4, 13, 17
probability = find(N, a, b)
# Print the answer
print('%.6f'%probability)
# This code is contributed by divyesh072019.C#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
public class GFG
{
static float [,]dp = new float[105, 605];
// Function to calculate probability
// that the sum of numbers on N throws
// of dice lies between A and B
static float find(int N, int a, int b)
{
float probability = 0.0f;
// Base case
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1, i] = (float) (1.0 / 6);
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= 6 && k <= j; k++)
{
dp[i, j] = dp[i, j]
+ dp[i - 1, j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
// Add the probability for all
// the numbers between a and b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N, sum];
return probability;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = find(N, a, b);
// Print the answer
Console.Write("{0:F6}",probability);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput输出:
0.505401时间复杂度: O((b-a + 1)6 n )
辅助空间: O(1)
动态规划方法:上述递归方法需要通过处理重叠的子问题和最佳子结构进行优化:
重叠子问题:
对于N = 4和sum = 15的部分递归树:
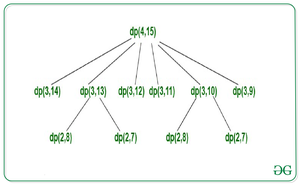
最佳子结构:
对于每个状态,对其他6个状态进行递归,因此f(N,sum)的递归定义为:
自上而下的方法:
C++
// C++ program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
float dp[105][605];
// Function to calculate the
// probability for the given
// sum to be equal to sum in
// N throws of dice
float find(int N, int sum)
{
if (dp[N][sum])
return dp[N][sum];
// Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return 1.0 / 6;
else
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum]
+ find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = 0.0;
// Calculate probability of all
// sums from a to b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
// Print the answer
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << probability;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for above approach
class GFG
{
static float[][] dp = new float[105][605];
// Function to calculate the
// probability for the given
// sum to be equal to sum in
// N throws of dice
static float find(int N, int sum)
{
if (N < 0 | sum < 0)
return 0;
if (dp[N][sum] > 0)
return dp[N][sum];
// Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return (float) (1.0 / 6);
else
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum] + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = 0.0f;
// Calculate probability of all
// sums from a to b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
// Print the answer
System.out.printf("%.6f", probability);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Python3
# Python program for above approach
dp = [[0 for i in range(605)] for j in range(105)];
# Function to calculate the
# probability for the given
# sum to be equal to sum in
# N throws of dice
def find(N, sum):
if (N < 0 | sum < 0):
return 0;
if (dp[N][sum] > 0):
return dp[N][sum];
# Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N or sum < N):
return 0;
if (N == 1):
if (sum >= 1 and sum <= 6):
return (float)(1.0 / 6);
else:
return 0;
for i in range(1,7):
dp[N][sum] = dp[N][sum] + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N][sum];
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 4; a = 13; b = 17;
probability = 0.0
f = 0;
# Calculate probability of all
# sums from a to b
for sum in range(a,b+1):
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
# Prthe answer
print("%.6f"% probability);
# This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
C#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
static float[,] dp = new float[105, 605];
// Function to calculate the
// probability for the given
// sum to be equal to sum in
// N throws of dice
static float find(int N, int sum)
{
if (N < 0 | sum < 0)
return 0;
if (dp[N, sum] > 0)
return dp[N, sum];
// Base cases
if (sum > 6 * N || sum < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1) {
if (sum >= 1 && sum <= 6)
return (float) (1.0 / 6);
else
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[N, sum] = dp[N, sum] + find(N - 1, sum - i) / 6;
return dp[N, sum];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = 0.0f;
// Calculate probability of all
// sums from a to b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + find(N, sum);
// Print the answer
Console.Write("{0:F6}", probability);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
输出:
0.505401时间复杂度: O(n * sum)
辅助空间: O(n * sum)
自下而上的方法:
C++
// C++ program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
float dp[105][605];
// Function to calculate probability
// that the sum of numbers on N throws
// of dice lies between A and B
float find(int N, int a, int b)
{
float probability = 0.0;
// Base case
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1][i] = 1.0 / 6;
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++) {
for (int k = 1; k <= 6; k++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j]
+ dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
// Add the probability for all
// the numbers between a and b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N][sum];
return probability;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = find(N, a, b);
// Print the answer
cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << probability;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static float [][]dp = new float[105][605];
// Function to calculate probability
// that the sum of numbers on N throws
// of dice lies between A and B
static float find(int N, int a, int b)
{
float probability = 0.0f;
// Base case
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1][i] = (float) (1.0 / 6);
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= 6 && k <= j; k++)
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j]
+ dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
// Add the probability for all
// the numbers between a and b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N][sum];
return probability;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = find(N, a, b);
// Print the answer
System.out.printf("%.6f",probability);
}
}
// This codeis contributed by shikhasingrajput
Python3
# Python3 program for above approach
dp = [[0 for i in range(605)] for j in range(105)]
# Function to calculate probability
# that the sum of numbers on N throws
# of dice lies between A and B
def find(N, a, b) :
probability = 0.0
# Base case
for i in range(1, 7) :
dp[1][i] = 1.0 / 6
for i in range(2, N + 1) :
for j in range(i, (6*i) + 1) :
for k in range(1, 7) :
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] + dp[i - 1][j - k] / 6
# Add the probability for all
# the numbers between a and b
for Sum in range(a, b + 1) :
probability = probability + dp[N][Sum]
return probability
N, a, b = 4, 13, 17
probability = find(N, a, b)
# Print the answer
print('%.6f'%probability)
# This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
C#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
public class GFG
{
static float [,]dp = new float[105, 605];
// Function to calculate probability
// that the sum of numbers on N throws
// of dice lies between A and B
static float find(int N, int a, int b)
{
float probability = 0.0f;
// Base case
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
dp[1, i] = (float) (1.0 / 6);
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j <= 6 * i; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= 6 && k <= j; k++)
{
dp[i, j] = dp[i, j]
+ dp[i - 1, j - k] / 6;
}
}
}
// Add the probability for all
// the numbers between a and b
for (int sum = a; sum <= b; sum++)
probability = probability + dp[N, sum];
return probability;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, a = 13, b = 17;
float probability = find(N, a, b);
// Print the answer
Console.Write("{0:F6}",probability);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
输出:
0.505401时间复杂度: O(N *总和)
辅助空间: O(N *总和)