先决条件:
- 图的BFS
- Python的字典
在本文中,我们将研究如何构建无向图,然后使用Python语言中的字典轻松地找到该图的两个节点/顶点之间的最短路径。
使用字典建立图
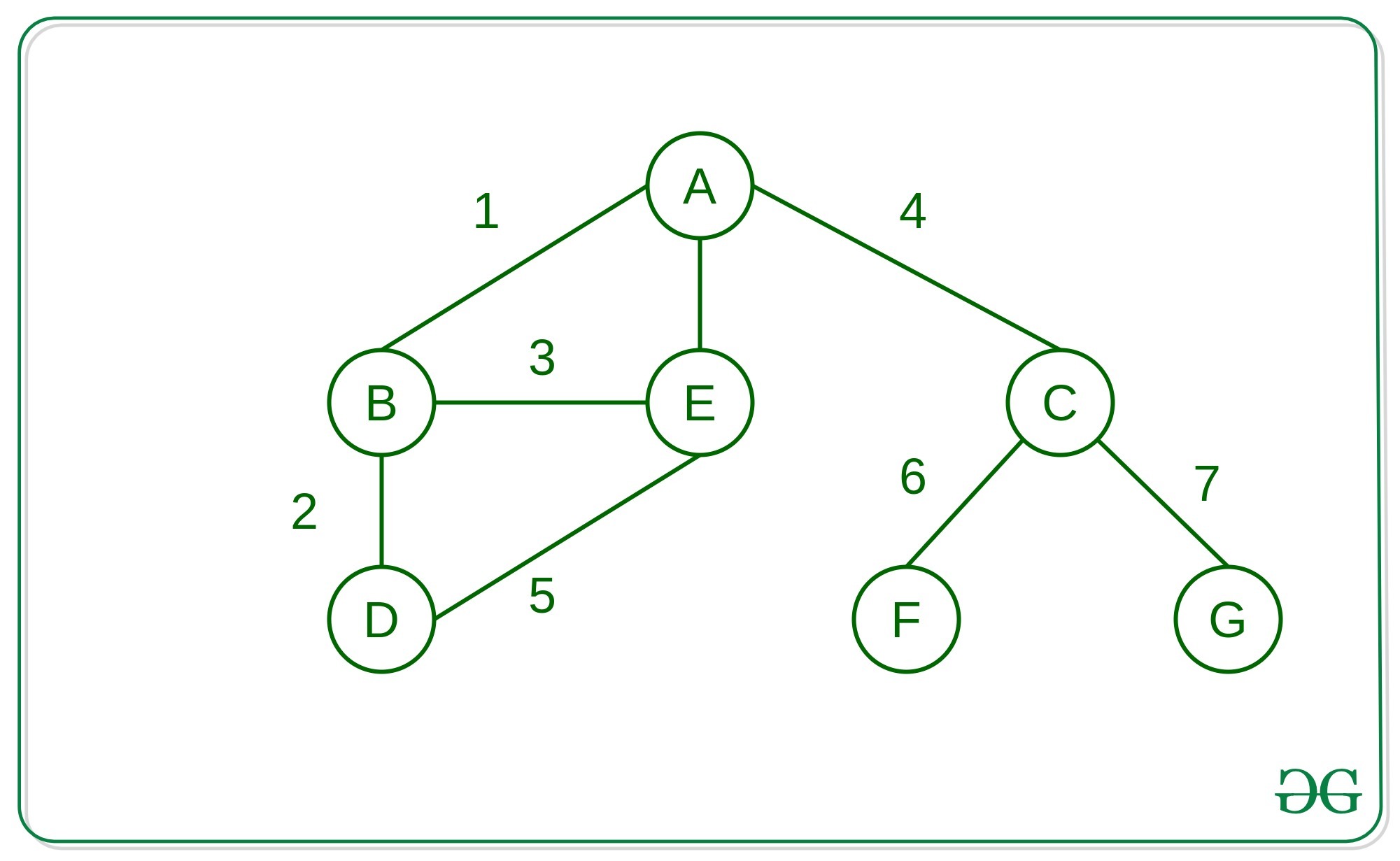
方法:想法是将邻接表存储到字典中,这有助于以任意格式存储图,而不仅是整数形式。在这里,我们将字符用作所有自定义对象也可以使用的地方的参考。
下面是上述方法的实现:
Python3
# Python3 implementation to build a
# graph using Dictonaries
from collections import defaultdict
# Function to build the graph
def build_graph():
edges = [
["A", "B"], ["A", "E"],
["A", "C"], ["B", "D"],
["B", "E"], ["C", "F"],
["C", "G"], ["D", "E"]
]
graph = defaultdict(list)
# Loop to iterate over every
# edge of the graph
for edge in edges:
a, b = edge[0], edge[1]
# Creating the graph
# as adjacency list
graph[a].append(b)
graph[b].append(a)
return graph
if __name__ == "__main__":
graph = build_graph()
print(graph)Python3
# Python implementation to find the
# shortest path in the graph using
# dictionaries
# Function to find the shortest
# path between two nodes of a graph
def BFS_SP(graph, start, goal):
explored = []
# Queue for traversing the
# graph in the BFS
queue = [[start]]
# If the desired node is
# reached
if start == goal:
print("Same Node")
return
# Loop to traverse the graph
# with the help of the queue
while queue:
path = queue.pop(0)
node = path[-1]
# Condition to check if the
# current node is not visited
if node not in explored:
neighbours = graph[node]
# Loop to iterate over the
# neighbours of the node
for neighbour in neighbours:
new_path = list(path)
new_path.append(neighbour)
queue.append(new_path)
# Condition to check if the
# neighbour node is the goal
if neighbour == goal:
print("Shortest path = ", *new_path)
return
explored.append(node)
# Condition when the nodes
# are not connected
print("So sorry, but a connecting"\
"path doesn't exist :(")
return
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Graph using dictionaries
graph = {'A': ['B', 'E', 'C'],
'B': ['A', 'D', 'E'],
'C': ['A', 'F', 'G'],
'D': ['B', 'E'],
'E': ['A', 'B', 'D'],
'F': ['C'],
'G': ['C']}
# Function Call
BFS_SP(graph, 'A', 'D')输出:
{
'G': ['C'],
'F': ['C'],
'E': ['A', 'B', 'D'],
'A': ['B', 'E', 'C'],
'B': ['A', 'D', 'E'],
'D': ['B', 'E'],
'C': ['A', 'F', 'G']
}图的两个节点之间的最短路径
方法:想法是使用队列并以“广度优先搜索”方式访问遍历图形的起始节点的每个相邻节点,以找到图形的两个节点之间的最短路径。
下面是上述方法的实现:
Python3
# Python implementation to find the
# shortest path in the graph using
# dictionaries
# Function to find the shortest
# path between two nodes of a graph
def BFS_SP(graph, start, goal):
explored = []
# Queue for traversing the
# graph in the BFS
queue = [[start]]
# If the desired node is
# reached
if start == goal:
print("Same Node")
return
# Loop to traverse the graph
# with the help of the queue
while queue:
path = queue.pop(0)
node = path[-1]
# Condition to check if the
# current node is not visited
if node not in explored:
neighbours = graph[node]
# Loop to iterate over the
# neighbours of the node
for neighbour in neighbours:
new_path = list(path)
new_path.append(neighbour)
queue.append(new_path)
# Condition to check if the
# neighbour node is the goal
if neighbour == goal:
print("Shortest path = ", *new_path)
return
explored.append(node)
# Condition when the nodes
# are not connected
print("So sorry, but a connecting"\
"path doesn't exist :(")
return
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Graph using dictionaries
graph = {'A': ['B', 'E', 'C'],
'B': ['A', 'D', 'E'],
'C': ['A', 'F', 'G'],
'D': ['B', 'E'],
'E': ['A', 'B', 'D'],
'F': ['C'],
'G': ['C']}
# Function Call
BFS_SP(graph, 'A', 'D')
输出:
Shortest path = A B D