给定有n个顶点和m个边的有向无环图。任务是查找从源顶点到目标顶点之间存在的不同路径的数量。
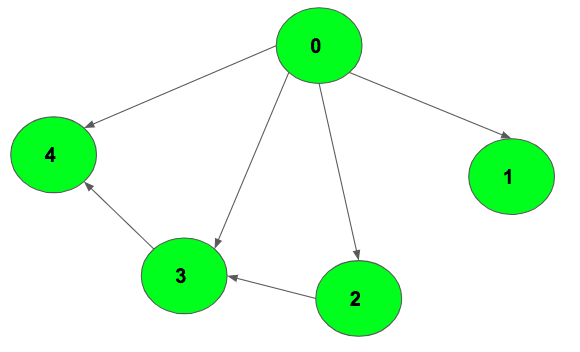
例子:
Input: source = 0, destination = 4
Output: 3
Explanation:
0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
0 -> 3 -> 4
0 -> 4
Input: source = 0, destination = 1
Output: 1
Explanation: There exists only one path 0->1
方法:令f(u)为一个人可以从节点u到达目的地顶点的方式。因此,f(source)是必需的答案。由于此处的f(destination)= 1 ,因此只有一条从目标到自身的路径。可以观察到,f(u)依赖于所有可能从u传播的节点的f值。这是有道理的,因为从u到目标的不同路径数是从v1,v2,v3…vn到目标顶点的所有不同路径的总和,其中v1到vn都是具有从顶点u的直接路径的所有顶点。但是,这种方法太慢而无法使用。每个函数调用都会分支为进一步的调用,然后分支为进一步的调用,直到每条路径都被探索一次。
这种方法的问题是,每次使用参数u调用函数时,都会一次又一次地计算f(u)。由于此问题同时显示出重叠的子问题和最佳子结构,因此可以在此处应用动态编程。为了仅对每个u评估f(u),请在评估f(u)之前对可从u访问的所有v评估f(v)。通过图的节点的反向拓扑排序,可以满足此条件。
下面是上述方法的实现:
CPP
// C++ program for Number of paths
// from one vertex to another vertex
// in a Directed Acyclic Graph
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1000005
// to make graph
vector v[MAXN];
// function to add edge in graph
void add_edge(int a, int b, int fre[])
{
// there is path from a to b.
v[a].push_back(b);
fre[b]++;
}
// function to make topological sorting
vector topological_sorting(int fre[], int n)
{
queue q;
// insert all vertices which
// don't have any parent.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (!fre[i])
q.push(i);
vector l;
// using kahn's algorithm
// for topological sorting
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
// insert front element of queue to vector
l.push_back(u);
// go through all it's childs
for (int i = 0; i < v[u].size(); i++) {
fre[v[u][i]]--;
// whenever the freqency is zero then add
// this vertex to queue.
if (!fre[v[u][i]])
q.push(v[u][i]);
}
}
return l;
}
// Function that returns the number of paths
int numberofPaths(int source, int destination, int n, int fre[])
{
// make topological sorting
vector s = topological_sorting(fre, n);
// to store required answer.
int dp[n] = { 0 };
// answer from destination
// to destination is 1.
dp[destination] = 1;
// traverse in reverse order
for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < v[s[i]].size(); j++) {
dp[s[i]] += dp[v[s[i]][j]];
}
}
return dp;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// here vertices are numbered from 0 to n-1.
int n = 5;
int source = 0, destination = 4;
// to count number of vertex which don't
// have any parents.
int fre[n] = { 0 };
// to add all edges of graph
add_edge(0, 1, fre);
add_edge(0, 2, fre);
add_edge(0, 3, fre);
add_edge(0, 4, fre);
add_edge(2, 3, fre);
add_edge(3, 4, fre);
// Function that returns the number of paths
cout << numberofPaths(source, destination, n, fre);
} Python3
# Python3 program for Number of paths
# from one vertex to another vertex
# in a Directed Acyclic Graph
from collections import deque
MAXN = 1000005
# to make graph
v = [[] for i in range(MAXN)]
# function to add edge in graph
def add_edge(a, b, fre):
# there is path from a to b.
v[a].append(b)
fre[b] += 1
# function to make topological sorting
def topological_sorting(fre, n):
q = deque()
# insert all vertices which
# don't have any parent.
for i in range(n):
if (not fre[i]):
q.append(i)
l = []
# using kahn's algorithm
# for topological sorting
while (len(q) > 0):
u = q.popleft()
#q.pop()
# insert front element of queue to vector
l.append(u)
# go through all it's childs
for i in range(len(v[u])):
fre[v[u][i]] -= 1
# whenever the freqency is zero then add
# this vertex to queue.
if (not fre[v[u][i]]):
q.append(v[u][i])
return l
# Function that returns the number of paths
def numberofPaths(source, destination, n, fre):
# make topological sorting
s = topological_sorting(fre, n)
# to store required answer.
dp = [0]*n
# answer from destination
# to destination is 1.
dp[destination] = 1
# traverse in reverse order
for i in range(len(s) - 1,-1,-1):
for j in range(len(v[s[i]])):
dp[s[i]] += dp[v[s[i]][j]]
return dp
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# here vertices are numbered from 0 to n-1.
n = 5
source, destination = 0, 4
# to count number of vertex which don't
# have any parents.
fre = [0]*n
# to add all edges of graph
add_edge(0, 1, fre)
add_edge(0, 2, fre)
add_edge(0, 3, fre)
add_edge(0, 4, fre)
add_edge(2, 3, fre)
add_edge(3, 4, fre)
# Function that returns the number of paths
print (numberofPaths(source, destination, n, fre))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29.输出:
3