有向无环图中的最短路径
给定一个加权有向无环图和图中的一个源顶点,找到从给定源到所有其他顶点的最短路径。
对于一般的加权图,我们可以使用 Bellman-Ford 算法在 O(VE) 时间内计算单源最短距离。对于没有负权重的图,我们可以做得更好,并使用 Dijkstra 算法在 O(E + VLogV) 时间内计算单源最短距离。我们可以为有向无环图(DAG)做得更好吗?我们可以在 O(V+E) 时间内计算 DAG 的单源最短距离。这个想法是使用拓扑排序。
我们将到所有顶点的距离初始化为无限,到源的距离初始化为 0,然后我们找到图的拓扑排序。图的拓扑排序表示图的线性排序(见下图(b)是图(a)的线性表示)。一旦我们有了拓扑顺序(或线性表示),我们就按拓扑顺序一个一个地处理所有顶点。对于每个正在处理的顶点,我们使用当前顶点的距离更新其相邻的距离。
下图来自此来源。它显示了寻找最短路径的逐步过程。

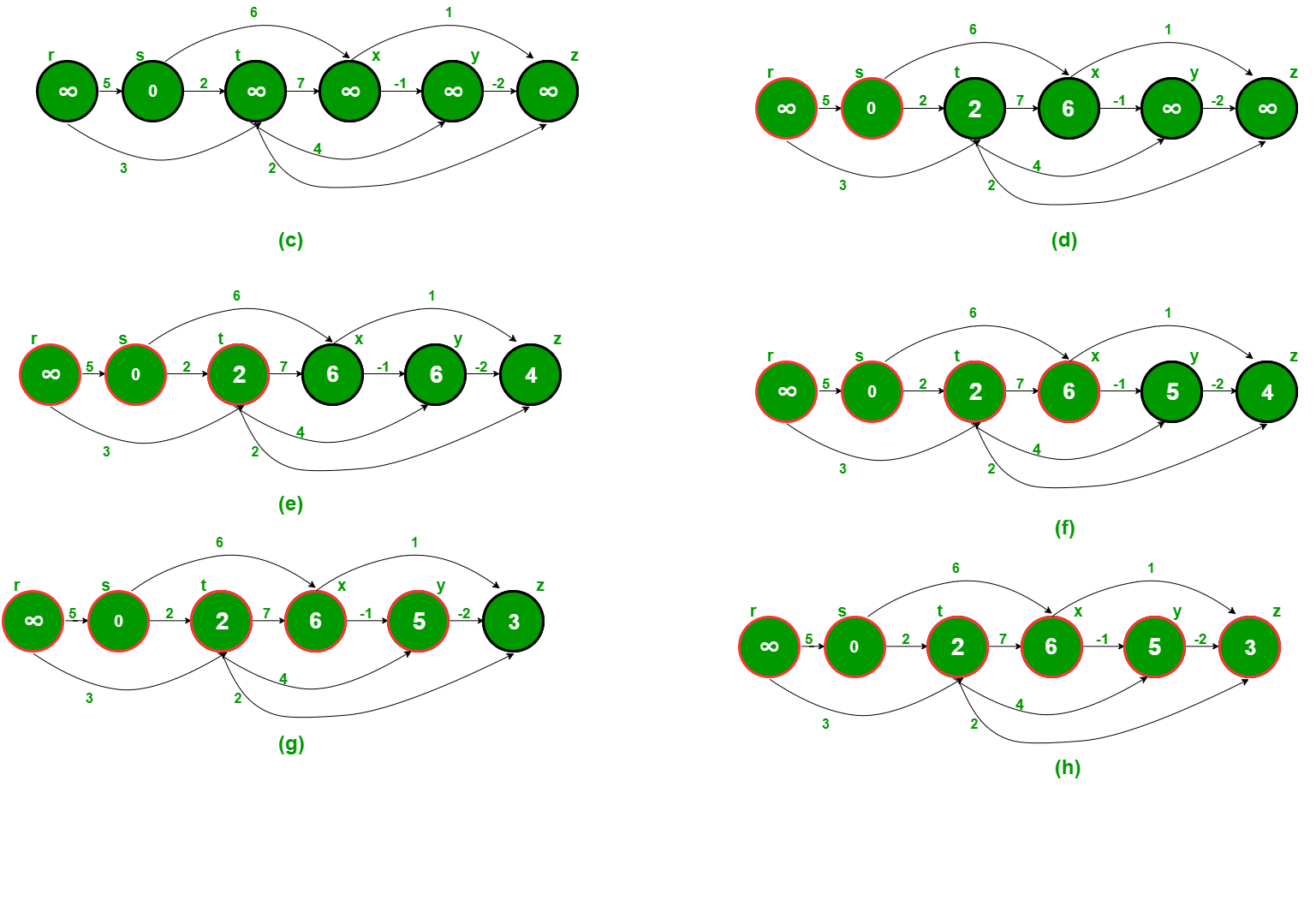
以下是查找最短距离的完整算法。
1)初始化 dist[] = {INF, INF, ....} 和 dist[s] = 0 其中 s 是源顶点。
2)创建所有顶点的拓扑顺序。
3)按照拓扑顺序对每个顶点 u 执行以下操作。
………..对 u 的每个相邻顶点 v 执行以下操作
……………… if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight(u, v))
…………………………dist[v] = dist[u] + weight(u, v)
C++
// C++ program to find single source shortest paths for Directed Acyclic Graphs
#include
#include
#define INF INT_MAX
using namespace std;
// Graph is represented using adjacency list. Every node of adjacency list
// contains vertex number of the vertex to which edge connects. It also
// contains weight of the edge
class AdjListNode
{
int v;
int weight;
public:
AdjListNode(int _v, int _w) { v = _v; weight = _w;}
int getV() { return v; }
int getWeight() { return weight; }
};
// Class to represent a graph using adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices'
// Pointer to an array containing adjacency lists
list *adj;
// A function used by shortestPath
void topologicalSortUtil(int v, bool visited[], stack &Stack);
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int u, int v, int weight);
// Finds shortest paths from given source vertex
void shortestPath(int s);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v, int weight)
{
AdjListNode node(v, weight);
adj[u].push_back(node); // Add v to u's list
}
// A recursive function used by shortestPath. See below link for details
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/topological-sorting/
void Graph::topologicalSortUtil(int v, bool visited[], stack &Stack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
{
AdjListNode node = *i;
if (!visited[node.getV()])
topologicalSortUtil(node.getV(), visited, Stack);
}
// Push current vertex to stack which stores topological sort
Stack.push(v);
}
// The function to find shortest paths from given vertex. It uses recursive
// topologicalSortUtil() to get topological sorting of given graph.
void Graph::shortestPath(int s)
{
stack Stack;
int dist[V];
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool *visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive helper function to store Topological Sort
// starting from all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, Stack);
// Initialize distances to all vertices as infinite and distance
// to source as 0
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dist[i] = INF;
dist[s] = 0;
// Process vertices in topological order
while (Stack.empty() == false)
{
// Get the next vertex from topological order
int u = Stack.top();
Stack.pop();
// Update distances of all adjacent vertices
list::iterator i;
if (dist[u] != INF)
{
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i)
if (dist[i->getV()] > dist[u] + i->getWeight())
dist[i->getV()] = dist[u] + i->getWeight();
}
}
// Print the calculated shortest distances
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
(dist[i] == INF)? cout << "INF ": cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram. Here vertex numbers are
// 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 with following mappings:
// 0=r, 1=s, 2=t, 3=x, 4=y, 5=z
Graph g(6);
g.addEdge(0, 1, 5);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 6);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 4);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(3, 4, -1);
g.addEdge(4, 5, -2);
int s = 1;
cout << "Following are shortest distances from source " << s <<" n";
g.shortestPath(s);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find single source shortest paths in Directed Acyclic Graphs
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class ShortestPath
{
static final int INF=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
class AdjListNode
{
private int v;
private int weight;
AdjListNode(int _v, int _w) { v = _v; weight = _w; }
int getV() { return v; }
int getWeight() { return weight; }
}
// Class to represent graph as an adjacency list of
// nodes of type AdjListNode
class Graph
{
private int V;
private LinkedListadj[];
Graph(int v)
{
V=v;
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for (int i=0; i();
}
void addEdge(int u, int v, int weight)
{
AdjListNode node = new AdjListNode(v,weight);
adj[u].add(node);// Add v to u's list
}
// A recursive function used by shortestPath.
// See below link for details
void topologicalSortUtil(int v, Boolean visited[], Stack stack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited.
visited[v] = true;
Integer i;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
Iterator it = adj[v].iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
AdjListNode node =it.next();
if (!visited[node.getV()])
topologicalSortUtil(node.getV(), visited, stack);
}
// Push current vertex to stack which stores result
stack.push(new Integer(v));
}
// The function to find shortest paths from given vertex. It
// uses recursive topologicalSortUtil() to get topological
// sorting of given graph.
void shortestPath(int s)
{
Stack stack = new Stack();
int dist[] = new int[V];
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
Boolean visited[] = new Boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive helper function to store Topological
// Sort starting from all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, stack);
// Initialize distances to all vertices as infinite and
// distance to source as 0
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dist[i] = INF;
dist[s] = 0;
// Process vertices in topological order
while (stack.empty() == false)
{
// Get the next vertex from topological order
int u = (int)stack.pop();
// Update distances of all adjacent vertices
Iterator it;
if (dist[u] != INF)
{
it = adj[u].iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
AdjListNode i= it.next();
if (dist[i.getV()] > dist[u] + i.getWeight())
dist[i.getV()] = dist[u] + i.getWeight();
}
}
}
// Print the calculated shortest distances
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (dist[i] == INF)
System.out.print( "INF ");
else
System.out.print( dist[i] + " ");
}
}
}
// Method to create a new graph instance through an object
// of ShortestPath class.
Graph newGraph(int number)
{
return new Graph(number);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram. Here vertex
// numbers are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 with following mappings:
// 0=r, 1=s, 2=t, 3=x, 4=y, 5=z
ShortestPath t = new ShortestPath();
Graph g = t.newGraph(6);
g.addEdge(0, 1, 5);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 6);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 4);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(3, 4, -1);
g.addEdge(4, 5, -2);
int s = 1;
System.out.println("Following are shortest distances "+
"from source " + s );
g.shortestPath(s);
}
}
//This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
# Python program to find single source shortest paths
# for Directed Acyclic Graphs Complexity :OV(V+E)
from collections import defaultdict
# Graph is represented using adjacency list. Every
# node of adjacency list contains vertex number of
# the vertex to which edge connects. It also contains
# weight of the edge
class Graph:
def __init__(self,vertices):
self.V = vertices # No. of vertices
# dictionary containing adjacency List
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self,u,v,w):
self.graph[u].append((v,w))
# A recursive function used by shortestPath
def topologicalSortUtil(self,v,visited,stack):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
if v in self.graph.keys():
for node,weight in self.graph[v]:
if visited[node] == False:
self.topologicalSortUtil(node,visited,stack)
# Push current vertex to stack which stores topological sort
stack.append(v)
''' The function to find shortest paths from given vertex.
It uses recursive topologicalSortUtil() to get topological
sorting of given graph.'''
def shortestPath(self, s):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False]*self.V
stack =[]
# Call the recursive helper function to store Topological
# Sort starting from source vertices
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False:
self.topologicalSortUtil(s,visited,stack)
# Initialize distances to all vertices as infinite and
# distance to source as 0
dist = [float("Inf")] * (self.V)
dist[s] = 0
# Process vertices in topological order
while stack:
# Get the next vertex from topological order
i = stack.pop()
# Update distances of all adjacent vertices
for node,weight in self.graph[i]:
if dist[node] > dist[i] + weight:
dist[node] = dist[i] + weight
# Print the calculated shortest distances
for i in range(self.V):
print (("%d" %dist[i]) if dist[i] != float("Inf") else "Inf" ,end=" ")
g = Graph(6)
g.addEdge(0, 1, 5)
g.addEdge(0, 2, 3)
g.addEdge(1, 3, 6)
g.addEdge(1, 2, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 4, 4)
g.addEdge(2, 5, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 3, 7)
g.addEdge(3, 4, -1)
g.addEdge(4, 5, -2)
# source = 1
s = 1
print ("Following are shortest distances from source %d " % s)
g.shortestPath(s)
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// C# program to find single source shortest
// paths in Directed Acyclic Graphs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class ShortestPath
{
static readonly int INF = int.MaxValue;
class AdjListNode
{
public int v;
public int weight;
public AdjListNode(int _v, int _w) { v = _v; weight = _w; }
public int getV() { return v; }
public int getWeight() { return weight; }
}
// Class to represent graph as an adjacency list of
// nodes of type AdjListNode
class Graph
{
public int V;
public List[]adj;
public Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[V];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List();
}
public void addEdge(int u, int v, int weight)
{
AdjListNode node = new AdjListNode(v,weight);
adj[u].Add(node);// Add v to u's list
}
// A recursive function used by shortestPath.
// See below link for details
public void topologicalSortUtil(int v, Boolean []visited,
Stack stack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited.
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
foreach(AdjListNode it in adj[v])
{
AdjListNode node = it;
if (!visited[node.getV()])
topologicalSortUtil(node.getV(), visited, stack);
}
// Push current vertex to stack which stores result
stack.Push(v);
}
// The function to find shortest paths from given vertex. It
// uses recursive topologicalSortUtil() to get topological
// sorting of given graph.
public void shortestPath(int s)
{
Stack stack = new Stack();
int []dist = new int[V];
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
Boolean []visited = new Boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive helper function to store Topological
// Sort starting from all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, stack);
// Initialize distances to all vertices as infinite and
// distance to source as 0
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dist[i] = INF;
dist[s] = 0;
// Process vertices in topological order
while (stack.Count != 0)
{
// Get the next vertex from topological order
int u = (int)stack.Pop();
// Update distances of all adjacent vertices
if (dist[u] != INF)
{
foreach(AdjListNode it in adj[u])
{
AdjListNode i= it;
if (dist[i.getV()] > dist[u] + i.getWeight())
dist[i.getV()] = dist[u] + i.getWeight();
}
}
}
// Print the calculated shortest distances
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (dist[i] == INF)
Console.Write( "INF ");
else
Console.Write( dist[i] + " ");
}
}
}
// Method to create a new graph instance through an object
// of ShortestPath class.
Graph newGraph(int number)
{
return new Graph(number);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram. Here vertex
// numbers are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 with following mappings:
// 0=r, 1=s, 2=t, 3=x, 4=y, 5=z
ShortestPath t = new ShortestPath();
Graph g = t.newGraph(6);
g.addEdge(0, 1, 5);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 6);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 4);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(3, 4, -1);
g.addEdge(4, 5, -2);
int s = 1;
Console.WriteLine("Following are shortest distances "+
"from source " + s );
g.shortestPath(s);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji 输出:
Following are shortest distances from source 1
INF 0 2 6 5 3