线性搜索是最简单的搜索算法,可以按顺序搜索列表中的元素。我们从一端开始,检查每个元素,直到找不到所需的元素。
线性搜索如何工作?
遵循以下步骤在下面的列表中搜索元素k = 1 。
- 从第一个元素开始,将k与每个元素x进行比较。
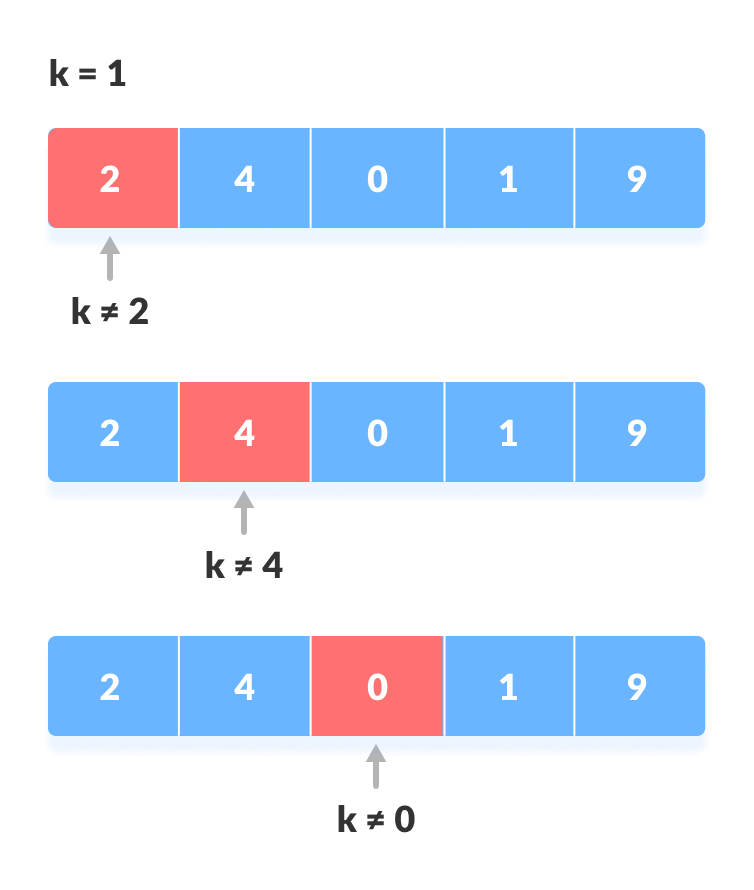
与每个元素比较 - 如果
x == k,则返回索引。
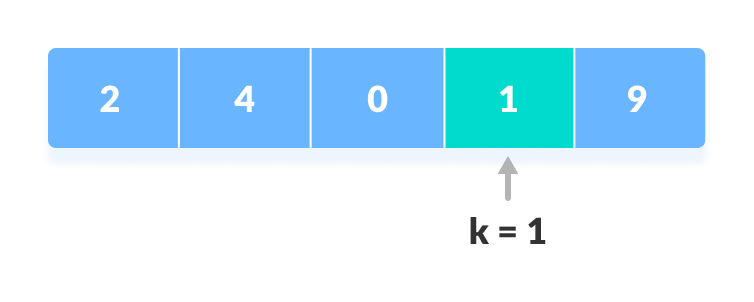
找到元素 - 否则, 找不到返回。
线性搜索算法
LinearSearch(array, key)
for each item in the array
if item == value
return its indexPython,Java和C / C++示例
Python
爪哇
C
C++
# Linear Search in Python
def linearSearch(array, n, x):
# Going through array sequencially
for i in range(0, n):
if (array[i] == x):
return i
return -1
array = [2, 4, 0, 1, 9]
x = 1
n = len(array)
result = linearSearch(array, n, x)
if(result == -1):
print("Element not found")
else:
print("Element found at index: ", result)// Linear Search in Java
class LinearSearch {
public static int linearSearch(int array[], int x) {
int n = array.length;
// Going through array sequencially
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (array[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int array[] = { 2, 4, 0, 1, 9 };
int x = 1;
int result = linearSearch(array, x);
if (result == -1)
System.out.print("Element not found");
else
System.out.print("Element found at index: " + result);
}
}// Linear Search in C
#include
int search(int array[], int n, int x) {
// Going through array sequencially
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
int main() {
int array[] = {2, 4, 0, 1, 9};
int x = 1;
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
int result = search(array, n, x);
(result == -1) ? printf("Element not found") : printf("Element found at index: %d", result);
} // Linear Search in C++
#include
using namespace std;
int search(int array[], int n, int x) {
// Going through array sequencially
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
int main() {
int array[] = {2, 4, 0, 1, 9};
int x = 1;
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
int result = search(array, n, x);
(result == -1) ? cout << "Element not found" : cout << "Element found at index: " << result;
} 线性搜索的复杂性
时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(1)
线性搜索应用
- 用于较小数组(<100个项目)中的搜索操作。