最长共同子序列(LCS)定义为所有给定序列共同的最长子序列,前提是不需要该子序列的元素占据原始序列内的连续位置。
如果S1和S2是两个给定序列,则Z是S1和S2的公共子序列,如果Z是S1和S2两者的子序列。此外, Z必须是S1和S2的索引的严格增加的序列 。
在严格增加的序列中,从原始序列中选择的元素的索引必须在Z中按升序排列。
如果
S1 = {B, C, D, A, A, C, D}然后, {A, D, B}不能是S1的子序列,因为元素的顺序不相同(即,不是严格递增的序列)。
让我们通过一个例子来了解LCS。
如果
S1 = {B, C, D, A, A, C, D}
S2 = {A, C, D, B, A, C}然后,常见的子序列是{B, C}, {C, D, A, C}, {D, A, C}, {A, A, C}, {A, C}, {C, D}, ...
在这些子序列中, {C, D, A, C}是最长的公共子序列。我们将使用动态编程来找到这个最长的公共子序列。
在继续进行之前,如果您不了解动态编程,请进行动态编程。
使用动态编程查找LCS
让我们采取两个顺序:

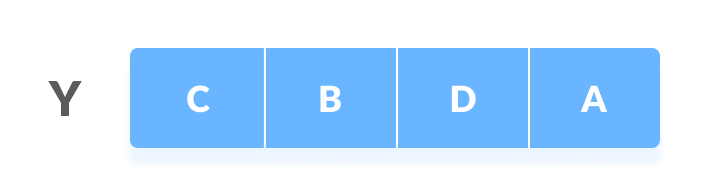
按照以下步骤查找最长的公共子序列。
- 创建一个尺寸为
n+1*m+1的表,其中n和m分别为X和Y的长度。第一行和第一列用零填充。
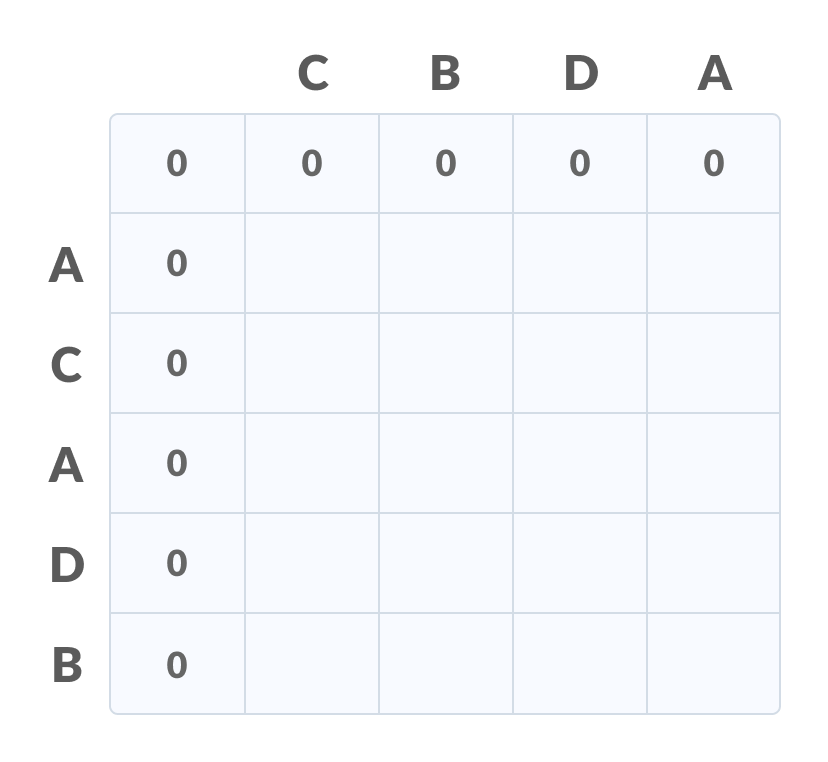
初始化表格 - 使用以下逻辑填充表的每个单元格。
- 如果对应于当前行和当前列的字符匹配,则通过在对角线元素上添加一个来填充当前单元格。用箭头指向对角线单元。
- 否则,取前一列和前一行元素中的最大值来填充当前单元格。用箭头指向具有最大值的单元格。如果它们相等,则指向它们中的任何一个。
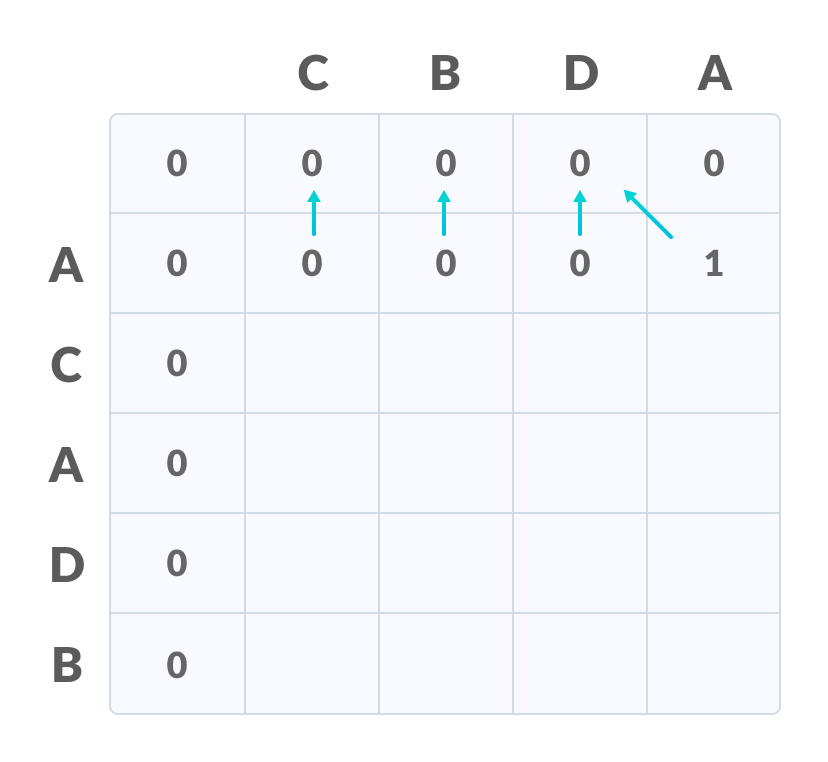
填写值 - 重复步骤2 ,直到表格填满。
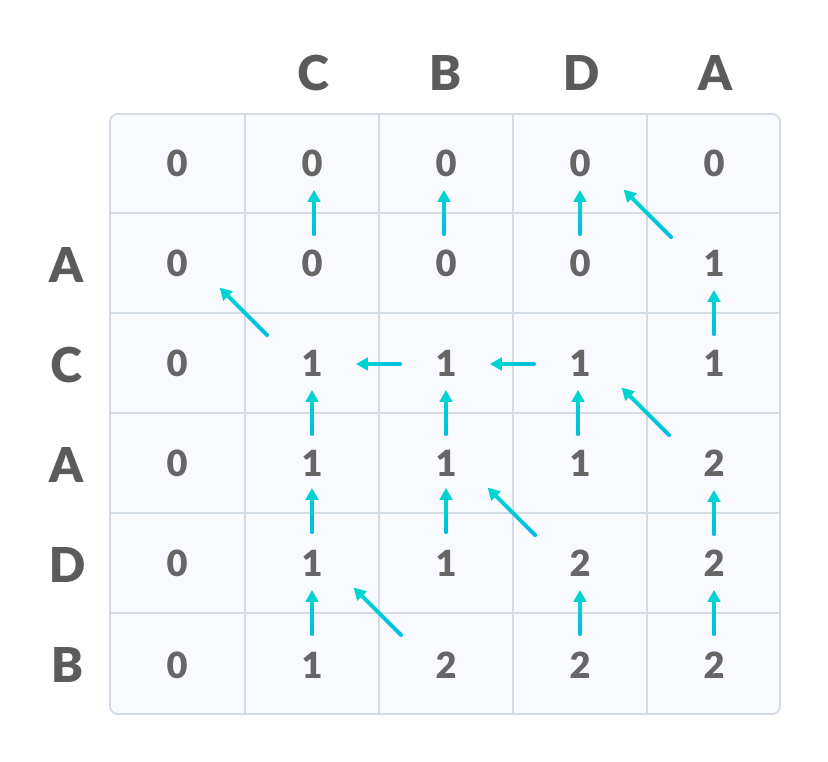
填写所有值 - 最后一行和最后一列中的值是最长公共子序列的长度。
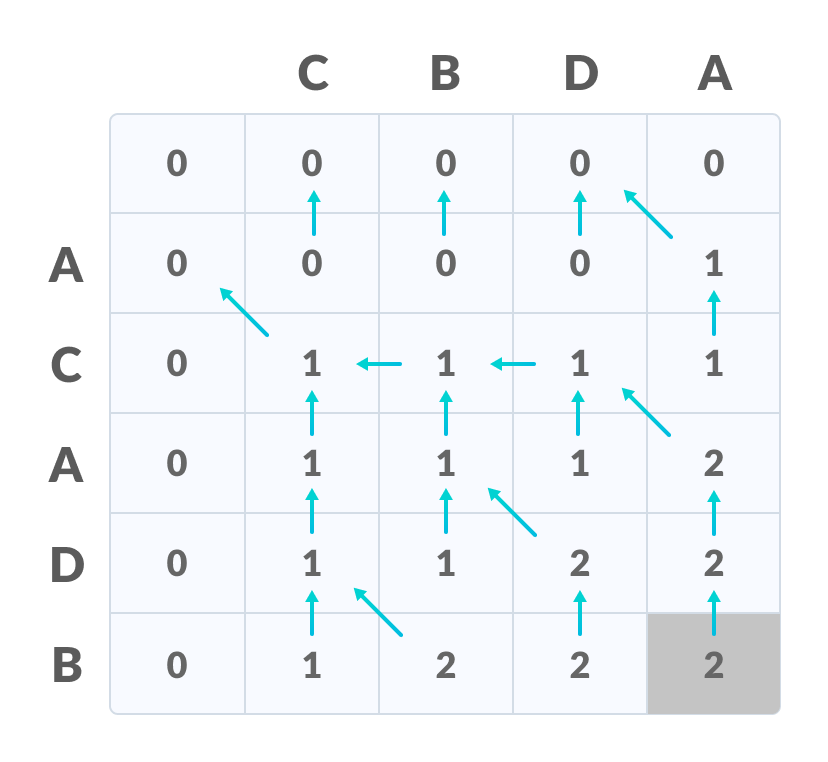
右下角是LCS的长度 - 为了找到最长的公共子序列,请从最后一个元素开始并遵循箭头的方向。与()符号相对应的元素形成最长的公共子序列。
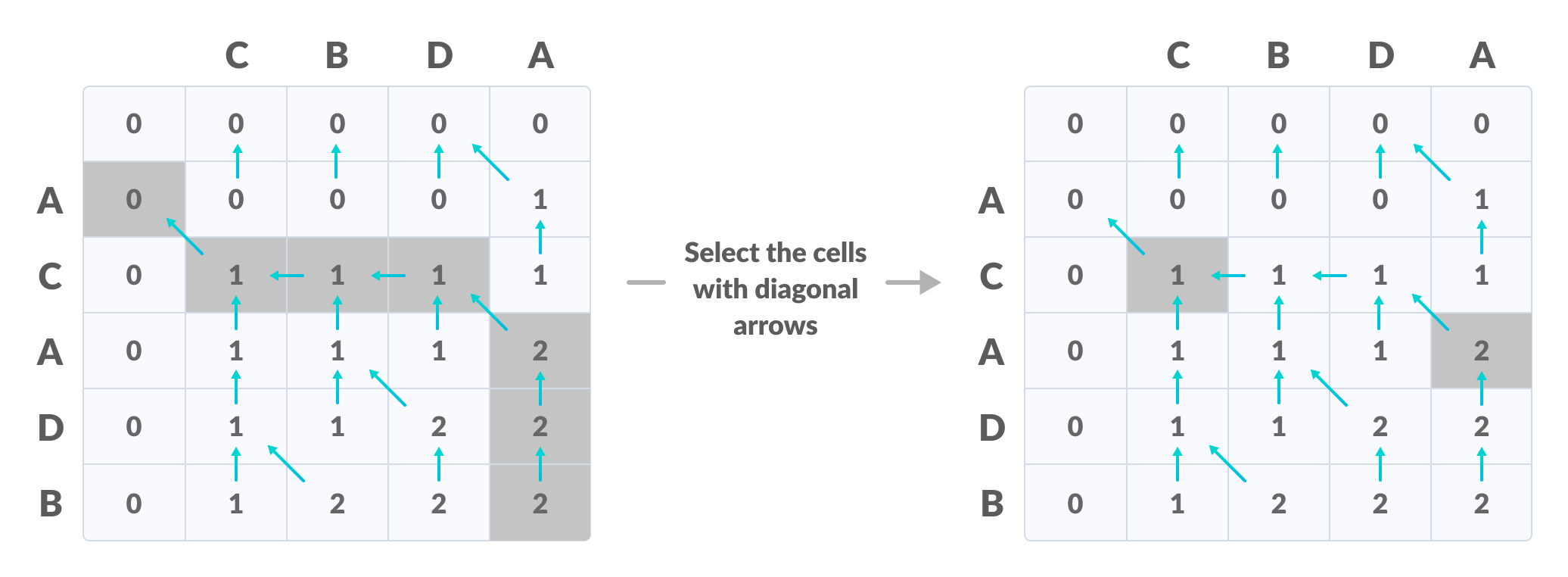
根据箭头创建路径
因此,最长的公共子序列是CD 。

在解决LCS问题时,动态编程算法比递归算法更有效率吗?
动态编程的方法减少了函数调用的次数。它存储每个函数调用的结果,以便可以在以后的调用中使用它,而无需冗余调用。
在上述动态算法中,将从X元素和Y元素之间的每次比较获得的结果存储在表中,以便可以在将来的计算中使用它们。
因此,动态方法所花费的时间就是填写表格所花费的时间(即O(mn))。而递归算法的复杂度为2 max(m,n) 。
最长公共子序列算法
X and Y be two given sequences
Initialize a table LCS of dimension X.length * Y.length
X.label = X
Y.label = Y
LCS[0][] = 0
LCS[][0] = 0
Start from LCS[1][1]
Compare X[i] and Y[j]
If X[i] = Y[j]
LCS[i][j] = 1 + LCS[i-1, j-1]
Point an arrow to LCS[i][j]
Else
LCS[i][j] = max(LCS[i-1][j], LCS[i][j-1])
Point an arrow to max(LCS[i-1][j], LCS[i][j-1])Python,Java和C / C++示例
Python
爪哇
C
C++
# The longest common subsequence in Python
# Function to find lcs_algo
def lcs_algo(S1, S2, m, n):
L = [[0 for x in range(n+1)] for x in range(m+1)]
# Building the mtrix in bottom-up way
for i in range(m+1):
for j in range(n+1):
if i == 0 or j == 0:
L[i][j] = 0
elif S1[i-1] == S2[j-1]:
L[i][j] = L[i-1][j-1] + 1
else:
L[i][j] = max(L[i-1][j], L[i][j-1])
index = L[m][n]
lcs_algo = [""] * (index+1)
lcs_algo[index] = ""
i = m
j = n
while i > 0 and j > 0:
if S1[i-1] == S2[j-1]:
lcs_algo[index-1] = S1[i-1]
i -= 1
j -= 1
index -= 1
elif L[i-1][j] > L[i][j-1]:
i -= 1
else:
j -= 1
# Printing the sub sequences
print("S1 : " + S1 + "\nS2 : " + S2)
print("LCS: " + "".join(lcs_algo))
S1 = "ACADB"
S2 = "CBDA"
m = len(S1)
n = len(S2)
lcs_algo(S1, S2, m, n)// The longest common subsequence in Java
class LCS_ALGO {
static void lcs(String S1, String S2, int m, int n) {
int[][] LCS_table = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
// Building the mtrix in bottom-up way
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0)
LCS_table[i][j] = 0;
else if (S1.charAt(i - 1) == S2.charAt(j - 1))
LCS_table[i][j] = LCS_table[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else
LCS_table[i][j] = Math.max(LCS_table[i - 1][j], LCS_table[i][j - 1]);
}
}
int index = LCS_table[m][n];
int temp = index;
char[] lcs = new char[index + 1];
lcs[index] = '\0';
int i = m, j = n;
while (i > 0 && j > 0) {
if (S1.charAt(i - 1) == S2.charAt(j - 1)) {
lcs[index - 1] = S1.charAt(i - 1);
i--;
j--;
index--;
}
else if (LCS_table[i - 1][j] > LCS_table[i][j - 1])
i--;
else
j--;
}
// Printing the sub sequences
System.out.print("S1 : " + S1 + "\nS2 : " + S2 + "\nLCS: ");
for (int k = 0; k <= temp; k++)
System.out.print(lcs[k]);
System.out.println("");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String S1 = "ACADB";
String S2 = "CBDA";
int m = S1.length();
int n = S2.length();
lcs(S1, S2, m, n);
}
}// The longest common subsequence in C
#include
#include
int i, j, m, n, LCS_table[20][20];
char S1[20] = "ACADB", S2[20] = "CBDA", b[20][20];
void lcsAlgo() {
m = strlen(S1);
n = strlen(S2);
// Filling 0's in the matrix
for (i = 0; i <= m; i++)
LCS_table[i][0] = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
LCS_table[0][i] = 0;
// Building the mtrix in bottom-up way
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (S1[i - 1] == S2[j - 1]) {
LCS_table[i][j] = LCS_table[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else if (LCS_table[i - 1][j] >= LCS_table[i][j - 1]) {
LCS_table[i][j] = LCS_table[i - 1][j];
} else {
LCS_table[i][j] = LCS_table[i][j - 1];
}
}
int index = LCS_table[m][n];
char lcsAlgo[index + 1];
lcsAlgo[index] = '\0';
int i = m, j = n;
while (i > 0 && j > 0) {
if (S1[i - 1] == S2[j - 1]) {
lcsAlgo[index - 1] = S1[i - 1];
i--;
j--;
index--;
}
else if (LCS_table[i - 1][j] > LCS_table[i][j - 1])
i--;
else
j--;
}
// Printing the sub sequences
printf("S1 : %s \nS2 : %s \n", S1, S2);
printf("LCS: %s", lcsAlgo);
}
int main() {
lcsAlgo();
printf("\n");
} // The longest common subsequence in C++
#include
using namespace std;
void lcsAlgo(char *S1, char *S2, int m, int n) {
int LCS_table[m + 1][n + 1];
// Building the mtrix in bottom-up way
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0)
LCS_table[i][j] = 0;
else if (S1[i - 1] == S2[j - 1])
LCS_table[i][j] = LCS_table[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else
LCS_table[i][j] = max(LCS_table[i - 1][j], LCS_table[i][j - 1]);
}
}
int index = LCS_table[m][n];
char lcsAlgo[index + 1];
lcsAlgo[index] = '\0';
int i = m, j = n;
while (i > 0 && j > 0) {
if (S1[i - 1] == S2[j - 1]) {
lcsAlgo[index - 1] = S1[i - 1];
i--;
j--;
index--;
}
else if (LCS_table[i - 1][j] > LCS_table[i][j - 1])
i--;
else
j--;
}
// Printing the sub sequences
cout << "S1 : " << S1 << "\nS2 : " << S2 << "\nLCS: " << lcsAlgo << "\n";
}
int main() {
char S1[] = "ACADB";
char S2[] = "CBDA";
int m = strlen(S1);
int n = strlen(S2);
lcsAlgo(S1, S2, m, n);
} 最长的通用子序列应用
- 在压缩基因组重排数据中
- 通过空中签名在手机中验证用户身份