给定一个由N个元素组成的数组arr []和多个查询,其中每个查询将包含三个整数L , R和K。对于每个查询,任务是找到子数组arr [L…R]中大于K的元素数。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {7, 3, 9, 13, 5, 4}, q[] = {{0, 3, 6}, {1, 5, 8}}
Output:
3
2
Query 1: Only 7, 9 and 13 are greater
than 6 in the subarray {7, 3, 9, 13}.
Query 2: Only 9 and 13 are greater
than 8 in the subarray {3, 9, 13, 5, 4}.
Input: arr[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}, q[] = {{0, 7, 3}, {4, 6, 10}}
Output:
4
0
先决条件:段树
天真的方法:只需从索引l遍历到r遍历该数组,即可找到每个查询的答案,并在数组元素大于k时,继续向计数加1 。这种方法的时间复杂度将是O(n * q) 。
高效的方法:在每个节点上建立一个带有向量的分段树,其中包含按排序顺序包含子范围的所有元素。使用段树回答每个查询,其中可以使用二元搜索来计算子节点位于查询范围内大于K的每个节点中存在多少个数字。此方法的时间复杂度将为O(q * log(n)* log(n))
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Merge procedure to merge two
// vectors into a single vector
vector merge(vector& v1, vector& v2)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
// Final vector to return
// after merging
vector v;
// Loop continues until it reaches
// the end of one of the vectors
while (i < v1.size() && j < v2.size()) {
if (v1[i] <= v2[j]) {
v.push_back(v1[i]);
i++;
}
else {
v.push_back(v2[j]);
j++;
}
}
// Here, simply add the remaining
// elements to the vector v
for (int k = i; k < v1.size(); k++)
v.push_back(v1[k]);
for (int k = j; k < v2.size(); k++)
v.push_back(v2[k]);
return v;
}
// Procedure to build the segment tree
void buildTree(vector* tree, int* arr,
int index, int s, int e)
{
// Reached the leaf node
// of the segment tree
if (s == e) {
tree[index].push_back(arr[s]);
return;
}
// Recursively call the buildTree
// on both the nodes of the tree
int mid = (s + e) / 2;
buildTree(tree, arr, 2 * index, s, mid);
buildTree(tree, arr, 2 * index + 1, mid + 1, e);
// Storing the final vector after merging
// the two of its sorted child vector
tree[index] = merge(tree[2 * index], tree[2 * index + 1]);
}
// Query procedure to get the answer
// for each query l and r are query range
int query(vector* tree, int index, int s,
int e, int l, int r, int k)
{
// out of bound or no overlap
if (r < s || l > e)
return 0;
// Complete overlap
// Query range completely lies in
// the segment tree node range
if (s >= l && e <= r) {
// binary search to find index of k
return (tree[index].size()
- (lower_bound(tree[index].begin(),
tree[index].end(), k)
- tree[index].begin()));
}
// Partially overlap
// Query range partially lies in
// the segment tree node range
int mid = (s + e) / 2;
return (query(tree, 2 * index, s,
mid, l, r, k)
+ query(tree, 2 * index + 1, mid + 1,
e, l, r, k));
}
// Function to perform the queries
void performQueries(int L[], int R[], int K[],
int n, int q, vector tree[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
cout << query(tree, 1, 0, n - 1,
L[i] - 1, R[i] - 1, K[i])
<< endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 7, 3, 9, 13, 5, 4 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
vector tree[4 * n + 1];
buildTree(tree, arr, 1, 0, n - 1);
// 1-based indexing
int L[] = { 1, 2 };
int R[] = { 4, 6 };
int K[] = { 6, 8 };
// Number of queries
int q = sizeof(L) / sizeof(L[0]);
performQueries(L, R, K, n, q, tree);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Merge procedure to merge two
// vectors into a single vector
static Vector merge(Vector v1,
Vector v2)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
// Final vector to return
// after merging
Vector v = new Vector<>();
// Loop continues until it reaches
// the end of one of the vectors
while (i < v1.size() && j < v2.size())
{
if (v1.elementAt(i) <= v2.elementAt(j))
{
v.add(v1.elementAt(i));
i++;
}
else
{
v.add(v2.elementAt(j));
j++;
}
}
// Here, simply add the remaining
// elements to the vector v
for (int k = i; k < v1.size(); k++)
v.add(v1.elementAt(k));
for (int k = j; k < v2.size(); k++)
v.add(v2.elementAt(k));
return v;
}
// Procedure to build the segment tree
static void buildTree(Vector[] tree, int[] arr,
int index, int s, int e)
{
// Reached the leaf node
// of the segment tree
if (s == e)
{
tree[index].add(arr[s]);
return;
}
// Recursively call the buildTree
// on both the nodes of the tree
int mid = (s + e) / 2;
buildTree(tree, arr, 2 * index, s, mid);
buildTree(tree, arr, 2 * index + 1, mid + 1, e);
// Storing the final vector after merging
// the two of its sorted child vector
tree[index] = merge(tree[2 * index], tree[2 * index + 1]);
}
// Query procedure to get the answer
// for each query l and r are query range
static int query(Vector[] tree, int index, int s,
int e, int l, int r, int k)
{
// out of bound or no overlap
if (r < s || l > e)
return 0;
// Complete overlap
// Query range completely lies in
// the segment tree node range
if (s >= l && e <= r)
{
// binary search to find index of k
return (tree[index].size() - lowerBound(tree[index],
tree[index].size(), k));
}
// Partially overlap
// Query range partially lies in
// the segment tree node range
int mid = (s + e) / 2;
return (query(tree, 2 * index, s, mid, l, r, k) +
query(tree, 2 * index + 1, mid + 1, e, l, r, k));
}
// Function to perform the queries
static void performQueries(int L[], int R[], int K[],
int n, int q, Vector tree[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
System.out.println(query(tree, 1, 0, n - 1,
L[i] - 1, R[i] - 1, K[i]));
}
}
static int lowerBound(Vector array,
int length, int value)
{
int low = 0;
int high = length;
while (low < high)
{
final int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (value <= array.elementAt(mid))
{
high = mid;
}
else
{
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 7, 3, 9, 13, 5, 4 };
int n = arr.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector[] tree = new Vector[4 * n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < (4 * n + 1); i++)
{
tree[i] = new Vector<>();
}
buildTree(tree, arr, 1, 0, n - 1);
// 1-based indexing
int L[] = { 1, 2 };
int R[] = { 4, 6 };
int K[] = { 6, 8 };
// Number of queries
int q = L.length;
performQueries(L, R, K, n, q, tree);
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
from bisect import bisect_left as lower_bound
# Merge procedure to merge two
# vectors into a single vector
def merge(v1, v2):
i = 0
j = 0
# Final vector to return
# after merging
v = []
# Loop continues until it reaches
# the end of one of the vectors
while (i < len(v1) and j < len(v2)):
if (v1[i] <= v2[j]):
v.append(v1[i])
i += 1
else:
v.append(v2[j])
j += 1
# Here, simply add the remaining
# elements to the vector v
for k in range(i, len(v1)):
v.append(v1[k])
for k in range(j, len(v2)):
v.append(v2[k])
return v
# Procedure to build the segment tree
def buildTree(tree,arr,index, s, e):
# Reached the leaf node
# of the segment tree
if (s == e):
tree[index].append(arr[s])
return
# Recursively call the buildTree
# on both the nodes of the tree
mid = (s + e) // 2
buildTree(tree, arr, 2 * index, s, mid)
buildTree(tree, arr, 2 * index + 1, mid + 1, e)
# Storing the final vector after merging
# the two of its sorted child vector
tree[index] = merge(tree[2 * index], tree[2 * index + 1])
# Query procedure to get the answer
# for each query l and r are query range
def query(tree, index, s, e, l, r, k):
# out of bound or no overlap
if (r < s or l > e):
return 0
# Complete overlap
# Query range completely lies in
# the segment tree node range
if (s >= l and e <= r):
# binary search to find index of k
return len(tree[index]) - (lower_bound(tree[index], k))
# Partially overlap
# Query range partially lies in
# the segment tree node range
mid = (s + e) // 2
return (query(tree, 2 * index, s,mid, l, r, k)
+ query(tree, 2 * index + 1, mid + 1,e, l, r, k))
# Function to perform the queries
def performQueries(L, R, K,n, q,tree):
for i in range(q):
print(query(tree, 1, 0, n - 1,L[i] - 1, R[i] - 1, K[i]))
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [7, 3, 9, 13, 5, 4]
n = len(arr)
tree = [[] for i in range(4 * n + 1)]
buildTree(tree, arr, 1, 0, n - 1)
# 1-based indexing
L = [1, 2]
R = [4, 6]
K = [6, 8]
# Number of queries
q = len(L)
performQueries(L, R, K, n, q, tree)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Merge procedure to merge two
// vectors into a single vector
static List merge(List v1,
List v2)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
// Final vector to return
// after merging
List v = new List();
// Loop continues until it reaches
// the end of one of the vectors
while (i < v1.Count && j < v2.Count)
{
if (v1[i] <= v2[j])
{
v.Add(v1[i]);
i++;
}
else
{
v.Add(v2[j]);
j++;
}
}
// Here, simply add the remaining
// elements to the vector v
for (int k = i; k < v1.Count; k++)
v.Add(v1[k]);
for (int k = j; k < v2.Count; k++)
v.Add(v2[k]);
return v;
}
// Procedure to build the segment tree
static void buildTree(List[] tree, int[] arr,
int index, int s, int e)
{
// Reached the leaf node
// of the segment tree
if (s == e)
{
tree[index].Add(arr[s]);
return;
}
// Recursively call the buildTree
// on both the nodes of the tree
int mid = (s + e) / 2;
buildTree(tree, arr, 2 * index, s, mid);
buildTree(tree, arr, 2 * index + 1, mid + 1, e);
// Storing the readonly vector after merging
// the two of its sorted child vector
tree[index] = merge(tree[2 * index], tree[2 * index + 1]);
}
// Query procedure to get the answer
// for each query l and r are query range
static int query(List[] tree, int index, int s,
int e, int l, int r, int k)
{
// out of bound or no overlap
if (r < s || l > e)
return 0;
// Complete overlap
// Query range completely lies in
// the segment tree node range
if (s >= l && e <= r)
{
// binary search to find index of k
return (tree[index].Count - lowerBound(tree[index],
tree[index].Count, k));
}
// Partially overlap
// Query range partially lies in
// the segment tree node range
int mid = (s + e) / 2;
return (query(tree, 2 * index, s, mid, l, r, k) +
query(tree, 2 * index + 1, mid + 1, e, l, r, k));
}
// Function to perform the queries
static void performQueries(int []L, int []R, int []K,
int n, int q, List []tree)
{
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(query(tree, 1, 0, n - 1,
L[i] - 1, R[i] - 1, K[i]));
}
}
static int lowerBound(List array,
int length, int value)
{
int low = 0;
int high = length;
while (low < high)
{
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (value <= array[mid])
{
high = mid;
}
else
{
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 7, 3, 9, 13, 5, 4 };
int n = arr.Length;
List[] tree = new List[4 * n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < (4 * n + 1); i++)
{
tree[i] = new List();
}
buildTree(tree, arr, 1, 0, n - 1);
// 1-based indexing
int []L = { 1, 2 };
int []R = { 4, 6 };
int []K = { 6, 8 };
// Number of queries
int q = L.Length;
performQueries(L, R, K, n, q, tree);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
vector arr(1000000), tree(4 * arr.size());
// combine function to make parent node
int combine(int a, int b)
{
if (a != 0 && b != 0) {
return a;
}
if (a >= b) {
return a;
}
return b;
}
// building the tree
void buildTree(int ind, int low, int high, int x)
{
// leaf node
if (low == high) {
if (arr[low] > x) {
tree[ind] = arr[low];
}
else {
tree[ind] = 0;
}
return;
}
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
buildTree(2 * ind + 1, low, mid, x);
buildTree(2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, high, x);
// merging the nodes while backtracking.
tree[ind]
= combine(tree[2 * ind + 1], tree[2 * ind + 2]);
}
// performing query
int query(int ind, int low, int high, int l, int r)
{
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
// Out of Bounds
if (low > r || high < l) {
return 0;
}
// completely overlaps
if (l <= low && r >= high) {
return tree[ind];
}
// partially overlaps
return combine(query(2 * ind + 1, low, mid, l, r),
query(2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, high, l, r));
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
arr = { 7, 3, 9, 13, 5, 4 };
int n = 6;
int k = 6;
// 1-based indexing
int l = 1, r = 4;
buildTree(0, 0, n - 1, k);
cout << query(0, 0, n - 1, l - 1, r - 1);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by yashbeersingh42 3
2另一种方法:
使用段树的另一种方法是在该范围内的每个节点(如果存在)中存储大于K的第一个元素,否则存储0 。
在这里,我们需要考虑3种情况来构建树。
- 如果左和右子级都包含非0的数字,则答案始终是左子级。 (我们需要考虑大于K的数字的第一次出现。)
- 如果左或右子级中的任何一个包含0 ,则答案始终是非0的数字。
- 如果左右两个孩子都包含0 ,则答案始终为0 (表示该范围内不存在大于K的数字)。
查询函数始终保持不变。
请考虑以下示例: arr [] = {7,3,9,13,13,5,4},K = 6
在这种情况下,树将如下所示:
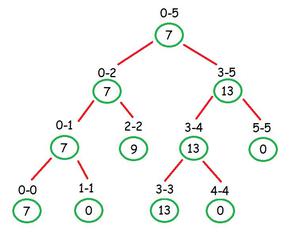
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
vector arr(1000000), tree(4 * arr.size());
// combine function to make parent node
int combine(int a, int b)
{
if (a != 0 && b != 0) {
return a;
}
if (a >= b) {
return a;
}
return b;
}
// building the tree
void buildTree(int ind, int low, int high, int x)
{
// leaf node
if (low == high) {
if (arr[low] > x) {
tree[ind] = arr[low];
}
else {
tree[ind] = 0;
}
return;
}
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
buildTree(2 * ind + 1, low, mid, x);
buildTree(2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, high, x);
// merging the nodes while backtracking.
tree[ind]
= combine(tree[2 * ind + 1], tree[2 * ind + 2]);
}
// performing query
int query(int ind, int low, int high, int l, int r)
{
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
// Out of Bounds
if (low > r || high < l) {
return 0;
}
// completely overlaps
if (l <= low && r >= high) {
return tree[ind];
}
// partially overlaps
return combine(query(2 * ind + 1, low, mid, l, r),
query(2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, high, l, r));
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
arr = { 7, 3, 9, 13, 5, 4 };
int n = 6;
int k = 6;
// 1-based indexing
int l = 1, r = 4;
buildTree(0, 0, n - 1, k);
cout << query(0, 0, n - 1, l - 1, r - 1);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by yashbeersingh42
输出:
7时间复杂度: O(N * log N)来构建树,O(log N)用于每个查询。
空间复杂度: O(N)