- 机器学习和数据科学(1)
- 数据科学 VS 机器学习
- 大数据和机器学习的区别(1)
- 大数据和机器学习的区别
- 用于机器学习和数据科学的 10 大 Javascript 库
- 用于机器学习和数据科学的 10 大 Javascript 库(1)
- 机器学习和深度学习之间的区别
- 机器学习和深度学习之间的区别(1)
- 大数据与数据科学的区别(1)
- 大数据与数据科学的区别
- 大数据与数据科学的区别
- C++中的机器学习(1)
- 机器学习 (1)
- C++中的机器学习
- 机器学习中的 P 值(1)
- 机器学习中的 P 值
- 机器学习和人工智能之间的区别(1)
- 机器学习和人工智能之间的区别
- 人工智能和机器学习之间的区别
- 数据科学和数据挖掘之间的区别(1)
- 数据科学和数据挖掘之间的区别(1)
- 数据科学和数据挖掘之间的区别
- 数据科学和数据挖掘之间的区别
- 数据科学和数据分析之间的区别
- 数据科学和数据分析之间的区别(1)
- 机器学习 python (1)
- 计算机科学和数据科学之间的区别
- 计算机科学和数据科学之间的区别(1)
- 人工智能与机器学习与深度学习之间的区别
📅 最后修改于: 2020-09-29 04:42:56 🧑 作者: Mango
数据科学与机器学习之间的区别
数据科学是数据清洗,准备和分析的研究,而机器学习是AI和数据科学子领域的分支。数据科学和机器学习是两种流行的现代技术,并且以不适当的速度在增长。但是,这两个流行语以及人工智能和深度学习是一个非常令人困惑的术语,因此了解它们之间的区别非常重要。在本主题中,我们将仅了解数据科学和机器学习之间的区别,以及它们之间的关系。
数据科学和机器学习彼此密切相关,但是功能不同,目标也不同。数据科学一目了然,是研究从原始数据中寻找见解的方法的领域。鉴于机器学习是一组数据科学家使用的技术,它使机器能够从过去的数据中自动学习。为了深入了解两者之间的差异,我们首先简要介绍这两种技术。
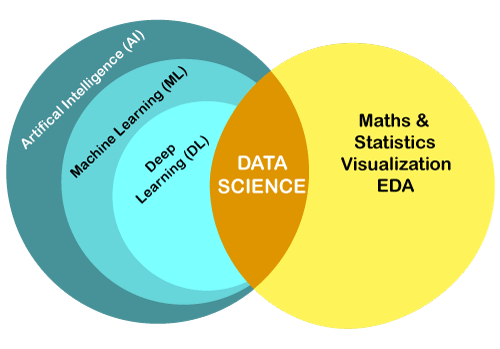
注意:数据科学和机器学习彼此密切相关,但不能视为同义词。
什么是数据科学?
顾名思义,数据科学就是关于数据的。因此,我们可以将其定义为“深入研究数据的领域,包括从数据中提取有用的见解,并使用不同的工具,统计模型和机器学习算法来处理信息。”该概念用于处理大数据,包括数据清理,数据准备,数据分析和数据可视化。
数据科学家从各种来源收集原始数据,准备和预处理数据,并应用机器学习算法,预测分析以从收集的数据中提取有用的见解。
例如,Netflix使用数据科学技术通过挖掘数据和查看用户的模式来了解用户的兴趣。
成为数据科学家所需的技能
- 精通Python,R,SAS或Scala的编程知识。
- 有SQL数据库编码方面的经验。
- 机器学习算法知识。
- 精通统计概念。
- 数据挖掘,清理和可视化技能。
- 使用大数据工具(例如Hadoop)的技巧。
什么是机器学习?
机器学习是人工智能的一部分,也是数据科学的子领域。它是一项不断发展的技术,使机器能够从过去的数据中学习并自动执行给定的任务。可以定义为:
机器学习使计算机可以自己学习过去的经验,它使用统计方法来改进性能并预测输出,而无需进行显式编程。
ML的流行应用是电子邮件垃圾邮件过滤,产品推荐,在线欺诈检测等。
机器学习工程师需要的技能:
- 理解和实现机器学习算法。
- 自然语言处理。
- 对Python或R有良好的编程知识。
- 统计知识和概率概念。
- 数据建模和数据评估方面的知识。
数据科学在哪里使用机器学习?
数据科学的发展过程或生命周期可以理解机器学习在数据科学中的使用。数据科学生命周期中发生的不同步骤如下:
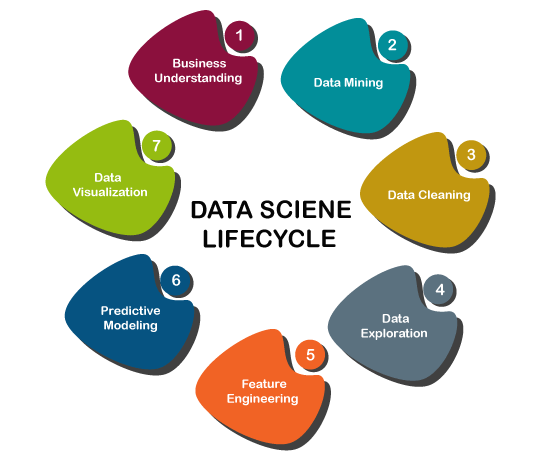
- 业务需求:在此步骤中,我们尝试了解我们要使用的业务问题的需求。假设我们要创建一个推荐系统,并且业务需求是增加销售额。
- 数据获取:在此步骤中,数据被获取以解决给定的问题。对于推荐系统,我们可以获得用户针对不同产品,评论,购买记录等提供的评分。
- 数据处理:在此步骤中,从以前的步骤中获取的原始数据被变换成合适的格式,以便它可以通过进一步的步骤很容易地使用。
- 数据探索:这是我们了解数据模式并尝试从数据中找到有用的见解的步骤。
- 建模:数据建模是使用机器学习算法的步骤。因此,此步骤包括整个机器学习过程。机器学习过程包括导入数据,清理数据,构建模型,训练模型,测试模型以及提高模型的效率。
- 部署和优化:这是在实际项目中部署模型并检查模型性能的最后一步。
数据科学与机器学习之间的比较
下表描述了数据科学与ML之间的基本区别:
| Data Science | Machine Learning |
|---|---|
| It deals with understanding and finding hidden patterns or useful insights from the data, which helps to take smarter business decisions. | It is a subfield of data science that enables the machine to learn from the past data and experiences automatically. |
| It is used for discovering insights from the data. | It is used for making predictions and classifying the result for new data points. |
| It is a broad term that includes various steps to create a model for a given problem and deploy the model. | It is used in the data modeling step of the data science as a complete process. |
| A data scientist needs to have skills to use big data tools like Hadoop, Hive and Pig, statistics, programming in Python, R, or Scala. | Machine Learning Engineer needs to have skills such as computer science fundamentals, programming skills in Python or R, statistics and probability concepts, etc. |
| It can work with raw, structured, and unstructured data. | It mostly requires structured data to work on. |
| Data scientists spent lots of time in handling the data, cleansing the data, and understanding its patterns. | ML engineers spend a lot of time for managing the complexities that occur during the implementation of algorithms and mathematical concepts behind that. |