用于对按升序和降序交替排序的链表进行排序的Java程序
给定一个链表。链接列表按升序和降序交替排列。有效地对列表进行排序。
例子:
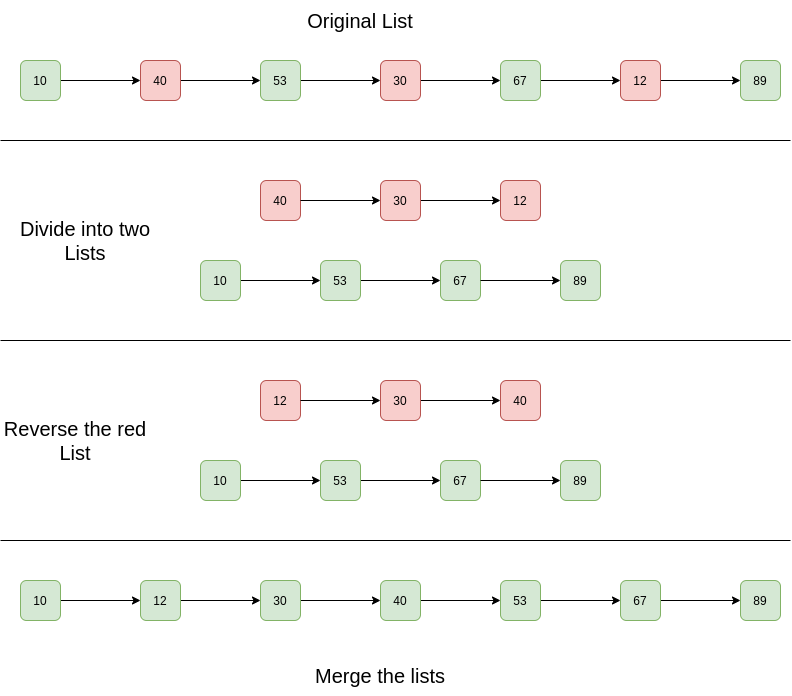
Input List: 10 -> 40 -> 53 -> 30 -> 67 -> 12 -> 89 -> NULL
Output List: 10 -> 12 -> 30 -> 40 -> 53 -> 67 -> 89 -> NULL
Input List: 1 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 5 -> NULL
Output List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL简单的解决方案:
方法:基本思想是在链表上应用归并排序。
本文讨论了实现:链表的合并排序。
复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度:链表的归并排序需要 O(n log n) 时间。在归并排序树中,高度为 log n。对每个级别进行排序将花费 O(n) 时间。所以时间复杂度是O(n log n)。
- 辅助空间: O(n log n),在归并排序树中,高度为 log n。存储每个级别将占用 O(n) 空间。所以空间复杂度是O(n log n)。
高效解决方案:
方法:
- 分开两个列表。
- 按降序反转一个
- 合并两个列表。
图表:
下面是上述算法的实现:
Java
// Java program to sort a linked list
// that is alternatively sorted in
// increasing and decreasing order
class LinkedList
{
// head of list
Node head;
// Linked list Node
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
Node newNode(int key)
{
return new Node(key);
}
/* This is the main function that sorts
the linked list.*/
void sort()
{
/* Create 2 dummy nodes and initialise
as heads of linked lists */
Node Ahead = new Node(0),
Dhead = new Node(0);
// Split the list into lists
splitList(Ahead, Dhead);
Ahead = Ahead.next;
Dhead = Dhead.next;
// Reverse the descending list
Dhead = reverseList(Dhead);
// Merge the 2 linked lists
head = mergeList(Ahead, Dhead);
}
// Function to reverse the linked list
Node reverseList(Node Dhead)
{
Node current = Dhead;
Node prev = null;
Node next;
while (current != null)
{
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
Dhead = prev;
return Dhead;
}
// Function to print linked list
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// A utility function to merge
// two sorted linked lists
Node mergeList(Node head1, Node head2)
{
// Base cases
if (head1 == null)
return head2;
if (head2 == null)
return head1;
Node temp = null;
if (head1.data < head2.data)
{
temp = head1;
head1.next = mergeList(head1.next,
head2);
}
else
{
temp = head2;
head2.next = mergeList(head1,
head2.next);
}
return temp;
}
// This function alternatively splits
// a linked list with head as head into two:
// For example, 10->20->30->15->40->7 is
// splitted into 10->30->40 and 20->15->7
// "Ahead" is reference to head of ascending
// linked list
// "Dhead" is reference to head of descending
// linked list
void splitList(Node Ahead, Node Dhead)
{
Node ascn = Ahead;
Node dscn = Dhead;
Node curr = head;
// Link alternate nodes
while (curr != null)
{
// Link alternate nodes in
// ascending order
ascn.next = curr;
ascn = ascn.next;
curr = curr.next;
if (curr != null)
{
dscn.next = curr;
dscn = dscn.next;
curr = curr.next;
}
}
ascn.next = null;
dscn.next = null;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.head = llist.newNode(10);
llist.head.next = llist.newNode(40);
llist.head.next.next =
llist.newNode(53);
llist.head.next.next.next =
llist.newNode(30);
llist.head.next.next.next.next =
llist.newNode(67);
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next =
llist.newNode(12);
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next.next =
llist.newNode(89);
System.out.println("Given linked list");
llist.printList();
llist.sort();
System.out.println("Sorted linked list");
llist.printList();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra输出:
Given Linked List is
10 40 53 30 67 12 89
Sorted Linked List is
10 12 30 40 53 67 89复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
需要一次遍历来分离列表并将它们反转。排序列表的合并需要 O(n) 时间。 - 辅助空间: O(1)。
不需要额外的空间。
请参阅完整文章对按升序和降序交替排序的链表进行排序?更多细节!