Python|熊猫系列.dt.ceil
Series.dt可用于以 datetimelike 的形式访问系列的值并返回多个属性。 Pandas Series.dt.ceil()函数对指定频率的数据执行 ceil 操作。
Syntax: Series.dt.ceil(*args, **kwargs)
Parameter :
freq : The frequency level to ceil the index to
Returns : DatetimeIndex, TimedeltaIndex, or Series
示例 #1:使用Series.dt.ceil()函数将给定系列对象的日期时间数据设置为指定频率。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['2012-12-31 08:45', '2019-1-1 12:30', '2008-02-2 10:30',
'2010-1-1 09:25', '2019-12-31 00:00'])
# Creating the index
idx = ['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3', 'Day 4', 'Day 5']
# set the index
sr.index = idx
# Convert the underlying data to datetime
sr = pd.to_datetime(sr)
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :

现在我们将使用Series.dt.ceil()函数将给定系列对象中的日期时间值设置为每日频率。
# ceil to daily frequency
result = sr.dt.ceil(freq = 'D')
# print the result
print(result)
输出 :

正如我们在输出中看到的, Series.dt.ceil()函数已成功地将给定系列对象中的日期时间值上限设置为指定的频率。
示例 #2:使用Series.dt.ceil()函数将给定系列对象的日期时间数据设置为指定频率。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(pd.date_range('2012-12-31 09:45', periods = 5, freq = 'T',
tz = 'Asia / Calcutta'))
# Creating the index
idx = ['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3', 'Day 4', 'Day 5']
# set the index
sr.index = idx
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
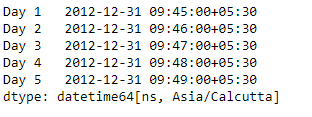
现在我们将使用Series.dt.ceil()函数将给定系列对象中的日期时间值设置为每小时频率。
# ceil to hourly frequency
result = sr.dt.ceil(freq = 'H')
# print the result
print(result)
输出 :
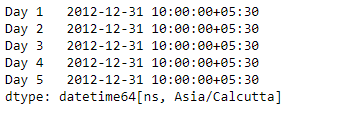
正如我们在输出中看到的, Series.dt.ceil()函数已成功地将给定系列对象中的日期时间值上限设置为指定的频率。