用Java实现 Coppersmith Freivald 算法
概念: Coppersmith Freivald's Algorithm 是检查矩阵 A 乘以矩阵 B 是否等于给定的矩阵 C。它用于验证矩阵乘法。借助 A*(B*r)-(C*r)=0 等式对其进行验证,其中 r 是仅由 0/1 组成的随机列向量。
插图:
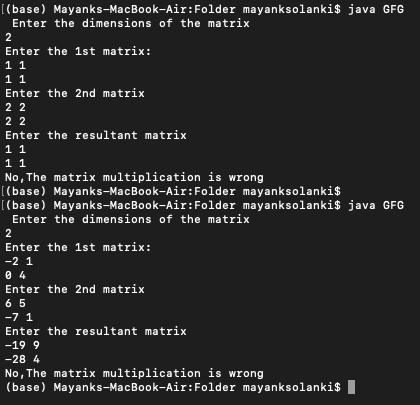
Input:
Enter the dimensions of the matrices:
2
Enter the 1st matrix:
-2 1
0 4
Enter the 2st matrix:
6 5
-7 1
Enter the result matrix:
-19 9
-28 4
Output: Yes, The matrix multiplication is correct.方法:
将矩阵的大小作为用户的输入。
目标:根据等式我们需要验证矩阵 A * 矩阵 B = 矩阵 C。
将矩阵 A(n*n) 的输入矩阵 B(n*n) 和结果矩阵 C(n*n) 作为输入。
1) 随机取数组 r[n][1] 只包含 0/1 的元素。
2) 计算矩阵 B*r、矩阵 C*r 和矩阵 A*(matrix B*r) 用于评估表达式矩阵 A*(matrix B * r) – (matrix C*r)
3) 检查方程矩阵 A*(matrix B * r) – (matrix C*r)=0 是否。
4)如果为零,则打印“是”,否则打印“否”。
实现:按上面的顺序输入,否则会导致错误的结果。以下是供考虑的示例
Java
// Importing class to create objects
// generating pseudo random numbers
import java.util.Random;
// Importing class to take input from user
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GFG {
public static double[][] multiplyVector(double[][] a,
double[][] b,
int n)
// Method to check the result of the equation.
{
double result[][] = new double[n][1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 1; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
result[i][j]
= result[i][j] + a[i][k] * b[i][j];
}
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Driver main method
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(
" Enter the dimensions of the matrix");
int n = input.nextInt();
// n- size or dimensions of matrix
System.out.println("Enter the 1st matrix:");
// Taking input for 1st matrix
double a[][] = new double[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
a[i][j] = input.nextDouble();
}
}
//
System.out.println("Enter the 2nd matrix");
double b[][] = new double[n][n];
// Taking input for second matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
b[i][j] = input.nextDouble();
}
}
// Covering up Resultant matrix
System.out.println("Enter the resultant matrix");
double c[][] = new double[n][n];
// the resultant matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
c[i][j] = input.nextDouble();
}
}
// generating random matrix r consisting of 0/1 only
double[][] r = new double[n][1];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
r[i][0] = random.nextInt(2);
}
// testing of the standard equation A*(B*r)-(C*r)=0
double br[][] = new double[n][1];
double cr[][] = new double[n][1];
double abr[][] = new double[n][1];
br = multiplyVector(b, r, n);
cr = multiplyVector(c, r, n);
abr = multiplyVector(a, br, n);
// check for all zeroes in abr
boolean flag = true;
// Setting flag wth true
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (abr[i][0] == 0)
continue;
else
// Set flag to false(change flag)
flag = false;
}
// Boolean comparison resulting in message printing
if (flag == true)
System.out.println(
"Yes,The matrix multiplication is correct");
else
System.out.println(
"No,The matrix multiplication is wrong");
input.close();
}
}输出: 2 阶 2 随机矩阵的自定义输入
时间复杂度: O(kN^2) 其中 N 是矩阵的大小。