检查删除给定边是否断开图
给定一个无向图和一条边,任务是找出给定边是否是图中的桥,即移除边断开图。
以下是一些示例图,其中以红色突出显示的桥梁。
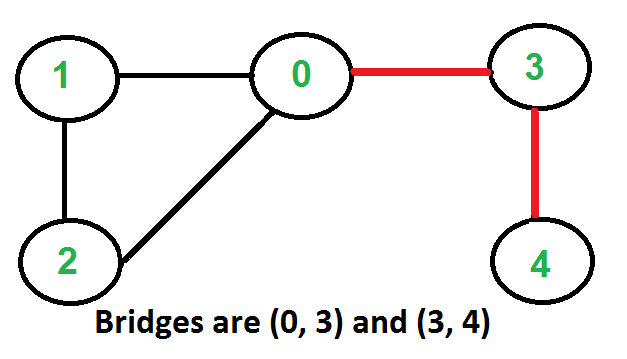
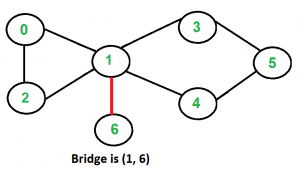
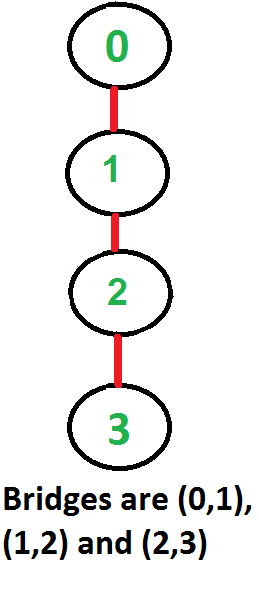
一种解决方案是找到给定图中的所有桥,然后检查给定边是否是桥。
一个更简单的解决方案是删除边,检查删除后图形是否仍然连接,最后添加边。我们总是可以通过从任何顶点查找所有可到达的顶点来确定无向是否连接。如果可达顶点数等于图中的顶点数,则图是连通的,否则不连通。我们可以使用 BFS 或 DFS 找到所有可到达的顶点。以下是完整的步骤。
1)删除给定的边缘
2) 从任意顶点查找所有可达顶点。我们在下面的实现中选择了第一个顶点。
3) 如果可达节点数为 V,则返回 false [given is not Bridge]。否则返回是。
C++
// C++ program to check if removing an
// edge disconnects a graph or not.
#include
using namespace std;
// Graph class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj;
void DFS(int v, bool visited[]);
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Returns true if graph is connected
bool isConnected();
bool isBridge(int u, int v);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v); // Add w to v’s list.
adj[v].push_back(u); // Add w to v’s list.
}
void Graph::DFS(int v, bool visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to
// this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFS(*i, visited);
}
// Returns true if given graph is connected, else false
bool Graph::isConnected()
{
bool visited[V];
memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
// Find all reachable vertices from first vertex
DFS(0, visited);
// If set of reachable vertices includes all,
// return true.
for (int i=1; i Java
// Java program to check if removing an
// edge disconnects a graph or not.
import java.util.*;
// Graph class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph {
int V; // No. of vertices
ArrayList > adj;
private void DFS(int v, boolean[] visited)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to
// this vertex
for (Integer i : adj.get(v)) {
if (!visited[i]) {
DFS(i, visited);
}
}
}
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
public void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj.get(u).add(v); // Add v to u’s list.
adj.get(v).add(u); // Add u to v’s list.
}
// Returns true if given graph is connected, else false
public boolean isConnected()
{
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
// Find all reachable vertices from first vertex
DFS(0, visited);
// If set of reachable vertices includes all,
// return true.
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// This function assumes that edge (u, v)
// exists in graph or not,
public boolean isBridge(int u, int v)
{
// Remove edge from undirected graph
adj.get(u).remove(Integer.valueOf(v));
adj.get(v).remove(Integer.valueOf(u));
boolean res = isConnected();
// Adding the edge back
addEdge(u, v);
// Return true if graph becomes disconnected
// after removing the edge.
return (res == false);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
if (g.isBridge(1, 2)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
}
else {
System.out.println("No");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Karandeep Singh Python3
# Python3 program to check if removing
# an edge disconnects a graph or not.
# Graph class represents a directed graph
# using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.adj = [[] for i in range(V)]
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.adj[u].append(v) # Add w to v’s list.
self.adj[v].append(u) # Add w to v’s list.
def DFS(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as
# visited and print it
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices
# adjacent to this vertex
i = 0
while i != len(self.adj[v]):
if (not visited[self.adj[v][i]]):
self.DFS(self.adj[v][i], visited)
i += 1
# Returns true if given graph is
# connected, else false
def isConnected(self):
visited = [False] * self.V
# Find all reachable vertices
# from first vertex
self.DFS(0, visited)
# If set of reachable vertices
# includes all, return true.
for i in range(1, self.V):
if (visited[i] == False):
return False
return True
# This function assumes that edge
# (u, v) exists in graph or not,
def isBridge(self, u, v):
# Remove edge from undirected graph
indU = self.adj[v].index(u)
indV = self.adj[u].index(v)
del self.adj[u][indV]
del self.adj[v][indU]
res = self.isConnected()
# Adding the edge back
self.addEdge(u, v)
# Return true if graph becomes
# disconnected after removing
# the edge.
return (res == False)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create a graph given in the
# above diagram
g = Graph(4)
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
if g.isBridge(1, 2):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by PranchalK输出 :
Yes