原子轨道的形状和能量
原子轨道是数学函数,描述了原子中电子(或电子对)的波动行为。它们提供了一种计算在原子核的某个位置找到电子的可能性的方法。有四种类型的轨道,每种都有不同的形式,并用字母 s、p、d 和 f 表示。 s 和 p 轨道被考虑在内,因为它们在化学和生物化学中是最丰富的。一个 s 轨道在中心有一个球形核,一个 p 轨道是哑铃形的,五个 d 轨道中有四个是三叶草形的。第五个 d 轨道的形状像一个长哑铃,中间有一个甜甜圈。原子的轨道被组织成层或电子壳。
什么是原子轨道?
根据量子原子模型,一个原子可以有无数个轨道。这些轨道可以根据它们的大小、形状或方向进行分类。更窄的轨道意味着在原子核附近捕获电子的可能性更高。轨道波函数,通常被称为是用于表示电子坐标的数学函数。定位电子的可能性由轨道波函数的平方表示。该波函数还有助于创建边界面图。
s-轨道形状
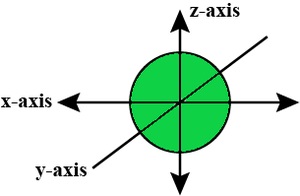
- s轨道边界面图类似于一个以原子核为中心的球体,可以在二维中显示为一个圆。
- S轨道是球对称的,这意味着在给定距离处找到电子的概率在所有方向上都是相同的。
- s 轨道的大小同样显示为随着初级量子数 (n) 值的增加而增加;因此,4s > 3s > 2s > 1s。
- 节点是没有机会定位电子的位置。节点分为两种类型:径向节点和角节点。与核的距离由径向节点计算,而方向由角度节点确定。
S-轨道
p轨道的形状
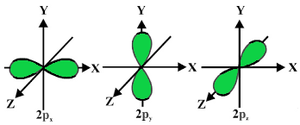
- p 轨道像哑铃一样形成。
- p 轨道节点位于原子核的中心。
- 由于存在三个轨道,p 轨道最多可以占据六个电子。
- 每个 p 轨道由两个称为裂片的部分组成,它们位于穿过原子核的平面的两侧。
- 每个 p 轨道在穿过原子核的平面的两侧都有称为裂片的部分。在两个裂片相交的平面上,找到电子的可能性为零。
- 这三个轨道被称为简并轨道,因为它们具有相同的大小、形状和能量。
- 轨道之间的唯一区别是裂片的方向。因为叶沿 x、y 或 z 轴定向,所以它们被命名为 2 px 、 2 py和 2 pz 。公式 n –2 用于计算节点数。
- 与 s 轨道类似,p 轨道的大小和能量随着初级量子数的增加(4p > 3p > 2p)而增加。
P轨道
d轨道的形状
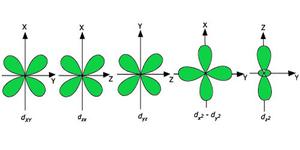
- 对于 d 轨道,磁轨道量子数为 (-2,-1,0, 1,2)。因此,我们可以声称有五个 d 轨道。
- 这些轨道由符号 d xy 、d yz 、d xz 、d x 2 –y 2和d z 2表示。
- 前四个 d 轨道的形式彼此相似,与 d z 2轨道不同,但所有五个 d 轨道的能量相同。
D-轨道
f轨道的形状
f 轨道的形式是分散的。因为 f 轨道的 l=3,初级量子数 n 的最小值为 4。 f 轨道的等效 ml 值为 (-3,–2, –1, 0, +1, +2 , +3)。因此,对于 l = 3,有 7 个 f 轨道。
简并轨道
简并轨道是具有相同能量的轨道。这些轨道是不同的(它们在原子核周围的空间方向可能不同),但它们具有相同的能量。在存在外场的情况下,p 轨道的简并性不受影响;但是,可以通过对系统施加外部场(电场或磁场)来打破 f 和 d 轨道的简并性。
很少有轨道具有更高的能量,而其他轨道的能量更低。系统中将不再存在退化。例如,d 轨道由五个具有相同能量的简并轨道组成。
示例问题
问题1:轨道如何工作?
回答:
An atomic orbital is a mathematical expression that expresses the wave-like behaviour of one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom in atomic theory and quantum mechanics. Each orbital will take up a maximum of two electrons, each with its own amount of spin.
问题2:有多少个轨道?
回答:
Because the s sublevel has just one orbital, only two electrons can be present. Because the p sublevel comprises three orbitals, a maximum of six electrons can be present. Because the d sublevel comprises 5 orbitals, a maximum of 10 electrons can be present. And each of the four sub-levels has seven orbitals that may hold a maximum of 14 electrons.
问题 3:哪些轨道的能量最高?
回答:
The orbital 1s has the most energy. An electron’s energy is the amount of energy required to get it out of the atom’s electrical bubble.
问题4:壳和轨道有什么区别?
回答:
In an atom, a shell is a collection of subshells of the same quantum number theory, n. Orbitals each have two electrons, and electrons in the same orbital have the same definition of size, angular momentum size, and magnetic quantum number.
问题 5:什么是 sigma 和 pi 键?
回答:
Atomic orbital overlap creates sigma and pi bonds. Sigma bonds are created by overlapping atomic orbital lobes, whereas Pi bonds are generated when one atomic orbital lobe overlaps another.