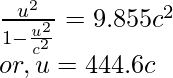能量动量公式
能量-动量关系是一个相对论方程,可用于连接物体静止时的质量、总能量和动量。该相对论方程适用于静止质量为 m 0 、总能量为 E、动量大小为 p 的宏观物体,其中 c 表示光速为常数。该方程适用于总能量 E、质量不变 m 0和大小为 p 的系统;常数c是光速。它考虑了平面时空的狭义相对论场景。总能量是静止能量和动能的总和,而不变质量是在质心框架中测量的质量。
在这两种含义中,能量-动量关系与众所周知的质能关系一致:E = mc 2描述了总能量 E 和(总)相对论质量 m(也称为 mrel 或 mtot)之间的关系,而E 0 = m 0 c 2描述了静止能量E 0和(不变的)静止质量m 0之间的关系。
能量动量公式
能量-动量关系的公式如下:
![]()
Where,
- E depicts the energy.
- p is the momentum of the object.
- c = speed of light
- m0 = rest mass
推导能量动量公式
能量-动量关系可以通过将爱因斯坦关系与相对论动量表达式混合得到。

E = mc2
p = 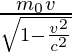
⇒ ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com p^2c^2=\frac{m_0^2v^2c^2}{1-\frac{v^2}{c^2}}\\=\frac{m_0^2\frac{v^2}{c^2}c^4}{1-\frac{v^2}{c^2}}\\= \frac{m_0^2c^4[\frac{v^2}{c^2}-1]}{1-\frac{v^2}{c^2}}+\frac{m_0^2c^4}{1-\frac{v^2}{c^2}} \\=-m_0^2c^4+(mc^2)^2 \\⇒E=\sqrt{p^2c^2+(m_0c^2)^2}](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Energy_Momentum_Formula_3.jpg)
Hence proved.
示例问题
问题 1:求一个质量为 2 × 10 -9 kg、能量为 400 KJ 的粒子的动量。
解决方案:
Given: E = 400 KJ and m0 = 2 × 10-9 kg
The formula for the energy- momentum relation is
![]()
Substituting the values in the formula we have,
![]()
p = 119070.4 × 108 kg .m/s
问题 2:求动量为 3 × 10 -4 kg⋅m/s 的质子的速度。
解决方案:
Given: m = 1.67 × 10-27 kg and P = 3 × 10−4 kg⋅m/s
Since, 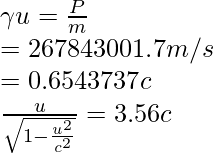
Squaring both sides, we obtain
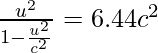
u = 5.3 × 108 m/s
问题 3:在 12.0 V 时,汽车电池被评估为可充电 600 安培小时 (Ah)。假设没有发生化学反应,确定电池从完全耗尽到充电的静止质量增量。
解决方案:
Given: Ebatt = (Δm)c2
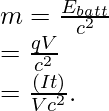
⇒ ![]()
Time needs to be converted into hours. Thus,
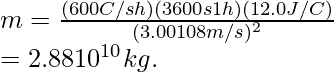
问题 4:求动量为 4.48 × 10 -19 kg·m/s 的质子的速度。
解决方案:
Given: m = 1.67 × 10-27 kg and P = 4.48 × 10−19 kg⋅m/s
Since, 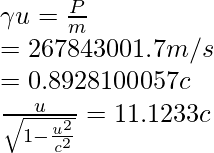
Squaring both sides, we obtain
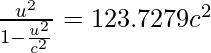
⇒ u = 0.665996204 c
or, u = 1.997988 x 108 m/s
问题5:有动量的物体总是有能量吗?反过来也是真的吗?解释。
解决方案:
Yes, an object with momentum always has energy. If the object has momentum (mv) it must be moving, and if it is moving it has kinetic energy.
No, an object with energy does NOT always have momentum. An object can be at rest and have potential energy (a book resting on a desk, for instance). Since this object’s velocity = 0, its momentum is zero.
问题 6:求动量为 3.04 × 10 -21 kg·m/s 的电子的速度。
解决方案:
Given: m = 9.11 × 10-31 kg and P = 4.48 × 10−19 kg⋅m/s
Since, 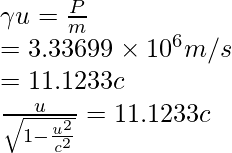
Squaring both sides, we obtain
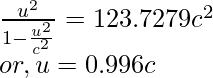
问题 7:求动量为 5 × 10 -19 kg⋅m/s 的电子的速度。
解决方案:
Given: m = 9.11 × 10-31 kg and P = 5 × 10−19 kg⋅m/s
Since, 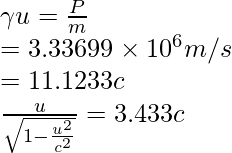
Squaring both sides, we obtain: