异常摩尔质量
在化学中,当估计的摩尔质量高于或低于预测值时,就会出现异常的摩尔质量。依数性质用于计算这些。沸点升高、相对蒸汽压降低、冰点降低和渗透压降低都是依数性质。名称中有异常一词,暗示使用范特霍夫因子计算摩尔质量的方式是异常的。我们来看一下。
异常摩尔质量
通过这些方法确定的摩尔质量与预期值或理论值不一致。只有满足以下两个条件,才能得到准确的摩尔质量值。
- 溶液应稀释:用于测量依数性质的溶液不应太浓。在浓缩溶液中,颗粒之间以及与溶剂相互作用。因此,蒸气压和其他共轭特性取决于溶质的性质,而不仅仅是溶质颗粒的数量。
- 所需的溶质在溶液中不是单独的或协同的:用于测量依数性质的导数方程适用于不发生任何解离或具有缔合溶液的非电解质溶质。然而,当溶质在溶剂中解离或结合时,摩尔质量的测定就会出现差异。这是因为溶液中分子的数量由于溶质分子的添加或解离而发生变化。因此,如下所述获得异常摩尔质量:
对于在溶液中发生缔合、解离等的物质,由共轭性质决定的分子质量与预期值不同。这被称为异常分子质量。这可以通过 Van't 半因子知道。
因此,当从溶液的依数性质计算时,有时会发现分子质量的理论值与称为异常摩尔质量的经验测量值不同。
溶质粒子的结合
在某些溶剂中,通常是非极性的溶质分子发生键合,即两个、三个甚至更多的分子相互作用形成更大的分子。例如,假设 n 个简单分子结合形成一个关联分子:
nA ⇆ A n
(单分子) (一分子)
因此,溶液中的分子总数变得少于添加的物质的分子数,因此共价性质将减少。由于依数性质与溶质的摩尔质量成反比,在这种情况下,摩尔质量超过了理论值。例如,在苯溶剂中,乙酸(乙酸)和苯甲酸均以二聚体形式存在:

二聚体乙酸和苯甲酸的摩尔质量约为 120 和 244,分别是其正常值 60 和 122 的两倍。由于这些分子之间的氢键,溶液中溶质分子的键合是正常的。举例来说,苯甲酸和乙酸(乙酸)由于氢键的形成而作为二聚体存在。
溶质分子的解离
电解质分子(酸、碱和盐)在排气孔中分离或电离,产生两个或多个粒子。例如,AB 解离得到双琥珀色的粒子:
AB ⇆ A + + B –
结果,溶液中的粒子总数增加,因此,这种溶液的依数性质会很大。由于依数性质与摩尔质量成反比,因此观察到的摩尔质量将小于理论值。例如,KCI、K。搁置以提供 ed Cl-离子。
KCI ⇆ K + + Cl –
这意味着如果我们将 1 mol KCl (74.5 g) 溶解在水中,我们预计溶液中有 1 mol K 和 1 mol Cl -离子。所以不是 1 摩尔的溶液,而是 2 摩尔的粒子。因此,抵押资产也将几乎是预期的两倍。例如,如果 E 忽略离子间的吸引力,1 kg 水中的 1 mol KCl 将使沸点增加 2 x 0.52 K (K = 0.52 Km¹) = 1.04 K。明显地,盐的摩尔质量应该是大约一半其正常值,即 37.25。
范特霍夫因子
Van't Hoff 因子定义为溶质的正常摩尔质量与观察到的摩尔质量(或异常摩尔质量)之比,即 i= 正常摩尔质量/观察到(或异常)摩尔质量
- 在关联的情况下,观察到的摩尔质量大于正常值,因子 T 的值小于 1。
- 在解离的情况下,Van't Hoff 因子大于 1,因为观察到的摩尔质量具有较低的值。
- 对于在溶剂中不发生任何缔合或解离的溶质,Van't Hoff 因子将等于 1,因为观察到的摩尔质量与正常摩尔质量相同。
由于摩尔质量与依数性成反比,因此范特霍夫因子也可以定义为依数性的观测值与依数性的普通值的比值。
i = Observed value of the colligative property / Normal value of colligative property
or
i = Total number of moles of particles after association or dissociation / Total number of moles of particles before association or dissociation
如果 i > 1 ,溶质发生解离,如果 i < 1 ,溶质发生缔合。
- 对于联想,
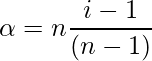
其中,n = 关联或解离的粒子数。
- 对于解离,
![]()
对于解离溶质,范特霍夫因子总是大于 1。对于既不显示关联也不显示解离的粒子,Van't Hoff 因子设置为 1。因此,在加入 Van't Hoff 因子后,依数性质方程将是,
- 包含 Van't Hoff 因子将依数性质的方程修改如下:
- 溶剂蒸气压的相对降低,(p 1 ° -p 1 )/p 1 ° = i(n 2 /n 1 )
- 沸点升高,ΔT b = iK b m
- 冰点下降,ΔT f = iK f m
- 溶液的渗透压,π = (in 2 /V) RT
示例问题
问题 1. 为什么静脉注射与蔬菜和血浆溶液中的浓度相同?
回答:
During intravenous injection, the concentration of the solution for injection should be equal to that of blood plasma. If the solution is less concentrated, its osmotic pressure will be lower. Water will try to get into the red blood cells through the cell walls. As an outcome, the cells will swell and burst. On the other hand, if the solution is more concentrated, the water in the cells will try to move into the more concentrated solution outside the cell by osmosis. This causes the cells to shrink and consequently stop functioning.
问题 2. 表征大分子的摩尔质量有哪些依数性质?
回答:
Osmotic pressure premeditate is preferred to complete all other conjugate properties because-
- Even in dilute solutions, the osmotic pressure values are very high and can be measured accurately.
- Osmotic pressure can be premeditated at room temperature. On the other hand, the height in boiling point is measured at the higher temperature where the solute can dissociate. The depression in freezing point is measured at low temperature.
问题3:如果将0.1mol糖或0.1mol葡萄糖溶解在一升水中,冰点的降低是相同的还是不同的?
回答:
The depression in the freezing point will be the same in both the solutions as both are non-electrolyte and give an equal number of solute particles.
问题 4. 去掉两个鸡蛋的外层硬壳。一个鸡蛋放在纯水中,另一个放在饱和氯化钠溶液中。会看到什么,为什么?
回答:
An egg placed in water will swell due to the osmosis of pure water in the egg. On the other hand, an egg placed in a saturated solution of NaCl will shrink due to the osmosis of water from the egg. This is because osmosis always occurs from a high concentration of solvent to a low concentration of solvent.
问题 5. 为什么建议在山站行驶时在汽车散热器中将乙二醇与水混合?
回答:
Ethylene glycol lowers the freezing point of water and hence, it does not freeze in a hill station.
问题 6. 氯化钠溶液在低于水的温度下结冰,但在高于水的温度下沸腾,解释。
回答:
The freezing point of a liquid decreases upon the addition of a non-volatile solute and, therefore, a solution of sodium chloride freezes at a temperature lower than the freezing point of water. The addition of a non-volatile solute as a replacement increases the boiling point and results in the boiling point of a sodium chloride solution.
问题 6. 氯化钠和尿素的赤道溶液是等渗的吗?为什么?
回答:
Sodium chloride dissociates to two ions (Na and Cl) and exerts approximately twice the osmotic pressure of 170 urea (which is non-electrolyte).