使用颜色检测有向图中的循环
给定一个有向图,检查该图是否包含循环。如果给定的图形包含至少一个循环,您的函数应该返回 true,否则返回 false。
例子:
Input: n = 4, e = 6
0 -> 1, 0 -> 2, 1 -> 2, 2 -> 0, 2 -> 3, 3 -> 3
Output: Yes
Explanation:
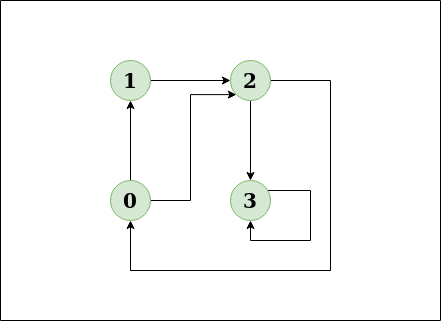
This diagram clearly shows a cycle 0 -> 2 -> 0.
Input:n = 4, e = 3
0 -> 1, 0 -> 2, 1 -> 2, 2 -> 3
Output:No
Explanation:
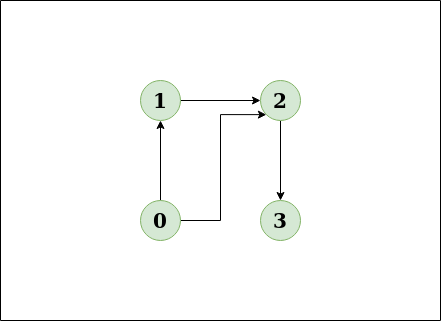
This diagram clearly shows no cycle.
解决方案
方法:深度优先遍历可用于检测图中的循环。连通图的 DFS 生成一棵树。仅当图中存在后边时,图中才存在循环。后边是从节点到自身(自循环)或其在 DFS 生成的树中的祖先之一的边。在下图中,有 3 个后边,用叉号标记。可以观察到,这 3 个后边缘表示图中存在 3 个循环。
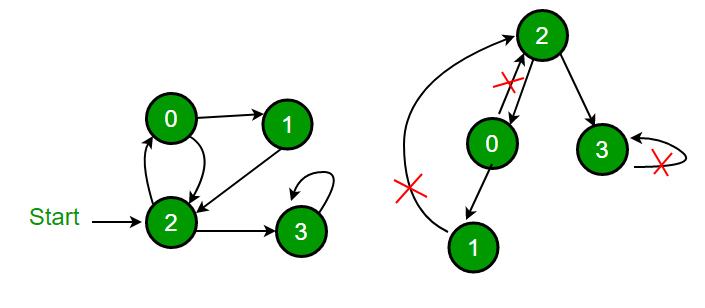
对于断开连接的图,我们将 DFS 森林作为输出。为了检测循环,我们可以通过检查后边来检查单个树中的循环。
图片来源: http ://www.cs.yale.edu/homes/aspnes/pinewiki/DepthFirstSearch.html
在上一篇文章中,我们讨论了将访问的顶点存储在一个单独的数组中的解决方案,该数组存储当前递归调用堆栈的顶点。
在这篇文章中,讨论了一个不同的解决方案。解决方案来自 CLRS 书。这个想法是对给定图形进行 DFS,并在进行遍历时,将以下三种颜色中的一种分配给每个顶点。
WHITE : Vertex is not processed yet. Initially, all vertices are WHITE.
GRAY: Vertex is being processed (DFS for this vertex has started, but not finished which means that all descendants (in DFS tree) of this vertex are not processed yet (or this vertex is in the function call stack)
BLACK : Vertex and all its descendants are processed. While doing DFS, if an edge is encountered from current vertex to a GRAY vertex, then this edge is back edge and hence there is a cycle.
算法:
- 创建一个接受边缘和颜色数组的递归函数(这也可以保存为全局变量)
- 将当前节点标记为灰色。
- 遍历所有相邻节点,如果任何节点标记为灰色,则返回 true,因为循环必然存在。
- 如果任何相邻顶点为白色,则调用该节点的递归函数。如果函数返回true。返回真。
- 如果没有相邻节点是灰色的或没有返回true,则将当前节点标记为黑色并返回false。
执行:
C++
// A DFS based approach to find if there is a cycle
// in a directed graph. This approach strictly follows
// the algorithm given in CLRS book.
#include
using namespace std;
enum Color {WHITE, GRAY, BLACK};
// Graph class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list* adj; // adjacency lists
// DFS traversal of the vertices reachable from v
bool DFSUtil(int v, int color[]);
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
bool isCyclic();
};
// Constructor
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
// Utility function to add an edge
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v's list.
}
// Recursive function to find if there is back edge
// in DFS subtree tree rooted with 'u'
bool Graph::DFSUtil(int u, int color[])
{
// GRAY : This vertex is being processed (DFS
// for this vertex has started, but not
// ended (or this vertex is in function
// call stack)
color[u] = GRAY;
// Iterate through all adjacent vertices
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i)
{
int v = *i; // An adjacent of u
// If there is
if (color[v] == GRAY)
return true;
// If v is not processed and there is a back
// edge in subtree rooted with v
if (color[v] == WHITE && DFSUtil(v, color))
return true;
}
// Mark this vertex as processed
color[u] = BLACK;
return false;
}
// Returns true if there is a cycle in graph
bool Graph::isCyclic()
{
// Initialize color of all vertices as WHITE
int *color = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
color[i] = WHITE;
// Do a DFS traversal beginning with all
// vertices
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (color[i] == WHITE)
if (DFSUtil(i, color) == true)
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver code to test above
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
if (g.isCyclic())
cout << "Graph contains cycle";
else
cout << "Graph doesn't contain cycle";
return 0;
} Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A DFS based approach to find if there is a cycle
// in a directed graph. This approach strictly follows
// the algorithm given in CLRS book.
static int WHITE = 0, GRAY = 1, BLACK = 2;
// Graph class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
static class Graph
{
int V;
LinkedList[] adjList;
// Constructor
Graph(int ver)
{
V = ver;
adjList = new LinkedList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adjList[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
}
// Utility function to add an edge
static void addEdge(Graph g, int u, int v)
{
g.adjList[u].add(v); // Add v to u's list.
}
// Recursive function to find if there is back edge
// in DFS subtree tree rooted with 'u'
static boolean DFSUtil(Graph g, int u, int[] color)
{
// GRAY : This vertex is being processed (DFS
// for this vertex has started, but not
// ended (or this vertex is in function
// call stack)
color[u] = GRAY;
// Iterate through all adjacent vertices
for (Integer in : g.adjList[u])
{
// If there is
if (color[in] == GRAY)
return true;
// If v is not processed and there is a back
// edge in subtree rooted with v
if (color[in] == WHITE && DFSUtil(g, in, color) == true)
return true;
}
// Mark this vertex as processed
color[u] = BLACK;
return false;
}
// Returns true if there is a cycle in graph
static boolean isCyclic(Graph g)
{
// Initialize color of all vertices as WHITE
int[] color = new int[g.V];
for (int i = 0; i < g.V; i++)
{
color[i] = WHITE;
}
// Do a DFS traversal beginning with all
// vertices
for (int i = 0; i < g.V; i++)
{
if (color[i] == WHITE)
{
if(DFSUtil(g, i, color) == true)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Driver code to test above
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g = new Graph(4);
addEdge(g, 0, 1);
addEdge(g, 0, 2);
addEdge(g, 1, 2);
addEdge(g, 2, 0);
addEdge(g, 2, 3);
addEdge(g, 3, 3);
if (isCyclic(g))
System.out.println("Graph contains cycle");
else
System.out.println("Graph doesn't contain cycle");
}
}
// This code is contributed by rachana soma Python3
# Python program to detect cycle in
# a directed graph
from collections import defaultdict
class Graph():
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
def DFSUtil(self, u, color):
# GRAY : This vertex is being processed (DFS
# for this vertex has started, but not
# ended (or this vertex is in function
# call stack)
color[u] = "GRAY"
for v in self.graph[u]:
if color[v] == "GRAY":
return True
if color[v] == "WHITE" and self.DFSUtil(v, color) == True:
return True
color[u] = "BLACK"
return False
def isCyclic(self):
color = ["WHITE"] * self.V
for i in range(self.V):
if color[i] == "WHITE":
if self.DFSUtil(i, color) == True:
return True
return False
# Driver program to test above functions
g = Graph(4)
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 3)
print ("Graph contains cycle" if g.isCyclic() == True\
else "Graph doesn't contain cycle")
# This program is contributed by Divyanshu MehtaC#
// A C# program to detect cycle in
// an undirected graph using BFS.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// A DFS based approach to find if
// there is a cycle in a directed graph.
// This approach strictly follows the
// algorithm given in CLRS book.
static int WHITE = 0, GRAY = 1, BLACK = 2;
// Graph class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
public class Graph
{
public int V;
public List[] adjList;
// Constructor
public Graph(int ver)
{
V = ver;
adjList = new List[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adjList[i] = new List();
}
}
// Utility function to add an edge
static void addEdge(Graph g, int u, int v)
{
g.adjList[u].Add(v); // Add v to u's list.
}
// Recursive function to find if there is back edge
// in DFS subtree tree rooted with 'u'
static bool DFSUtil(Graph g, int u, int[] color)
{
// GRAY : This vertex is being processed (DFS
// for this vertex has started, but not
// ended (or this vertex is in function
// call stack)
color[u] = GRAY;
// Iterate through all adjacent vertices
foreach (int iN in g.adjList[u])
{
// If there is
if (color[iN] == GRAY)
return true;
// If v is not processed and there is a back
// edge in subtree rooted with v
if (color[iN] == WHITE &&
DFSUtil(g, iN, color) == true)
return true;
}
// Mark this vertex as processed
color[u] = BLACK;
return false;
}
// Returns true if there is a cycle in graph
static bool isCyclic(Graph g)
{
// Initialize color of all vertices as WHITE
int[] color = new int[g.V];
for (int i = 0; i < g.V; i++)
{
color[i] = WHITE;
}
// Do a DFS traversal beginning with all
// vertices
for (int i = 0; i < g.V; i++)
{
if (color[i] == WHITE)
{
if(DFSUtil(g, i, color) == true)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g = new Graph(4);
addEdge(g, 0, 1);
addEdge(g, 0, 2);
addEdge(g, 1, 2);
addEdge(g, 2, 0);
addEdge(g, 2, 3);
addEdge(g, 3, 3);
if (isCyclic(g))
Console.WriteLine("Graph contains cycle");
else
Console.WriteLine("Graph doesn't contain cycle");
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 Javascript
输出:
Graph contains cycle复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(V + E),其中 V 是顶点数,E 是图中的边数。
- 空间复杂度: O(V)。
因为需要一个大小为 V 的额外颜色数组。