热力学——定义、定律、平衡、样本问题
由于温差而从一个物体转移到另一个物体的能量称为热量。做机械功可以产生热量。例如,当我们搓手时,它们会变热。这是因为将一只手移到另一只手上所做的功转化为热量。这个节拍温暖了我们的手。在 19 世纪。朗福德伯爵和詹姆斯·普雷斯科特·焦耳研究了功和beat le之间的关系,发现做相同量的功总是产生相同量的热量。
什么是热力学?
The study of the relationship between mechanical work, heat, and other forms of energy and energy transfer is known as thermodynamics.
因此,热力学是对热量、温度以及机械功转化为热的研究,反之亦然。在热力学中,主要关注系统的宏观量,例如压力、体积、温度。能量熵、焓等对系统内部状态有影响。因此,热力学提供了系统的宏观描述。
热力系统
A collection of an extremely large number of atoms or molecules confined within certain boundaries such that it has certain values of pressure (P), volume (V) and temperature (T) is called a thermodynamic system.
任何与能量或物质交换的热力学系统之外的事物都称为其环境。考虑到系统与周围环境之间的相互作用,如果一个系统可以与周围环境进行能量和物质的交换,那么就可以将其分为三类。
- 开放系统:如果系统可以与周围环境交换能量和物质,则称该系统为开放系统。见图 1(A)。
- 封闭系统:如果系统只能与周围环境交换能量(而非物质),则称该系统为封闭系统。见图 1(B)。
- 孤立系统:如果一个系统既不能与周围环境交换能量也不能交换物质,则称该系统为孤立系统。见图 1(C)。
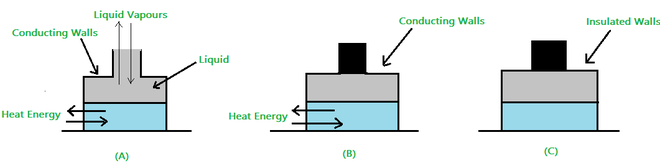
图1
热力学变量
A thermodynamic system can be described by specifying its pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy, enthalpy, and the number of moles. These parameters or variables are called thermodynamic variables.
因此,指定热力学系统状态所需的变量称为热力学变量。熵是系统或过程中存在的能量的度量,但不能用于做功。它也被定义为系统中无序的度量。焓是热力学系统总能量的量度。
热力学变量的类型
- 密集型变量:与系统规模无关的变量称为密集型变量。例如温度、压力和比拍容量。
- 外延变量:取决于系统大小或质量的变量称为外延变量。例如体积、能量、熵、热容量和焓。
热平衡
当两个具有不同温度的物体接触时,能量会从温度较高的物体流向温度较低的物体。能量从一个身体继续流动到另一个身体,以达到相同的温度。当接触的两个物体具有相同的温度并且没有能量为物体提供直到两个物体在它们之间时,那么这些物体处于热平衡状态。因此,如果两个物体或系统处于相同温度,则称它们处于热平衡状态。
- 如果热力学系统的压力、体积、温度、粒子数等变量不随时间变化,则称该热力学系统处于热力学平衡状态。
- 任何孤立系统都处于热力学平衡状态。
热力学过程
Any process in which the thermodynamic variables of a thermodynamic system change is known as the thermodynamic process.
- 准静态过程(准静态意味着几乎是静态的):系统仅无限偏离平衡状态的过程称为准静态过程。系统非常非常小。
- 等温过程:系统的压力和体积在恒定温度下发生变化的过程称为等温过程。在这种情况下,P 和 V 变化,但 T 不变。即 dT(温度变化)= 0。
- 绝热过程:系统的压力、体积和温度发生变化,但与周围环境没有热交换的过程称为绝热过程。在这种情况下,P. V 和 T 发生变化,但 Q = 0。系统应该被压缩或允许突然膨胀,这样系统与周围环境之间就没有时间进行热交换。由于这两个条件在实践中没有完全实现,所以没有一个过程是完全绝热的。
- 等容过程:以恒定体积发生的热力学过程称为等容过程。它也被称为等容过程。在这种情况下,dV = 0。
- 等压过程:在恒定压力下发生的热力学过程称为等压过程。在这种情况下,dP = 0。
- 循环过程:循环过程由一系列使系统返回其初始状态的变化组成。
示例问题
问题 1:定义隔离系统。
解决方案:
A system is said to be isolated if it can neither exchange energy nor matter with its surroundings.
问题 2:热力学变量是什么意思?
解决方案:
A thermodynamic system can be described by specifying its pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy, enthalpy and the number of moles. These parameters or variables are called thermodynamic variables. Thus, the variables which are required to specify the state of thermodynamic system are called thermodynamic variables.
问题3:绝热过程是什么意思?
解决方案:
A process in which pressure, volume and temperature of the system change, but there is no exchange of heat between the and its surroundings is called adiabatic process. In this case, P. V and T change but Q =0.
问题 4:定义广泛和密集的变量。
解决方案:
Intensive variables: The variables which are independent of the size of the system are called intensive variables. e.g. Temperature, pressure and specific beat capacity.
Extensive variables: The variables which depend on the size or mass of the system are called extensive variable. e.g. Volume, energy, entropy, heat capacity and enthalpy.
问题 5:准静态过程是什么意思?
解决方案:
A process in which the system departs only infinitesimally from the equilibrium state is known as quasi-static process In this process, the change in pressure or change in volume or change in temperature of the system is very very small .
问题六:水可以不加热就烧开吗?
解决方案:
Yes, water can be boiled inside a closed insulated vessel by increasing the pressure on the surface of water.