将给定的图划分为二分集
给定一个图G(V, E) ,将它分成两个集合,使得集合中没有两个顶点直接连接。如果不可能,请打印“不可能”。
例子:
Input: V = 7, E = 6,
Edge = {{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {3, 6}, {5, 6}, {6, 7}}
Output:
7 5 1 3
6 2 4

Explanation: node {7, 5, 1, 3} are not connected directly and nodes {6, 2, 4} are not connected directly
.Input: V = 3, E = 3,
Edge = {{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 1}}
Output: Not Possible
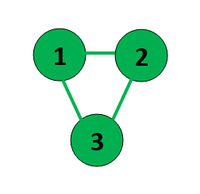
Explanation: Cannot be divided into two parts
方法:这个想法是使用两个集合( U和V )并以 BFS 方式遍历图。遍历每个顶点,将其标记为已访问,检查相邻顶点是否存在于集合中。如果没有,则将其插入与当前设置相反的集合中。如果是,那么如果它们在同一个集合中,则返回false。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 定义一个函数bipartite()并执行以下任务:
- 如果V等于0 ,则返回true。
- 否则,执行 BFS 来检查邻居是否属于相反的集合。
- 将布尔变量res初始化为true。
- 用值false初始化向量visited[V+1] 。
- 使用变量i遍历范围[1, V]并执行以下任务:
- 如果visited[i]为假,则将res 的值设置为res和bipartite()的按位与,函数检查是否可以进行除法。
- 执行上述步骤后,打印答案。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Unordered sets to store ans
unordered_set sets[2];
// Function to divide a graph into two sets,
// returns true if possible otherwise false
bool bipartite(vector >& edges,
int V, int i,
vector& visited)
{
if (V == 0) {
return true;
}
vector pending;
// Inserting source vertex in U(set[0])
sets[0].insert(i);
// Enqueue source vertex
pending.push_back(i);
while (pending.size() > 0) {
// Dequeue current vertex
int current = pending.back();
// Mark the current vertex true
visited[current] = true;
pending.pop_back();
// Finding the set of
// current vertex(parent vertex)
int currentSet
= sets[0].count(current)
> 0
? 0
: 1;
for (int i = 0; i
< edges[current].size();
i++) {
// Picking out neighbour
// of current vertex
int neighbor = edges[current][i];
// If not present
// in any of the set
if (sets[0].count(neighbor) == 0
&& sets[1].count(neighbor) == 0) {
// Inserting in opposite
// of current vertex
sets[1 - currentSet].insert(neighbor);
pending.push_back(neighbor);
}
// Else if present in the same
// current vertex set the partition
// is not possible
else if (sets[currentSet].count(neighbor)
> 0) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
bool possibleBipartition(int V,
vector >& G)
{
// To store graph as adjacency list in edges
vector > edges(V + 1);
for (auto v : G) {
edges[v[0]].push_back(v[1]);
edges[v[1]].push_back(v[0]);
}
vector visited(V + 1, false);
bool res = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
res = res and bipartite(edges, V,
i, visited);
}
}
return res;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int V = 7, E = 6;
vector > G
= { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 },
{ 3, 6 }, { 5, 6 }, { 6, 7 } };
// If partition is possible
if (possibleBipartition(V, G)) {
for (auto elem : sets[0]) {
cout << elem << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
for (auto elem : sets[1]) {
cout << elem << " ";
}
}
// If partition is not possible
else
cout << "Not Possible";
return 0;
} 输出
7 5 1 3
6 2 4 时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)