给定一个由 n 个元素组成的排序数组 arr[],编写一个函数来搜索 arr[] 中的给定元素 x。
一种简单的方法是进行线性搜索。上述算法的时间复杂度为 O(n)。执行相同任务的另一种方法是使用二分搜索。
二分搜索:通过重复将搜索间隔分成两半来搜索已排序的数组。从覆盖整个阵列的区间开始。如果搜索关键字的值小于区间中间的项,则将区间缩小到下半部分。否则,将其缩小到上半部分。反复检查直到找到值或间隔为空。
例子 :
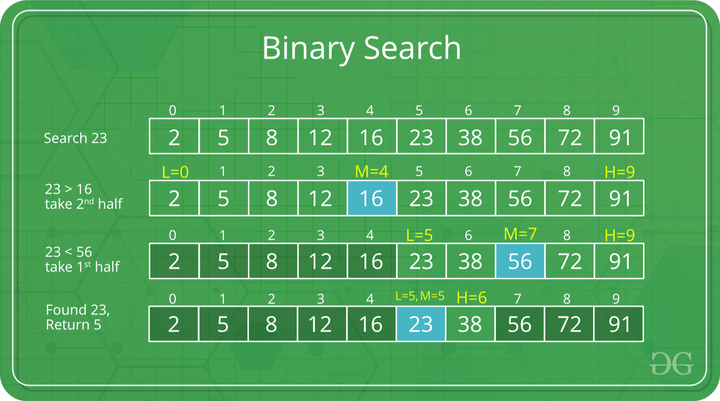
二分查找的思想是利用数组排序的信息,将时间复杂度降低到O(Log n)。
在一次比较之后,我们基本上忽略了一半的元素。
- 将 x 与中间元素进行比较。
- 如果 x 与中间元素匹配,我们返回中间索引。
- Else 如果 x 大于中间元素,则 x 只能位于中间元素之后的右半子阵列中。所以我们在右半场重复。
- 否则(x 较小)在左半部分重复出现。
二分查找的递归实现
C++
// C++ program to implement recursive Binary Search
#include
using namespace std;
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
if (r >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
} C
// C program to implement recursive Binary Search
#include
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
if (r >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? printf("Element is not present in array")
: printf("Element is present at index %d",
result);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of recursive Binary Search
class BinarySearch {
// Returns index of x if it is present in arr[l..
// r], else return -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
if (r >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
// If the element is present at the
// middle itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not present
// in array
return -1;
}
// Driver method to test above
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinarySearch ob = new BinarySearch();
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.length;
int x = 10;
int result = ob.binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println("Element not present");
else
System.out.println("Element found at index " + result);
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */Python3
# Python3 Program for recursive binary search.
# Returns index of x in arr if present, else -1
def binarySearch (arr, l, r, x):
# Check base case
if r >= l:
mid = l + (r - l) // 2
# If element is present at the middle itself
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If element is smaller than mid, then it
# can only be present in left subarray
elif arr[mid] > x:
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid-1, x)
# Else the element can only be present
# in right subarray
else:
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x)
else:
# Element is not present in the array
return -1
# Driver Code
arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ]
x = 10
# Function call
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)
if result != -1:
print ("Element is present at index % d" % result)
else:
print ("Element is not present in array")C#
// C# implementation of recursive Binary Search
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns index of x if it is present in
// arr[l..r], else return -1
static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int l,
int r, int x)
{
if (r >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
// If the element is present at the
// middle itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not present
// in array
return -1;
}
// Driver method to test above
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.Length;
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
if (result == -1)
Console.WriteLine("Element not present");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element found at index "
+ result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.PHP
= $l)
{
$mid = ceil($l + ($r - $l) / 2);
// If the element is present
// at the middle itself
if ($arr[$mid] == $x)
return floor($mid);
// If element is smaller than
// mid, then it can only be
// present in left subarray
if ($arr[$mid] > $x)
return binarySearch($arr, $l,
$mid - 1, $x);
// Else the element can only
// be present in right subarray
return binarySearch($arr, $mid + 1,
$r, $x);
}
// We reach here when element
// is not present in array
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);
$n = count($arr);
$x = 10;
$result = binarySearch($arr, 0, $n - 1, $x);
if(($result == -1))
echo "Element is not present in array";
else
echo "Element is present at index ",
$result;
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>Javascript
C++
#include
using namespace std;
//define array globally
const int N = 1e6 +4;
int a[N];
int n;//array size
//elememt to be searched in array
int k;
bool check(int dig)
{
//element at dig position in array
int ele=a[dig];
//if k is less than
//element at dig position
//then we need to bring our higher ending to dig
//and then continue further
if(k<=ele)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
void binsrch(int lo,int hi)
{
while(lo>n;
for(int i=0; i>a[i];
}
cin>>k;
//it is being given array is sorted
//if not then we have to sort it
//minimum possible point where our k can be is starting index
//so lo=0
//also k cannot be outside of array so end point
//hi=n
binsrch(0,n);
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program to implement recursive Binary Search
#include
using namespace std;
// A iterative binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] if present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// if we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
} C
// C program to implement iterative Binary Search
#include
// A iterative binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] if present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// if we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? printf("Element is not present"
" in array")
: printf("Element is present at "
"index %d",
result);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of iterative Binary Search
class BinarySearch {
// Returns index of x if it is present in arr[],
// else return -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int x)
{
int l = 0, r = arr.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// if we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
// Driver method to test above
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinarySearch ob = new BinarySearch();
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.length;
int x = 10;
int result = ob.binarySearch(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println("Element not present");
else
System.out.println("Element found at "
+ "index " + result);
}
}Python3
# Python3 code to implement iterative Binary
# Search.
# It returns location of x in given array arr
# if present, else returns -1
def binarySearch(arr, l, r, x):
while l <= r:
mid = l + (r - l) // 2;
# Check if x is present at mid
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If x is greater, ignore left half
elif arr[mid] < x:
l = mid + 1
# If x is smaller, ignore right half
else:
r = mid - 1
# If we reach here, then the element
# was not present
return -1
# Driver Code
arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ]
x = 10
# Function call
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)
if result != -1:
print ("Element is present at index % d" % result)
else:
print ("Element is not present in array")C#
// C# implementation of iterative Binary Search
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns index of x if it is present in arr[],
// else return -1
static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int x)
{
int l = 0, r = arr.Length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// if we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
// Driver method to test above
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.Length;
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
Console.WriteLine("Element not present");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element found at "
+ "index " + result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007PHP
Javascript
输出 :
Element is present at index 3您可以在此处创建一个检查函数,以便于实施。
这是带有检查函数的递归实现,我觉得这是一个更简单的实现:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
//define array globally
const int N = 1e6 +4;
int a[N];
int n;//array size
//elememt to be searched in array
int k;
bool check(int dig)
{
//element at dig position in array
int ele=a[dig];
//if k is less than
//element at dig position
//then we need to bring our higher ending to dig
//and then continue further
if(k<=ele)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
void binsrch(int lo,int hi)
{
while(lo>n;
for(int i=0; i>a[i];
}
cin>>k;
//it is being given array is sorted
//if not then we have to sort it
//minimum possible point where our k can be is starting index
//so lo=0
//also k cannot be outside of array so end point
//hi=n
binsrch(0,n);
return 0;
}
二分查找的迭代实现
C++
// C++ program to implement recursive Binary Search
#include
using namespace std;
// A iterative binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] if present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// if we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
C
// C program to implement iterative Binary Search
#include
// A iterative binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] if present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// if we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? printf("Element is not present"
" in array")
: printf("Element is present at "
"index %d",
result);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of iterative Binary Search
class BinarySearch {
// Returns index of x if it is present in arr[],
// else return -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int x)
{
int l = 0, r = arr.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// if we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
// Driver method to test above
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinarySearch ob = new BinarySearch();
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.length;
int x = 10;
int result = ob.binarySearch(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println("Element not present");
else
System.out.println("Element found at "
+ "index " + result);
}
}
蟒蛇3
# Python3 code to implement iterative Binary
# Search.
# It returns location of x in given array arr
# if present, else returns -1
def binarySearch(arr, l, r, x):
while l <= r:
mid = l + (r - l) // 2;
# Check if x is present at mid
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If x is greater, ignore left half
elif arr[mid] < x:
l = mid + 1
# If x is smaller, ignore right half
else:
r = mid - 1
# If we reach here, then the element
# was not present
return -1
# Driver Code
arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ]
x = 10
# Function call
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)
if result != -1:
print ("Element is present at index % d" % result)
else:
print ("Element is not present in array")
C#
// C# implementation of iterative Binary Search
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns index of x if it is present in arr[],
// else return -1
static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int x)
{
int l = 0, r = arr.Length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[m] == x)
return m;
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < x)
l = m + 1;
// If x is smaller, ignore right half
else
r = m - 1;
}
// if we reach here, then element was
// not present
return -1;
}
// Driver method to test above
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int n = arr.Length;
int x = 10;
int result = binarySearch(arr, x);
if (result == -1)
Console.WriteLine("Element not present");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element found at "
+ "index " + result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
PHP
Javascript
输出 :
Element is present at index 3时间复杂度:
二分查找的时间复杂度可以写成
T(n) = T(n/2) + c 上述递归可以使用递归树方法或主方法来解决。它属于主方法的情况 II,并且递归的解决方案是![]() .
.
辅助空间:在迭代实现的情况下为 O(1)。在递归实现的情况下,O(Logn) 递归调用堆栈空间。
算法范式:减少和征服。
笔记:
这里我们使用
int mid = low + (high – low)/2;
也许,你想知道为什么我们要计算中间指数 这样,我们可以简单地将较低和较高的索引相加,然后除以 2。
int mid = (low + high)/2;
但是如果我们计算 像这样的中间索引意味着我们的代码不是 100% 正确的,它包含错误。
也就是说,它对于 int 变量 low 和 high 的较大值失败。具体来说,如果 low 和 high 的总和大于最大正整数值(2 31 – 1 )。
总和溢出为负值,除以 2 时该值保持为负。在Java,它抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException。
int mid = low + (high – low)/2;
所以最好这样使用它。这个错误同样适用于归并排序和其他分治算法。
Geeksforgeeks 课程:
1.语言基础课程【C++/ Java / Python 】
借助 GeeksforGeeks 语言基础课程 – Java基础 | 以最简单的方式从头开始学习任何编程语言并了解其所有基础概念,以建立强大的编程基础。 Python基金会| C++基础
2.极客课堂直播
从任何地理位置获得以面试为中心的数据结构和算法在线直播课程,以学习和掌握 DSA 概念,以提高您的问题解决和编程技能,并破解任何基于产品的公司的面试 – Geeks Classes: Live Session
3.完成面试准备
通过完整的面试准备课程在一个地方满足您的所有面试准备需求,该课程为您提供所有必需的东西,以最实惠的价格为任何基于产品、基于服务或初创公司的公司做准备。
4. DSA 自定进度
开始学习数据结构和算法,为微软、亚马逊、Adobe 等顶级 IT 巨头的面试做准备,通过DSA 自定进度课程,您将学习和掌握从基础到高级的 DSA 以及您自己的学习速度和便利。
5. 公司特定课程——亚马逊、微软、TCS 和 Wipro
通过专门准备这些公司通常在他们的编码面试回合中提出的问题,破解任何基于产品的巨头公司的面试。请参阅 GeeksforGeeks 公司特定课程:Amazon SDE 测试系列等。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。