检查给定图是否为二分图
二分图是一个图,它的顶点可以分为两个独立的集合,U 和 V,使得每条边 (u, v) 要么连接从 U 到 V 的顶点,要么连接从 V 到 U 的顶点。换句话说,对于每个边(u, v),要么u属于U,v属于V,要么u属于V,v属于U。我们也可以说没有边连接同一个集合的顶点。
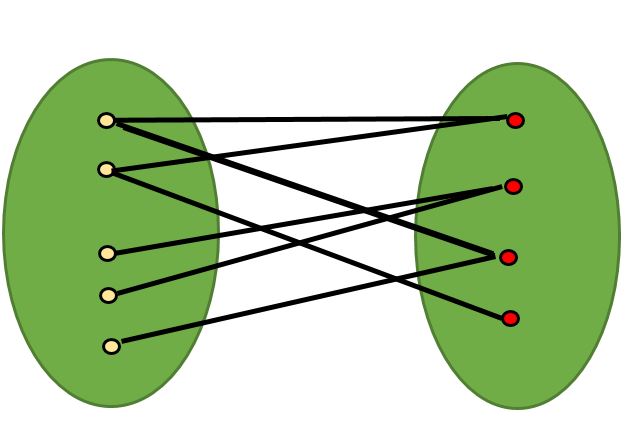
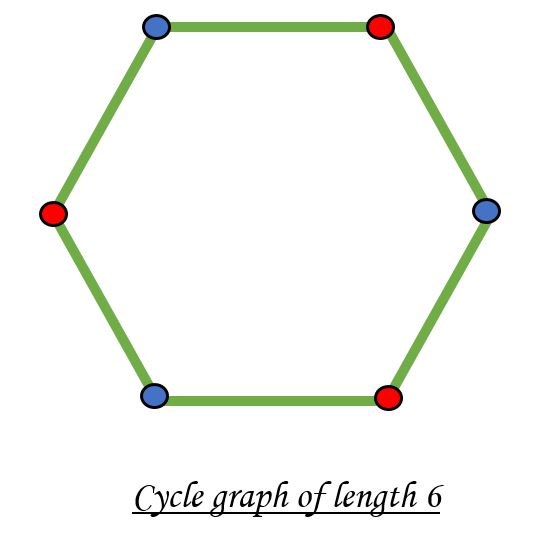
如果可以使用两种颜色对图着色,使得集合中的顶点用相同的颜色着色,则二分图是可能的。请注意,可以使用两种颜色为具有偶数循环的循环图着色。例如,请参见下图。
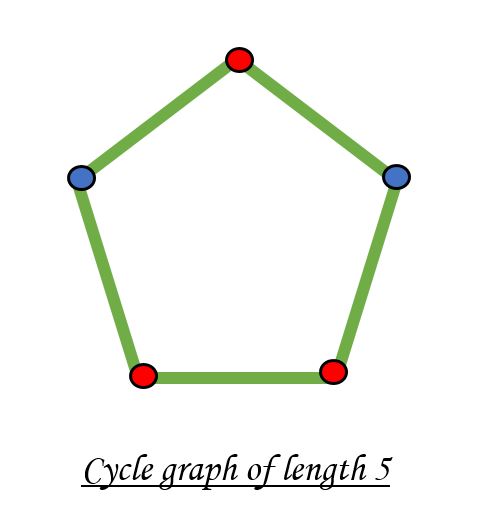
不可能使用两种颜色为具有奇数周期的周期图着色。
检查图是否为二分图的算法:
一种方法是使用回溯算法 m 着色问题来检查图形是否可 2 着色。
以下是使用广度优先搜索 (BFS) 确定给定图是否为二分图的简单算法。
1. 为源顶点指定红色(放入集合 U)。
2. 用蓝色为所有邻居着色(放入集合 V)。
3. 用红色为所有邻居的邻居着色(放入集合 U)。
4. 这样,为所有顶点分配颜色,使其满足 m = 2 的 m 路着色问题的所有约束。
5.在分配颜色时,如果我们找到一个与当前顶点颜色相同的邻居,那么图不能用2个顶点着色(或者图不是二分图)
C++
// C++ program to find out whether a
// given graph is Bipartite or not
#include
#include
#define V 4
using namespace std;
// This function returns true if graph
// G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartite(int G[][V], int src)
{
// Create a color array to store colors
// assigned to all vertices. Vertex
// number is used as index in this array.
// The value '-1' of colorArr[i]
// is used to indicate that no color
// is assigned to vertex 'i'. The value 1
// is used to indicate first color
// is assigned and value 0 indicates
// second color is assigned.
int colorArr[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// Assign first color to source
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex
// numbers and enqueue source vertex
// for BFS traversal
queue q;
q.push(src);
// Run while there are vertices
// in queue (Similar to BFS)
while (!q.empty())
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue ( Refer http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == -1)
{
// Assign alternate color to this adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and destination
// v is colored with same color as u
else if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent
// vertices can be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
int G[][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0}
};
isBipartite(G, 0) ? cout << "Yes" : cout << "No";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class Bipartite
{
final static int V = 4; // No. of Vertices
// This function returns true if
// graph G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
boolean isBipartite(int G[][],int src)
{
// Create a color array to store
// colors assigned to all vertices.
// Vertex number is used as index
// in this array. The value '-1'
// of colorArr[i] is used to indicate
// that no color is assigned
// to vertex 'i'. The value 1 is
// used to indicate first color
// is assigned and value 0 indicates
// second color is assigned.
int colorArr[] = new int[V];
for (int i=0; iq = new LinkedList();
q.add(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue (Similar to BFS)
while (q.size() != 0)
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
int u = q.poll();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v=0; v Python3
# Python program to find out whether a
# given graph is Bipartite or not
class Graph():
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.graph = [[0 for column in range(V)] \
for row in range(V)]
# This function returns true if graph G[V][V]
# is Bipartite, else false
def isBipartite(self, src):
# Create a color array to store colors
# assigned to all vertices. Vertex
# number is used as index in this array.
# The value '-1' of colorArr[i] is used to
# indicate that no color is assigned to
# vertex 'i'. The value 1 is used to indicate
# first color is assigned and value 0
# indicates second color is assigned.
colorArr = [-1] * self.V
# Assign first color to source
colorArr[src] = 1
# Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
# enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
queue = []
queue.append(src)
# Run while there are vertices in queue
# (Similar to BFS)
while queue:
u = queue.pop()
# Return false if there is a self-loop
if self.graph[u][u] == 1:
return False;
for v in range(self.V):
# An edge from u to v exists and destination
# v is not colored
if self.graph[u][v] == 1 and colorArr[v] == -1:
# Assign alternate color to this
# adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u]
queue.append(v)
# An edge from u to v exists and destination
# v is colored with same color as u
elif self.graph[u][v] == 1 and colorArr[v] == colorArr[u]:
return False
# If we reach here, then all adjacent
# vertices can be colored with alternate
# color
return True
# Driver program to test above function
g = Graph(4)
g.graph = [[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0]
]
print ("Yes" if g.isBipartite(0) else "No")
# This code is contributed by Divyanshu MehtaC#
// C# program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
readonly static int V = 4; // No. of Vertices
// This function returns true if
// graph G[V,V] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartite(int [,]G, int src)
{
// Create a color array to store
// colors assigned to all vertices.
// Vertex number is used as index
// in this array. The value '-1'
// of colorArr[i] is used to indicate
// that no color is assigned
// to vertex 'i'. The value 1 is
// used to indicate first color
// is assigned and value 0 indicates
// second color is assigned.
int []colorArr = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// Assign first color to source
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers
// and enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
Listq = new List();
q.Add(src);
// Run while there are vertices
// in queue (Similar to BFS)
while (q.Count != 0)
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
int u = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u, u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
// An edge from u to v exists
// and destination v is not colored
if (G[u, v] == 1 && colorArr[v] == -1)
{
// Assign alternate color
// to this adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.Add(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is colored with
// same color as u
else if (G[u, v] == 1 &&
colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices
// can be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]G = {{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0}};
GFG b = new GFG();
if (b.isBipartite(G, 0))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Javascript
C++
// C++ program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// It works for disconnected graph also.
#include
using namespace std;
const int V = 4;
// This function returns true if
// graph G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartiteUtil(int G[][V], int src, int colorArr[])
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers a
// nd enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
queue q;
q.push(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue (Similar to
// BFS)
while (!q.empty()) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue ( Refer
// http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == -1) {
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and destination
// v is colored with same color as u
else if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices can
// be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[][] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartite(int G[][V])
{
// Create a color array to store colors assigned to all
// vertices. Vertex/ number is used as index in this
// array. The value '-1' of colorArr[i] is used to
// indicate that no color is assigned to vertex 'i'.
// The value 1 is used to indicate first color is
// assigned and value 0 indicates second color is
// assigned.
int colorArr[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr) == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int G[][V] = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
isBipartite(G) ? cout << "Yes" : cout << "No";
return 0;
} Java
// JAVA Code to check whether a given
// graph is Bipartite or not
import java.util.*;
class Bipartite {
public static int V = 4;
// This function returns true if graph
// G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
public static boolean
isBipartiteUtil(int G[][], int src, int colorArr[])
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
// enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
LinkedList q = new LinkedList();
q.add(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue
// (Similar to BFS)
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
// ( Refer http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.getFirst();
q.pop();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v] == 1 && colorArr[v] == -1) {
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is colored with same
// color as u
else if (G[u][v] == 1
&& colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices
// can be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[][] is Bipartite, else false
public static boolean isBipartite(int G[][])
{
// Create a color array to store colors assigned
// to all vertices. Vertex/ number is used as
// index in this array. The value '-1' of
// colorArr[i] is used to indicate that no color
// is assigned to vertex 'i'. The value 1 is used
// to indicate first color is assigned and value
// 0 indicates second color is assigned.
int colorArr[] = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr)
== false)
return false;
return true;
}
/* Driver code*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int G[][] = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
if (isBipartite(G))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal. Python3
# Python3 program to find out whether a
# given graph is Bipartite or not
class Graph():
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.graph = [[0 for column in range(V)]
for row in range(V)]
self.colorArr = [-1 for i in range(self.V)]
# This function returns true if graph G[V][V]
# is Bipartite, else false
def isBipartiteUtil(self, src):
# Create a color array to store colors
# assigned to all vertices. Vertex
# number is used as index in this array.
# The value '-1' of self.colorArr[i] is used
# to indicate that no color is assigned to
# vertex 'i'. The value 1 is used to indicate
# first color is assigned and value 0
# indicates second color is assigned.
# Assign first color to source
# Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
# enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
queue = []
queue.append(src)
# Run while there are vertices in queue
# (Similar to BFS)
while queue:
u = queue.pop()
# Return false if there is a self-loop
if self.graph[u][u] == 1:
return False
for v in range(self.V):
# An edge from u to v exists and
# destination v is not colored
if (self.graph[u][v] == 1 and
self.colorArr[v] == -1):
# Assign alternate color to
# this adjacent v of u
self.colorArr[v] = 1 - self.colorArr[u]
queue.append(v)
# An edge from u to v exists and destination
# v is colored with same color as u
elif (self.graph[u][v] == 1 and
self.colorArr[v] == self.colorArr[u]):
return False
# If we reach here, then all adjacent
# vertices can be colored with alternate
# color
return True
def isBipartite(self):
self.colorArr = [-1 for i in range(self.V)]
for i in range(self.V):
if self.colorArr[i] == -1:
if not self.isBipartiteUtil(i):
return False
return True
# Driver Code
g = Graph(4)
g.graph = [[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0]]
print ("Yes" if g.isBipartite() else "No")
# This code is contributed by Anshuman SharmaC#
// C# Code to check whether a given
// graph is Bipartite or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
public static int V = 4;
// This function returns true if graph
// G[V,V] is Bipartite, else false
public static bool isBipartiteUtil(int[, ] G, int src,
int[] colorArr)
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
// enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
Queue q = new Queue();
q.Enqueue(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue
// (Similar to BFS)
while (q.Count != 0) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
// ( Refer http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u, u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u, v] == 1 && colorArr[v] == -1) {
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.Enqueue(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is colored with same
// color as u
else if (G[u, v] == 1
&& colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all
// adjacent vertices can be colored
// with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[,] is Bipartite,
// else false
public static bool isBipartite(int[, ] G)
{
// Create a color array to store
// colors assigned to all vertices.
// Vertex/ number is used as
// index in this array. The value '-1'
// of colorArr[i] is used to indicate
// that no color is assigned to vertex 'i'.
// The value 1 is used to indicate
// first color is assigned and value
// 0 indicates second color is assigned.
int[] colorArr = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr)
== false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[, ] G = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
if (isBipartite(G))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Javascript
C++
#include
using namespace std;
bool isBipartite(int V, vector adj[])
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
vector col(V, -1);
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
queue > q;
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
//if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
//colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.push({ i, 0 });
col[i] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
pair p = q.front();
q.pop();
//current vertex
int v = p.first;
//colour of current vertex
int c = p.second;
//traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for (int j : adj[v]) {
//if already coloured with parent vertex color
//then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return 0;
//if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1) {
//colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c) ? 0 : 1;
q.push({ j, col[j] });
}
}
}
}
}
//if all vertexes are coloured such that
//no two connected vertex have same colours
return 1;
}
// { Driver Code Starts.
int main()
{
int V, E;
V = 4 , E = 8;
//adjacency list for storing graph
vector adj[V];
adj[0] = {1,3};
adj[1] = {0,2};
adj[2] = {1,3};
adj[3] = {0,2};
bool ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
//returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
cout << "Yes\n";
//returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
// code Contributed By Devendra Kolhe Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG{
static class Pair{
int first, second;
Pair(int f, int s){
first = f;
second = s;
}
}
static boolean isBipartite(int V, ArrayList> adj)
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
int col[] = new int[V];
Arrays.fill(col, -1);
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
Queue q = new LinkedList();
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
// colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.add(new Pair(i, 0));
col[i] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Pair p = q.peek();
q.poll();
//current vertex
int v = p.first;
// colour of current vertex
int c = p.second;
// traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for (int j : adj.get(v))
{
// if already coloured with parent vertex color
// then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return false;
// if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1)
{
// colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c==1) ? 0 : 1;
q.add(new Pair(j, col[j]));
}
}
}
}
}
// if all vertexes are coloured such that
// no two connected vertex have same colours
return true;
}
// Driver Code Starts.
public static void main(String args[])
{
int V, E;
V = 4 ;
E = 8;
// adjacency list for storing graph
ArrayList> adj = new ArrayList>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++){
adj.add(new ArrayList());
}
adj.get(0).add(1);
adj.get(0).add(3);
adj.get(1).add(0);
adj.get(1).add(2);
adj.get(2).add(1);
adj.get(2).add(3);
adj.get(3).add(0);
adj.get(3).add(2);
boolean ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
// returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
System.out.println("Yes");
// returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by adityapande88. Python3
def isBipartite(V, adj):
# vector to store colour of vertex
# assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
# colours are either 0 or 1
# for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
col = [-1]*(V)
# queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
q = []
#loop incase graph is not connected
for i in range(V):
# if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1):
# colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.append([i, 0])
col[i] = 0
while len(q) != 0:
p = q[0]
q.pop(0)
# current vertex
v = p[0]
# colour of current vertex
c = p[1]
# traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for j in adj[v]:
# if already coloured with parent vertex color
# then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c):
return False
# if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1):
# colouring with opposite color to that of parent
if c == 1:
col[j] = 0
else:
col[j] = 1
q.append([j, col[j]])
# if all vertexes are coloured such that
# no two connected vertex have same colours
return True
V, E = 4, 8
# adjacency list for storing graph
adj = []
adj.append([1,3])
adj.append([0,2])
adj.append([1,3])
adj.append([0,2])
ans = isBipartite(V, adj)
# returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans):
print("Yes")
# returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by divyesh072019.C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static bool isBipartite(int V, List> adj)
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
int[] col = new int[V];
Array.Fill(col, -1);
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
List> q = new List>();
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
// colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.Add(new Tuple(i, 0));
col[i] = 0;
while (q.Count > 0) {
Tuple p = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
//current vertex
int v = p.Item1;
// colour of current vertex
int c = p.Item2;
// traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
foreach(int j in adj[v])
{
// if already coloured with parent vertex color
// then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return false;
// if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1)
{
// colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c==1) ? 0 : 1;
q.Add(new Tuple(j, col[j]));
}
}
}
}
}
// if all vertexes are coloured such that
// no two connected vertex have same colours
return true;
}
static void Main() {
int V;
V = 4 ;
// adjacency list for storing graph
List> adj = new List>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++){
adj.Add(new List());
}
adj[0].Add(1);
adj[0].Add(3);
adj[1].Add(0);
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(0);
adj[3].Add(2);
bool ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
// returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
// returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by decode2207. Javascript
C++
// C++ program to find out whether a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
#include
using namespace std;
#define V 4
bool colorGraph(int G[][V],int color[],int pos, int c){
if(color[pos] != -1 && color[pos] !=c)
return false;
// color this pos as c and all its neighbours and 1-c
color[pos] = c;
bool ans = true;
for(int i=0;i Java
// Java program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
class GFG
{
static final int V = 4;
static boolean colorGraph(int G[][],
int color[],
int pos, int c)
{
if (color[pos] != -1 &&
color[pos] != c)
return false;
// color this pos as c and
// all its neighbours as 1-c
color[pos] = c;
boolean ans = true;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (G[pos][i] == 1)
{
if (color[i] == -1)
ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1 - c);
if (color[i] != -1 && color[i] != 1 - c)
return false;
}
if (!ans)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static boolean isBipartite(int G[][])
{
int[] color = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
color[i] = -1;
// start is vertex 0;
int pos = 0;
// two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int G[][] = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
if (isBipartite(G))
System.out.print("Yes");
else
System.out.print("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# Python3 program to find out whether a given
# graph is Bipartite or not using recursion.
V = 4
def colorGraph(G, color, pos, c):
if color[pos] != -1 and color[pos] != c:
return False
# color this pos as c and all its neighbours and 1-c
color[pos] = c
ans = True
for i in range(0, V):
if G[pos][i]:
if color[i] == -1:
ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1-c)
if color[i] !=-1 and color[i] != 1-c:
return False
if not ans:
return False
return True
def isBipartite(G):
color = [-1] * V
#start is vertex 0
pos = 0
# two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
G = [[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0]]
if isBipartite(G): print("Yes")
else: print("No")
# This code is contributed by Rituraj JainC#
// C# program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
using System;
class GFG
{
static readonly int V = 4;
static bool colorGraph(int [,]G,
int []color,
int pos, int c)
{
if (color[pos] != -1 &&
color[pos] != c)
return false;
// color this pos as c and
// all its neighbours as 1-c
color[pos] = c;
bool ans = true;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (G[pos, i] == 1)
{
if (color[i] == -1)
ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1 - c);
if (color[i] != -1 && color[i] != 1 - c)
return false;
}
if (!ans)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static bool isBipartite(int [,]G)
{
int[] color = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
color[i] = -1;
// start is vertex 0;
int pos = 0;
// two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]G = {{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 }};
if (isBipartite(G))
Console.Write("Yes");
else
Console.Write("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
输出:
Yes上述算法仅在图形连接时才有效。在上面的代码中,我们总是从源 0 开始,并假设从它访问顶点。一个重要的观察是没有边的图也是二分图。请注意,二分条件表示所有边都应该从一组到另一组。
我们可以扩展上面的代码来处理图未连接的情况。对于所有尚未访问的顶点,该想法在上述方法中重复调用。
C++
// C++ program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// It works for disconnected graph also.
#include
using namespace std;
const int V = 4;
// This function returns true if
// graph G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartiteUtil(int G[][V], int src, int colorArr[])
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers a
// nd enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
queue q;
q.push(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue (Similar to
// BFS)
while (!q.empty()) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue ( Refer
// http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == -1) {
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and destination
// v is colored with same color as u
else if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices can
// be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[][] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartite(int G[][V])
{
// Create a color array to store colors assigned to all
// vertices. Vertex/ number is used as index in this
// array. The value '-1' of colorArr[i] is used to
// indicate that no color is assigned to vertex 'i'.
// The value 1 is used to indicate first color is
// assigned and value 0 indicates second color is
// assigned.
int colorArr[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr) == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int G[][V] = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
isBipartite(G) ? cout << "Yes" : cout << "No";
return 0;
}
Java
// JAVA Code to check whether a given
// graph is Bipartite or not
import java.util.*;
class Bipartite {
public static int V = 4;
// This function returns true if graph
// G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
public static boolean
isBipartiteUtil(int G[][], int src, int colorArr[])
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
// enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
LinkedList q = new LinkedList();
q.add(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue
// (Similar to BFS)
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
// ( Refer http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.getFirst();
q.pop();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v] == 1 && colorArr[v] == -1) {
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is colored with same
// color as u
else if (G[u][v] == 1
&& colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices
// can be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[][] is Bipartite, else false
public static boolean isBipartite(int G[][])
{
// Create a color array to store colors assigned
// to all vertices. Vertex/ number is used as
// index in this array. The value '-1' of
// colorArr[i] is used to indicate that no color
// is assigned to vertex 'i'. The value 1 is used
// to indicate first color is assigned and value
// 0 indicates second color is assigned.
int colorArr[] = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr)
== false)
return false;
return true;
}
/* Driver code*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int G[][] = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
if (isBipartite(G))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal.
Python3
# Python3 program to find out whether a
# given graph is Bipartite or not
class Graph():
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.graph = [[0 for column in range(V)]
for row in range(V)]
self.colorArr = [-1 for i in range(self.V)]
# This function returns true if graph G[V][V]
# is Bipartite, else false
def isBipartiteUtil(self, src):
# Create a color array to store colors
# assigned to all vertices. Vertex
# number is used as index in this array.
# The value '-1' of self.colorArr[i] is used
# to indicate that no color is assigned to
# vertex 'i'. The value 1 is used to indicate
# first color is assigned and value 0
# indicates second color is assigned.
# Assign first color to source
# Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
# enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
queue = []
queue.append(src)
# Run while there are vertices in queue
# (Similar to BFS)
while queue:
u = queue.pop()
# Return false if there is a self-loop
if self.graph[u][u] == 1:
return False
for v in range(self.V):
# An edge from u to v exists and
# destination v is not colored
if (self.graph[u][v] == 1 and
self.colorArr[v] == -1):
# Assign alternate color to
# this adjacent v of u
self.colorArr[v] = 1 - self.colorArr[u]
queue.append(v)
# An edge from u to v exists and destination
# v is colored with same color as u
elif (self.graph[u][v] == 1 and
self.colorArr[v] == self.colorArr[u]):
return False
# If we reach here, then all adjacent
# vertices can be colored with alternate
# color
return True
def isBipartite(self):
self.colorArr = [-1 for i in range(self.V)]
for i in range(self.V):
if self.colorArr[i] == -1:
if not self.isBipartiteUtil(i):
return False
return True
# Driver Code
g = Graph(4)
g.graph = [[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0]]
print ("Yes" if g.isBipartite() else "No")
# This code is contributed by Anshuman Sharma
C#
// C# Code to check whether a given
// graph is Bipartite or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
public static int V = 4;
// This function returns true if graph
// G[V,V] is Bipartite, else false
public static bool isBipartiteUtil(int[, ] G, int src,
int[] colorArr)
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
// enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
Queue q = new Queue();
q.Enqueue(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue
// (Similar to BFS)
while (q.Count != 0) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
// ( Refer http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u, u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u, v] == 1 && colorArr[v] == -1) {
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.Enqueue(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is colored with same
// color as u
else if (G[u, v] == 1
&& colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all
// adjacent vertices can be colored
// with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[,] is Bipartite,
// else false
public static bool isBipartite(int[, ] G)
{
// Create a color array to store
// colors assigned to all vertices.
// Vertex/ number is used as
// index in this array. The value '-1'
// of colorArr[i] is used to indicate
// that no color is assigned to vertex 'i'.
// The value 1 is used to indicate
// first color is assigned and value
// 0 indicates second color is assigned.
int[] colorArr = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr)
== false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[, ] G = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
if (isBipartite(G))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
输出:
Yes上述方法的时间复杂度与广度优先搜索相同。在上面的实现中是 O(V^2),其中 V 是顶点数。如果使用邻接表表示图,则复杂度变为 O(V+E)。
如果使用邻接列表表示图形,则时间复杂度将为 O(V+E)。
适用于连接图和断开图。
C++
#include
using namespace std;
bool isBipartite(int V, vector adj[])
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
vector col(V, -1);
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
queue > q;
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
//if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
//colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.push({ i, 0 });
col[i] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
pair p = q.front();
q.pop();
//current vertex
int v = p.first;
//colour of current vertex
int c = p.second;
//traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for (int j : adj[v]) {
//if already coloured with parent vertex color
//then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return 0;
//if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1) {
//colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c) ? 0 : 1;
q.push({ j, col[j] });
}
}
}
}
}
//if all vertexes are coloured such that
//no two connected vertex have same colours
return 1;
}
// { Driver Code Starts.
int main()
{
int V, E;
V = 4 , E = 8;
//adjacency list for storing graph
vector adj[V];
adj[0] = {1,3};
adj[1] = {0,2};
adj[2] = {1,3};
adj[3] = {0,2};
bool ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
//returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
cout << "Yes\n";
//returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
// code Contributed By Devendra Kolhe
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG{
static class Pair{
int first, second;
Pair(int f, int s){
first = f;
second = s;
}
}
static boolean isBipartite(int V, ArrayList> adj)
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
int col[] = new int[V];
Arrays.fill(col, -1);
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
Queue q = new LinkedList();
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
// colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.add(new Pair(i, 0));
col[i] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Pair p = q.peek();
q.poll();
//current vertex
int v = p.first;
// colour of current vertex
int c = p.second;
// traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for (int j : adj.get(v))
{
// if already coloured with parent vertex color
// then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return false;
// if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1)
{
// colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c==1) ? 0 : 1;
q.add(new Pair(j, col[j]));
}
}
}
}
}
// if all vertexes are coloured such that
// no two connected vertex have same colours
return true;
}
// Driver Code Starts.
public static void main(String args[])
{
int V, E;
V = 4 ;
E = 8;
// adjacency list for storing graph
ArrayList> adj = new ArrayList>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++){
adj.add(new ArrayList());
}
adj.get(0).add(1);
adj.get(0).add(3);
adj.get(1).add(0);
adj.get(1).add(2);
adj.get(2).add(1);
adj.get(2).add(3);
adj.get(3).add(0);
adj.get(3).add(2);
boolean ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
// returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
System.out.println("Yes");
// returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by adityapande88.
Python3
def isBipartite(V, adj):
# vector to store colour of vertex
# assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
# colours are either 0 or 1
# for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
col = [-1]*(V)
# queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
q = []
#loop incase graph is not connected
for i in range(V):
# if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1):
# colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.append([i, 0])
col[i] = 0
while len(q) != 0:
p = q[0]
q.pop(0)
# current vertex
v = p[0]
# colour of current vertex
c = p[1]
# traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for j in adj[v]:
# if already coloured with parent vertex color
# then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c):
return False
# if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1):
# colouring with opposite color to that of parent
if c == 1:
col[j] = 0
else:
col[j] = 1
q.append([j, col[j]])
# if all vertexes are coloured such that
# no two connected vertex have same colours
return True
V, E = 4, 8
# adjacency list for storing graph
adj = []
adj.append([1,3])
adj.append([0,2])
adj.append([1,3])
adj.append([0,2])
ans = isBipartite(V, adj)
# returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans):
print("Yes")
# returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static bool isBipartite(int V, List> adj)
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
int[] col = new int[V];
Array.Fill(col, -1);
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
List> q = new List>();
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
// colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.Add(new Tuple(i, 0));
col[i] = 0;
while (q.Count > 0) {
Tuple p = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
//current vertex
int v = p.Item1;
// colour of current vertex
int c = p.Item2;
// traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
foreach(int j in adj[v])
{
// if already coloured with parent vertex color
// then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return false;
// if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1)
{
// colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c==1) ? 0 : 1;
q.Add(new Tuple(j, col[j]));
}
}
}
}
}
// if all vertexes are coloured such that
// no two connected vertex have same colours
return true;
}
static void Main() {
int V;
V = 4 ;
// adjacency list for storing graph
List> adj = new List>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++){
adj.Add(new List());
}
adj[0].Add(1);
adj[0].Add(3);
adj[1].Add(0);
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(0);
adj[3].Add(2);
bool ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
// returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
// returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by decode2207.
Javascript
Yes锻炼:
1. DFS算法可以用来检查图的二分性吗?如果是,如何?
解决方案 :
C++
// C++ program to find out whether a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
#include
using namespace std;
#define V 4
bool colorGraph(int G[][V],int color[],int pos, int c){
if(color[pos] != -1 && color[pos] !=c)
return false;
// color this pos as c and all its neighbours and 1-c
color[pos] = c;
bool ans = true;
for(int i=0;i Java
// Java program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
class GFG
{
static final int V = 4;
static boolean colorGraph(int G[][],
int color[],
int pos, int c)
{
if (color[pos] != -1 &&
color[pos] != c)
return false;
// color this pos as c and
// all its neighbours as 1-c
color[pos] = c;
boolean ans = true;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (G[pos][i] == 1)
{
if (color[i] == -1)
ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1 - c);
if (color[i] != -1 && color[i] != 1 - c)
return false;
}
if (!ans)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static boolean isBipartite(int G[][])
{
int[] color = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
color[i] = -1;
// start is vertex 0;
int pos = 0;
// two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int G[][] = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
if (isBipartite(G))
System.out.print("Yes");
else
System.out.print("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 program to find out whether a given
# graph is Bipartite or not using recursion.
V = 4
def colorGraph(G, color, pos, c):
if color[pos] != -1 and color[pos] != c:
return False
# color this pos as c and all its neighbours and 1-c
color[pos] = c
ans = True
for i in range(0, V):
if G[pos][i]:
if color[i] == -1:
ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1-c)
if color[i] !=-1 and color[i] != 1-c:
return False
if not ans:
return False
return True
def isBipartite(G):
color = [-1] * V
#start is vertex 0
pos = 0
# two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
G = [[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0]]
if isBipartite(G): print("Yes")
else: print("No")
# This code is contributed by Rituraj Jain
C#
// C# program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
using System;
class GFG
{
static readonly int V = 4;
static bool colorGraph(int [,]G,
int []color,
int pos, int c)
{
if (color[pos] != -1 &&
color[pos] != c)
return false;
// color this pos as c and
// all its neighbours as 1-c
color[pos] = c;
bool ans = true;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (G[pos, i] == 1)
{
if (color[i] == -1)
ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1 - c);
if (color[i] != -1 && color[i] != 1 - c)
return false;
}
if (!ans)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static bool isBipartite(int [,]G)
{
int[] color = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
color[i] = -1;
// start is vertex 0;
int pos = 0;
// two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]G = {{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 }};
if (isBipartite(G))
Console.Write("Yes");
else
Console.Write("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
Yes