烯烃 – 定义、命名、制备、性质
在有机化学中,碳氢化合物是完全由氢和碳组成的有机分子。烃类是第 14 族氢化物的一个例子。碳氢化合物是无色疏水的,有轻微的气味。由于它们的化学结构不同,很难再一概而论。大部分人为碳氢化合物排放来自化石燃料的燃烧,包括燃料生产和燃烧。乙烯、异戊二烯和单萜是在植物排放物中发现的全天然碳氢化合物。
什么是烯烃?
Unsaturated hydrocarbons with a double bond between the carbon atoms are known as alkenes. Between carbon-carbon atoms, there is at least one double bond. Alkenes have the generic formula CnH2n. Alkenes are frequently used interchangeably with the term olefin.
The word olefin comes from the Greek phrase olefin gas, which meaning oil-forming gas. Alkenes are extremely reactive chemically due to the presence of double bonds.
我们都熟悉烷烃等饱和碳氢化合物,但原油中还有另一类更具反应性的不饱和碳氢化合物。让我们了解有关烯烃的所有知识,烯烃是一种不饱和碳氢化合物,在碳-碳原子之间至少有一个双键。
烯烃的命名
烯烃具有通式 CnH2n,其中 n-2、3、4、5,依此类推。根据 IUPAC 系统,烯烃的名称中包含后缀-烯,前缀由碳原子数决定。以下是烯烃名称的一些示例: Number of carbon atoms Formula IUPAC name 2 C2H4 Ethene 3 C3H6 Propene 4 C4H8 Butene 5 C5H10 Pentene 6 C6H12 Hexene 7 C7H14 Heptene 8 C8H16 Octene 9 C9H18 Nonene 10 C10H20 Decene
烯烃的异构现象
烯烃中都存在立体异构和结构异构。
烯烃中均存在立体异构和结构异构:乙烯和丙烯中仅存在一种结构,而碳原子数为四个或更多的烯烃则同时表现出链和位置异构。
- 双键的位置在链异构中没有改变。例如,丁烯中的链异构现象如下:

链异构
- 在位置异构中,异构体的双键位置不同。例如丁烯的两种异构体如下:

位置异构
立体异构或几何异构:几何异构体是具有相同结构式但在双键周围的原子或原子团的相对空间排列不同的异构体。几何异构是这种现象的名称。顺式异构体是一种异构体,其中相似的原子组存在于双键的同一侧。另一方面,反式异构是指在另一侧具有可比键的异构体。

立体异构的例子
烯烃制备的一般方法
使用下列方法制备烯烃:
- 通过炔烃的部分还原 - 烯烃是通过在特定催化剂(托盘化木炭)存在下氢化炔烃制成的,该催化剂使用喹啉或硫化合物轻度失活。
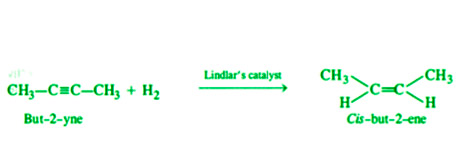
炔烃的部分还原制备烯烃
- 从卤代烷-卤代烷在与强碱(例如乙醇钠或氢氧化钾的浓醇溶液)加热时脱氢成烯烃。

由烷基卤化物制备烯烃
- 来自连卤化物-连卤化物是烷烃二卤素衍生物,其中两个卤素原子存在于相邻的碳原子上。通过在甲醇或乙醇中用锌粉加热适当的二卤化物,可以制备烯烃。

邻卤化物制备烯烃
- 来自醇 -当与无机酸(如强硫酸)一起加热时,醇会失去一个水分子,形成烯烃。

由醇制备烯烃
烯烃的物理性质
- 物理状态——最初的三个人是干气;以下十四个(C5-C18)个体是流体,而较高的个体是固体。
- 遮光和气味——除了乙烯有一种美妙的气味,任何剩余的烯烃都是无味无味的。
- 溶解性——烯烃不溶于水,但真正溶于苯、汽油、乙醚等非极性溶剂中。
- 沸点-沸腾的边缘随着原子质量的增加而增加。直链烯烃比异构的长链烯烃具有更高的限制。
- 就密度而言,烯烃都比水轻。烯烃密度随着分子量的增加而增加,直到达到0.8gcm -3的极限值。

烯烃的化学反应
- 氢气的添加——在室温下,烯烃在催化剂镍、钯或铂的存在下快速添加氢气以生成烷烃。举个例子,

- 卤素的加成-当烯烃在惰性溶液(例如 CCl 4 )中与卤素反应时,会形成卤素衍生物。
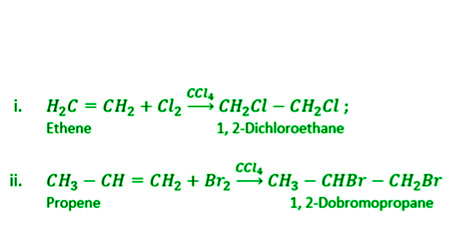
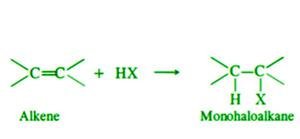
- 卤化卤化物的添加——烯烃与卤化卤化物(HCl、HBr、HI)反应生成卤代烷,它们是单卤代烷烃。
烯烃的用途
- 来自烯烃的低等个体被用作能量剂和照明剂。
- 从许多有价值的混合物(如聚乙烯、PVC、Teflon、orlon 等)聚合而成的烯烃和底质烯烃
- 烯烃被用于伪造熟化的有机产品。
- 乙烯用于组装乙基液和乙二醇。
- 烯烃用于制造敌对重击发动机。
- 乙烯用于制造氧气-乙烯火焰,用于切割和焊接。
示例问题
问题一:烯烃的函数是什么?
回答:
Alkenes are used to artificially ripen fruits, make anti-knock for vehicle engines, create ethyl alcohol and ethylene glycol, and a variety of other useful chemicals such as polythene, PVC, Teflon, and orlon.
问题2:化学中的烯烃是什么?
回答:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons with a double bond between the carbon atoms are known as alkenes. Between carbon-carbon atoms, there is at least one double bond. Alkenes have the generic formula CnH2n. Alkenes are frequently used interchangeably with the term olefin. The word olefin comes from the Greek phrase olefin gas, which meaning “oil-forming gas.” Alkenes are extremely reactive chemically due to the presence of double bonds.
问题3:烯烃有什么特点?
回答:
Except for ethene, which has a pleasant odour, all other alkenes are colourless and odourless. Alkenes are insoluble in water but relatively soluble in non-polar solvents such as benzene, petroleum, ether, and others. The boiling point of straight-chain alkenes is greater than that of isomeric branched-chain alkenes.
问题4:我们如何识别烯烃?
回答:
Bromine water can be used to evaluate alkenes. The solution is decolonized by alkenes
问题5:烯烃的两种用途是什么?
回答:
- Alkenes and substituted alkenes are used in the polymerization of several important chemicals such as polythene, PVC, Teflon, and orlon.
- Alkenes are used to make fruits mature artificially.
问题6:什么是几何异构体?
回答:
Geometrical isomers are isomers with the same structural formula that differ in the relative spatial arrangement of atoms or groups of atoms around the double bond. Geometrical isomerism is the name given to this occurrence. Cis-isomer is an isomer in which a similar group of atoms is present on the same side of the double bond. Trans-isomerism, on the other hand, refers to an isomer with comparable bonds on the opposite side.