过氧化氢 – 用途、性质、制备、示例
化学元素氢的符号为 H,原子序数为 1。最轻的元素是氢。在正常情况下,氢气是由分子式为H 2的双原子分子组成的气体。它无味、无色、无毒且极易燃。氢是宇宙中最丰富的化学元素,约占所有普通物质的 75%。例如,太阳主要由处于等离子体状态的氢组成。地球上的大部分氢以分子形式存在,如水和有机物质。最常见的氢同位素(符号 1H)的每个原子都有一个质子、一个电子和没有中子。
过氧化氢的发现
过氧化物家族中最简单的成员是过氧化氢,它最初是在 1818 年由法国化学家 JL Thenard 作为一种化学物质发现的。 H 2 O 2是它的分子式。过氧化氢在环境中的含量非常低。地球周围大气中的光化学反应产生气态过氧化氢。它用作消毒剂和漂白剂。它是酸性的,在 298 华氏度时的 pH 值为 6 到 7。
过氧化氢的结构
- 过氧化物离子 (O 2– 2 ) 存在于化学分子过氧化物中。 (O-O) 2-是过氧化物离子,它由两个氧原子之间的单键组成。它是一种强氧化剂。
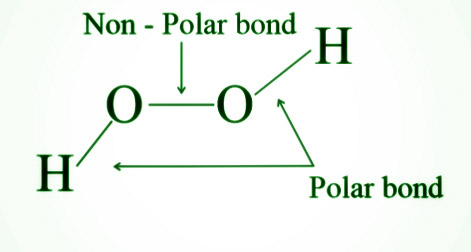
- 过氧化氢是一种非平面分子,由两个氧原子通过称为过氧化物键的单一共价键连接而成。
- 它像一本书一样布置。每个氧原子也通过单个链接连接到一个氢原子。因为孤对电子在氧原子上相互排斥,所以这两个键不在同一平面上。当过氧化氢处于气态时,两个平面之间的二面角(平面间)为 111.5 o ,但当它是结晶时,它是 90.2 o 。分子内氢键会导致这种情况发生。
气相和结晶相中的氢键参数为:

过氧化氢的用途
过氧化氢是一种可以以多种方式使用的流体。它适用于所有介质,包括水、空气、废水和土壤。为了改进和加速流程,它有时与其他代理结合使用。以下是它的一些应用:
- 纸浆和纸张漂白消耗了世界过氧化氢产量的大约一半。
- 人发用稀释过的过氧化氢和氨水漂白。
- 用过氧化氢去除新的血迹。
- H 2 O 2溶液用作鱼雷和潜艇的推进剂,以及火箭燃料的氧化剂。
- 在水产养殖中,过氧化氢用于降低由不同微生物引起的死亡率。
- 它可用于对化妆刷进行消毒和对牙刷进行消毒。
- 过氧化氢是一种温和的防腐剂,可用于小伤口、划痕和烧伤,以防止感染。
- 它也可以用作漱口水,以清除粘液并缓解轻微的口腔不适。
- 有助于治疗植物中的真菌感染和清理被藻类侵染的池塘。
- 它在纺织部门用作抗氯剂,以消除漂白后多余的氯。
- 广泛用于生产高硼酸钠、过碳酸钠等无机化学品,是高品质洗涤剂的重要成分。
- 它用于恢复由于空气中的H 2 S对含铅涂料的影响而变暗的含铅涂料的颜色。
过氧化氢的性质
以下是过氧化氢的物理和化学性质:
过氧化氢的物理性质
- 在无水状态下,过氧化氢呈淡蓝色。由于H-键合,它是一种无味的浓稠糖浆状液体。
- 它有一种苦味,会导致皮肤起水泡。
- 溶于水、醇和醚。
- 过氧化氢比水更粘稠(1.44g/cm 3 )。这是因为H 2 O 2分子比H 2 O 分子具有更强的H-键。
- 它的沸点为150摄氏度,冰点为–0.89摄氏度。过氧化氢的沸点甚至更高,因为分子间的氢键比水强。
- 过氧化氢的偶极矩 (2.1D) 比水 (1.84D) 稍高。
- 过氧化氢具有极性键和非极性键,并且是抗磁性的。
过氧化氢的化学性质
由于其分子结构,H 2 O 2是一种独一无二的材料。它由氧化态为-1的氧原子组成,与许多其他化合物中的氧化态0或-2相反。这表明,根据其溶液的 pH 值,这种化学物质既可以作为氧化剂,也可以作为还原剂。
- 分解
- 曝光分解:曝光也会分解 H 2 O 2 。因此,它被保存在带有稳定剂(如尿素)的蜡衬玻璃或塑料容器中。
- 自动氧化和自动还原:最纯净形式的过氧化氢是一种高度不稳定的液体。当长时间放置或加热时,它会分解成水和氧气。
铂、金、金属氧化物 (MnO 2 ) 等金属或 Fe 2+等特定金属离子的存在加速了击穿过程。即使是粗糙的表面也有助于其分解。
- 酸性性质
- H 2 O 2是一种弱酸,因为它会使蓝色石蕊呈红色。石蕊不受其水溶液的影响。 H 2 O 2略强于 H 2 O,因为它的解离常数(1.55×10 –12 at 293K)略高于 H 2 O(1.0×10 –14 )。
- 过氧化氢与氢氧化物和碳酸盐的中和反应证明了它的酸性。例如,Ba(OH) 2 +H 2 O 2 →BaO 2 +2H 2 O
- 由于 H 2 O 2包含两个可电离的 H 原子,它会生成两种盐:氢过氧化物(酸性盐)和过氧化物(过氧化物)(普通盐)。
- 减少财产-
当存在强氧化剂时,过氧化氢在酸性和碱性介质中都充当还原剂。在所有这些过程中,H 2 O 2和强氧化剂产生的新生氧 [O] 的结合产生了分子氧。
H 2 O 2 + [O](来自氧化剂)→ H 2 O + O 2
- In acidic medium: Hydrogen peroxide loses electrons and is oxidized to O2 in an acidic environment.
H2O2(O.S=–1)→2H++O2(O.S=0)+2e–[Oxidation]
For example,
1) H2O2 turns a pink acidified potassium permanganate solution into a colorless solution.
2KMnO4+3H2SO4+5H2O2→K2SO4+2MnSO4+8H2O+5O2
2) In the presence of dilute sulphuric acid, it converts manganese dioxide to manganese sulphate.
MnO2(aq)+2H+(aq)+H2O2→Mn2+(aq)+2H2O(l)+O2(g)
- In alkaline medium: Hydrogen peroxide is converted to O2 in an alkaline media.
H2O2+2OH–→2H2O+O2+2e
For example,
1) Ferric salts are converted to ferrous salts.
2Fe3+(aq)+H2O2(aq)+2OH–(aq)→2Fe2+(aq)+O2(g)+2H2O(l)
2) In the basic media, it converts iodine to iodide ions.
I2(s)+H2O2(aq)+2OH–(aq)→2I–(aq)+2H2O(l)+O2(g)
- 氧化性-
H 2 O 2是一种强大的氧化剂,因为它容易吸收电子并在碱性和酸性环境中都被还原。
- In an acidic medium: In the presence of an acidic media, H2O2 can receive electrons and behave as an oxidising agent. H2O2 is decomposed into H2O.
H2O2+2H++2e–→2H2O( Eo=+1.77V)
For example,
1) Acidified ferrous sulphate is converted to ferric sulphate.
2Fe2+(aq)+H2O2(aq)+2H+(aq)→2Fe3+(aq)+2H2O(l)
2) It extracts iodine from a potassium iodide solution that has been acidified.
2I–(aq)+H2O2(aq)+2H+(aq)→I2(s)+2H2O(l)
- In an alkaline medium: In an alkaline media, hydrogen peroxide can take electrons and operate as an oxidising agent.
H2O2+OH–+2e–→3OH–
For example,
1) When hydrogen peroxide oxidises manganese salts to manganese dioxide, a brownish precipitate results.
Mn2+(aq)+H2O2(aq)+2OH–(aq)→MnO2(s)+2H2O(l)
2) When chromium sulphate is oxidized by hydrogen peroxide in an alkaline media, the dark green colour changes to yellow sodium chromate.
Cr2(SO4)3+3H2O2+10NaOH→2Na2CrO4+3Na2SO4+8H2O
- In neutral medium: In a neutral media, hydrogen peroxide oxidises a wide range of substances. For example,
1) It oxidizes sulphites to sulphates.
SO2–3+H2O2→SO2–4+H2O
2) It converts nitrites to nitrates by oxidising them.
NO–2+H2O2→NO–3+H2O
过氧化氢的制备
实验室准备
- 过氧化钠(默克工艺):将少量过氧化钠加入到被冰包围的稀硫酸溶液(20%)中,并在此过程中不断搅拌。当溶液进一步冷却时,Na 2 SO 4结晶。 10H 2 O 型,可滤除。该溶液是 30% 的过氧化氢水溶液。
Na 2 O 2 +H 2 SO 4 →Na 2 SO 4 +H 2 O 2
- 来自过氧化钡:在冰冷的水中制成的水合过氧化钡 (BaO 2 .8H 2 O) 糊状物用 20% 冰冷的硫酸溶液处理。过滤用于去除白色的BaSO 4沉淀。大约 5% H 2 O 2留在溶液中。
BaO 2 ⋅8H 2 O+H 2 SO 4 →BaSO 4 (白色ppt)+H 2 O 2 +8H 2 O
这种方法效率低,因为硫酸钡会在 H 2 O 2周围生成一层保护涂层,从而抑制其继续进行化学反应。溶液中的 Ba 2+离子缓慢分解过氧化氢。结果,溶液不能长时间储存。磷酸,而不是硫酸,用于测试这一点。形成的磷酸钡完全沉淀,在没有 Ba 2+离子的情况下不会有过氧化氢分解的威胁。
3BaO 2 ⋅8H 2 O+2H 3 PO 4 →Ba 3 (PO 4 ) 2 (ppt)+24H 2 O+3H 2 O 2
工业制备
- 通过硫酸溶液的电解:在电池中,电解 50% 的硫酸溶液。在阳极产生过氧二硫酸,结果在阴极释放氢气。
H 2 SO 4 →HSO – 4 +H +
阳极: HSO – 4 →H 2 S 2 O 8 (过氧化硫酸) +2e –
阴极: 2H + +2e – →H 2
细胞的过氧化硫酸被去除并用水分解以产生过氧化氢。
H 2 S 2 O 8 +2H 2 O→2H 2 SO 4 +H 2 O 2
高沸点的硫酸不会蒸馏,但过氧化氢会。当电解等比例的硫酸铵和硫酸的混合物时,可以增加双氧水的产量。
过氧化氢是通过将在阳极产生的过氧化硫酸铵与水一起蒸馏而获得的。
(NH 4 )2S 2 O 8 +2H 2 O→2NH 4 HSO 4 (硫酸氢铵)+H 2 O 2
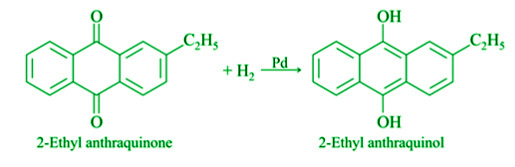
- 来自 2-乙基蒽醌:在钯催化剂存在下,氢气通过溶解在苯中的 2-乙基蒽醌传输。它被分解成2乙基蒽醌。然后使2乙基蒽醌、苯和环己醇的混合物在空气中循环。当过氧化氢被氧化回2乙基蒽醌时,就会产生过氧化氢。
- 通过异丙醇的氧化:当少量的过氧化氢与异丙醇结合时,它起引发剂的作用。在大约 340K 和一点压力下,氧气通过溶液转移。氧化反应产生丙酮和过氧化氢。
CH 3 CHOHCH 3 (异丙醇)+O 2 →CH 3 COCH 3 (丙酮)+H 2 O 2
示例问题
问题1:使用过氧化氢安全吗?
回答:
Most people are safe when they utilise hydrogen peroxide correctly. However, if a person takes the substance too frequently or in a high dosage, it might be dangerous. To avoid irritation, it’s critical to use a concentration of no more than 3% and to use it sparingly. Because there is a risk of swallowing hydrogen peroxide, children should avoid handling it.
问题2:过氧化氢能杀死细菌吗?
回答:
When hydrogen peroxide is allowed to stay on surfaces for at least 10 minutes at room temperature, it is most effective. Hydrogen peroxide can deactivate a wide range of microorganisms, including viruses, bacteria, fungus, and spores, and acts as a disinfectant by eliminating critical components of germ cells.
Hydrogen peroxide is a good option to use on inanimate surfaces like metal, glass, and plastics when it comes to reducing germs in your home and containing the spread of Covid19. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (CDC).
问题3:过氧化氢比漂白剂强吗?
回答:
When we talk about bleach, we’re talking about chlorine bleach, which is made up of sodium hypochlorite. Bleach, like hydrogen peroxide, produces nascent oxygen, which is a bleaching agent. Despite the fact that bleach is more powerful than hydrogen peroxide, it is a very dangerous toxin. It requires careful dilution for safe use, and only cold water should be used. Hydrogen peroxide, on the other hand, has a lower environmental impact and is effective in treating wastewater and disinfecting substances.
问题4:用双氧水洗牙能美白牙齿吗?
回答:
Gargling with hydrogen peroxide may help to relieve a sore throat, disinfect the mouth, and whiten the teeth. However, it should be diluted. If swallowed, a higher concentration of hydrogen peroxide causes internal organ damage as well as excessive bleeding. While rinsing with the diluted solution, prevent ingestion. To develop whiter teeth with merely gargling or rinsing, though, you’ll need to do it for a long time.
问题5:默克的流程是什么?
回答:
In this technique, sodium peroxide is added in minute amounts to a weak sulphuric acid (20%) solution covered by ice and regularly stirred. Crystals of Na2SO4. 10H2O occur as the solution is cooled further, and they can be filtered out. A 30 percent hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution is used.
Na2O2+H2SO4→Na2SO4+H2O2
问题6:水和双氧水有什么区别?
回答:
Water and hydrogen peroxide have different physical properties according to the extent of hydrogen bonding. Peroxide has a higher hydrogen bonding strength than water because it has one more oxygen atom than water, allowing for greater hydrogen bonding.
Because of the strain in the O–O bond in hydrogen peroxide, the chemical characteristics of water and hydrogen peroxide differ. The lone pairs on two oxygen atoms in hydrogen peroxide cause a lot of strain, weakening the O–O bond and allowing it to breakdown quickly into water and oxygen. With the exception of the water molecule, this is not the case. It doesn’t have any O–O bond tension.