帕斯卡原理公式
当出现如何在流体的帮助下通过施加较小的力来提升重物的问题时,法国数学家布莱斯·帕斯卡( Blaise Pascal )引入了帕斯卡定律,通过利用液体的性质和流体的压力来回答这个问题。大多数飞机在制动系统和起落架中使用液体的压力和特性。
帕斯卡定律
这个定律是由布莱斯帕斯卡给出的,他指出,在受限的不可压缩流体中任何点的压力变化都会传递到整个流体中,这样同样的变化就会发生在任何地方。考虑给定的数字,
最初设定
这里,P 1和 P 2是忽略大气压的流体内部特定点的压力。
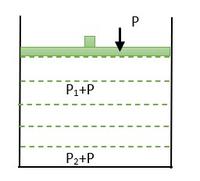
活塞作用力 P
然后,根据帕斯卡,这个压力 P 将在整个流体中传递,并且每个点的压力将增加 P 即; P 1 + P 和 P 2 + P。
要记住的几点
- 帕斯卡定律仅适用于封闭容器,即;容器内不应有泄漏。
- 活塞是一种防止容器从开口端泄漏的装置
- 所有液压的东西都是按照帕斯卡原理工作的
- JCB Machine, Injection 就在这个原理上工作
帕斯卡公式
Consider a closed vessel where two-piston is used, A1 and A2 are the areas of a cross-section of their respective sections.

Initial setup.
When a force F is applied on the narrower side the piston goes down and from the border side, the piston goes up. D1 and D2 are the displacements from the initial position of the piston.
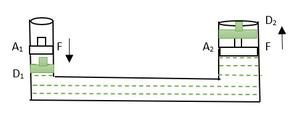
After applying pressure
Since the volume remain the same after displacement of fluid, therefore,
A1D1 = A2D2 ⇢ (Equation 1)
From the law of conservation of energy, Work done in both the cross-section will be equal.
F1D1 = F2D2 ⇢ (Equation 2)
Dividing equation 2 by equation 1,
F1/A1 = F2/A2
We know F(Force)/A(Area) = P(Pressure).
机械优势
Mechanical advantage is Calculated by,
(Output force)/(Input Force) = F2/F1.
示例问题
问题1:液压升降系统中直径为50cm的小活塞施加100N的向下力。直径为 2m 的大活塞所施加的向上的力是多少?
解决方案:
From Pascal’s law, we know force exerted on one side will be equal to force experienced on another side.
⇒ F1/A1 = F2/A2
Given, F1 = 100N , Diameter of small piston = 50cm = 0.5m, Area of cross section (A1) = π × 0.5 × 0.5.
Diameter of large piston = 2m, Area of cross section (A2) = π × 2 × 2, F2 = ?
⇒ 100/(π × 0.5 × 0.5) = F2/(π × 2 × 2)
⇒ 100/(π × 0.5 × 0.5) × (π × 2 × 2) = F2
⇒ F2 = 1600N.
问题2:计算上述问题的机械优势?
解决方案:
Mechanical Advantage is ⇒ F2/F1 = 1600/100= 16, which means, applying 1 unit of force on the smaller side will result in 16 times of force on the larger side.
问题3:如果输入100N的力将直径50cm的小活塞向下推2m,请问直径2m的大活塞会上升多高?
解决方案:
We Know Volume of fluid inside the vessel will be constant
⇒ A1D1 = A2D2
Given, A1 = π × 0.5 × 0.5, D1 = 2m, A2 = π × 2 × 2, D2 = ?
⇒ (π × 0.5 × 0.5) × 2 = (π × 2 × 2) × D2
⇒ D2 = (π × 0.5 × 0.5) × 2 ÷ (π × 2 × 2)
⇒ D2 = 0.125m
This shows larger piston will move less than the smaller piston when force is applied to the smaller piston.
问题4:在汽车举升机中,压缩空气将焦点F 1施加在半径为0.5cm 的小活塞上。该压力被传递到半径为 15 厘米的第二个活塞。如果要提升的汽车质量为1350kg,计算F 1 。完成这项任务所需的压力是多少? (g = 9.8 毫秒2 )
解决方案:
Given,
F1 (small piston), r1 = 5cm, r2 = 15cm, m2 = 1350.
⇒ F2 = m2 × g = 1350 × 10 = 13500N
⇒ F1/A1 = F2/A2
⇒ F1 = (F2/A2) × A1
⇒ F1 = (13500 × π × 5 × 5)/(π × 15 × 15)
⇒ F1 = 2250N
Pressure(P1) = F1/A1 = 2250/π × (5)2
⇒ P1 = 28.64N/cm2.
问题5:液压升降机的大活塞半径为20cm。必须对半径为 2.0cm 的小活塞施加多大的力才能抬起质量为 1500kg 的汽车? (g=10m/s 2 )
解决方案:
Radius of large piston (R2) = 20 cm = 0.2 m
Radius of small piston (R1) = 2 cm = 0.02m
Mass of car (M2) = 1500kg
Force due to car on large piston (F2) = M2 × g = 1500 × 10 = 15000N
Force on small piston (F1) = ?
We know,
F1/A1 = F2/A2
⇒ A1 = π × 0.02 × 0.02 m2
⇒ A2 = π × 0.2 × 0.2 m2
⇒ F1/(π × 0.02 × 0.02) = 15000/(π × 0.2 × 0.2)
⇒ F1 = 15000/(π × 0.2 × 0.2) × (π × 0.02 × 0.02)
⇒ F1 = 150N
问题 6:找到上面问题中将汽车提升到 0.3m 高度所做的功?
解决方案:
We know,
Work Done (W) = Force(F2) × height(displacement)
⇒ W = 15000 × 0.3
⇒ W = 4500N