毕奥-萨伐法则
Biot-Savart 方程表示由载流导线产生的磁场。该导体或导线表示为称为电流元素的矢量。让我们详细看一下biot-savart定律的规律和公式,
毕奥-萨伐法则
定律中规定了由载流导体的微小元素引起的某个地方的磁感应强度。
- 与电流成正比
- 与元素的长度成正比
- 与元素和连接元素中心到该点的线之间的角度的正弦成正比,并且,
- 与点到元素中心的距离的平方成反比
dB α I
dB α dl
dB α sinΘ
dB α 1 / r2
∴ dB α IdlsinΘ / r2
∴ dB = KIdlsinΘ / r2 (K is constant)
推导
考虑带有电流 (I) 和微小长度元件 (dl) 的任何形式的导体(参见下图)。电流垂直向上描绘。
令 (P) 为距载流元素 (r) 距离的任意点, (r) 为 (P) 相对于当前元素的位置向量, 为 (dl) 和 (r) 之间的角度,在电流的方向。
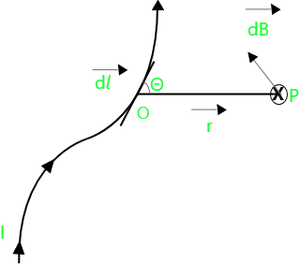
比奥——萨瓦特定律
根据 Biot – Savart 定律,点 (P) 处的磁感应由下式给出,
dB = KIdlsinΘ / r2 ⇢ (1)
这里,K 是常数,它的值取决于单位系统以及导体所在的介质。
在 SI 系统中,真空或空气的常数 K 写为 [μ o / 4π] 其中 μ 0称为真空或自由空间的渗透率。
将 K 代入等式 (1) 我们得到,
dB = μ0 / 4π [IdlsinΘ / r2] ⇢ (2)
SI unit of μ0 Wb / Am. It`s value is 4π X 10-7 Wb / Am
(μ0 / 4π = 10-7 Wb / Am)
磁感应的方向垂直于图的平面并指向平面内。 (根据右手拇指规则。)
以矢量形式,
其中 [r] 是从元素中心到该点的向量,[dl] 是元素在电流方向上的长度。通过添加所有此类元素 [dl] 的贡献,可以找到由整个导体引起的点 P 处的总磁感应,并表示为:
![]()
![]()
求和替换为∫
现在,由于无限长且直的导体在距导体距离为“a”的点处载有电流 I 的磁感应强度由下式给出,
Biot – savart 定律的应用
以下是 Biot-Savart 定律的一些重要性:
- 我们可以利用 Biot-Savart 定律来确定原子或分子水平的磁响应。
- 它可以在空气动力学理论中用于确定涡线促进的速度。
- 该规则可用于计算电流元件产生的磁场。
Biot-Savart 定律的重要性
以下是 Biot-Savart 定律的一些重要性:
- 在静电学中,Biot-Savart 定律类似于库仑定律。
- 该立法也适用于传输电流的极小导体。
概念问题
问题 1:State Biot – savart 定律并将其写成向量形式。
回答:
Law statement : The Magnitude of magnetic induction at a point due to a small element of a current-carrying conductor is, directly proportional to the current, directly proportional to the length of the element, directly proportional to the sine of the angle between the element and the line joining the center of the element to the point and, inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the point from the center of the element.
Boit savart Law in vector form is given by: ![]()
问题 2:陈述 Biot savart 定律的任意两个应用。
回答:
Applications of Biot savart`s law are:
- To calculate magnetic responses at the atomic or molecular level, we can use Biot–Savart law, and
- It may be used in aerodynamic theory to calculate the velocity induced by vortex lines.
示例问题
问题 1:沿南北方向保持的导线中,有 5A 的电流从南流向北。求一根 1cm 长的电线在距电线东北 2m 处产生的磁场。
解决方案:
Given Data: I = 5A
r = 2m
Θ = 45°
dl = 1cm = 1 × 10-2 m
To find: Magnetic field (dB)
Formula: dB = μ0 / 4π [IdlsinΘ / r2]
Calculation: From formula,
dB = 10-7 × 6 × 10-2 × sin45° / 22
= 8.84 × 10-10 T
The Magnetic field due to wire at point is 8.84 × 10-10.
问题 2:一根长直导线载有 35A 的电流。距离导线 20cm 处的磁场 B 是多少?
解决方案:
Given Data: I = 35A
a = 30cm = 0.3m
To find: The magnitude field (B)
Formula: B = μ0 / 2π (I / a)
Calculation: From formula,
B = 4π × 10-7 / 2π (35 / 0.3)
= 2 × 10-7 (116.66)
B = 233.32 × 10-7 T
The magnetic field at point 30cm is 233.32 × 10-7 T.
问题3:水平面的一根长直导线在南北方向上承载50A的电流。在导线以东 3m 处给出 B 的大小和方向。
解决方案:
Given Data: I = 50A
a = 3m
To find: Magnitude and the direction of B
Formula: B = μ0I / 2πa
Calculation: From Formula,
B = 4π × 10-7 × 50 / 2π × 3
= 2 × 10-7 × 50 / 3
B = 3.333 × 10-6 T
It acts in the vertically upward direction, so direction is downward.
“Note: The direction of the magnetic field is always in a plane perpendicular to the line of element and position vector.”
The magnitude of B is 4 × 10-6 T and the direction is vertically downward.
问题4:真空中两条长直平行线相距4m,同向分别承载6A和8A电流。找到中性点,即合成磁感应为零的点。
解决方案:
Given Data: I1 = 4A
I2 = 8A
r = 4m
To find: neutral point ( the point at which resultant magnetic induction is zero )
Formula: (i) B1 = μ0 / 4π (2I1 / r1)
(ii) B2 = μ0 / 4π (2I2 / r2)
The current flowing through the wire is all going in the same direction. As a result, at any location between the two wires, the two magnetic inductions B1 and B2 will have opposing orientations. As a result, the point must be located between the two wires.
For the resultant magnetic induction to be zero, we must have B = B2
Let the corresponding point (The neutral point) be at distance r1 from the first wire and r2 from the second wire.
Calculation:
B = μ0 / 4π ( 2I1 / r1) and B2 = μ0 / 4π ( 2I2 / r2)
Now, B1 = B2
∴ I1 / r1 = I2 / r2
∴ r2 / r1 = I2 / I1
∴ r2 / r1 = 8A / 4A
= 2
∴ r2 = 2r1
But, r1 + r2 = r
∴ r1 + 2r1 = 4m
∴ r1 = 4/3m and r2 = 8/3m
The neutral point lies at a distance of 4/3m from the wire carrying a current of 4A.