树中两条不相交路径的最大乘积
给定一棵有 N 个节点(和 N-1 条边)的无向连通树,我们需要在这棵树中找到两条不相交的路径,并且它们的长度的乘积最大。
例子:
In first tree two paths which are non-intersecting
and have highest product are, 1-2 and 3-4, so answer
is 1*1 = 1
In second tree two paths which are non-intersecting
and has highest product are, 1-3-5 and 7-8-6-2
(or 4-8-6-2), so answer is 3*2 = 6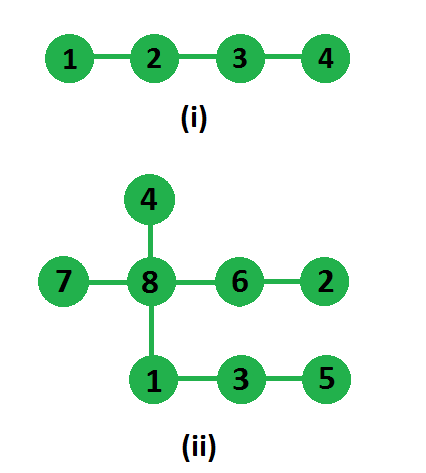
我们可以通过树的深度优先搜索来解决这个问题,方法如下,由于树是连接的并且路径不相交,如果我们采用任何一对这样的路径,则必须有第三条路径连接这两个路径,如果我们删除一个来自第三条路径的边,然后树将分为两个部分——一个包含第一个路径,另一个包含第二个路径。这一观察为我们提供了算法:迭代边缘;对于每条边删除它,在两个连接的组件中找到路径的长度并将这些路径的长度相乘。树中路径的长度可以通过修改后的深度优先搜索找到,我们将在每个邻居处调用最大路径,我们将添加两个返回的最大长度,这将是在当前节点为根的子树的最大路径长度。
实施细节:
输入是一棵树,但其中没有指定的根,因为我们只有边的集合。树表示为无向图。我们遍历邻接表。对于每条边,我们在它的两侧找到最大长度的路径(移除边之后)。我们跟踪由边缘去除引起的最大产品。
C++
// C++ program to find maximum product of two
// non-intersecting paths
#include
using namespace std;
/* Returns maximum length path in subtree rooted
at u after removing edge connecting u and v */
int dfs(vector g[], int& curMax, int u, int v)
{
// To find lengths of first and second maximum
// in subtrees. currMax is to store overall
// maximum.
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0, total = 0;
// loop through all neighbors of u
for (int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); i++)
{
// if neighbor is v, then skip it
if (g[u][i] == v)
continue;
// call recursively with current neighbor as root
total = max(total, dfs(g, curMax, g[u][i], u));
// get max from one side and update
if (curMax > max1)
{
max2 = max1;
max1 = curMax;
}
else
max2 = max(max2, curMax);
}
// store total length by adding max
// and second max
total = max(total, max1 + max2);
// update current max by adding 1, i.e.
// current node is included
curMax = max1 + 1;
return total;
}
// method returns maximum product of length of
// two non-intersecting paths
int maxProductOfTwoPaths(vector g[], int N)
{
int res = INT_MIN;
int path1, path2;
// one by one removing all edges and calling
// dfs on both subtrees
for (int i = 1; i < N+2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < g[i].size(); j++)
{
// calling dfs on subtree rooted at
// g[i][j], excluding edge from g[i][j]
// to i.
int curMax = 0;
path1 = dfs(g, curMax, g[i][j], i);
// calling dfs on subtree rooted at
// i, edge from i to g[i][j]
curMax = 0;
path2 = dfs(g, curMax, i, g[i][j]);
res = max(res, path1 * path2);
}
}
return res;
}
// Utility function to add an undirected edge (u,v)
void addEdge(vector g[], int u, int v)
{
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
int edges[][2] = {{1, 8}, {2, 6}, {3, 1},
{5, 3}, {7, 8}, {8, 4},
{8, 6} };
int N = sizeof(edges)/sizeof(edges[0]);
// there are N edges, so +1 for nodes and +1
// for 1-based indexing
vector g[N + 2];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
addEdge(g, edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
cout << maxProductOfTwoPaths(g, N) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find maximum product
// of two non-intersecting paths
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int curMax;
// Returns maximum length path in
// subtree rooted at u after
// removing edge connecting u and v
static int dfs(Vector g[],
int u, int v)
{
// To find lengths of first and
// second maximum in subtrees.
// currMax is to store overall
// maximum.
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0, total = 0;
// Loop through all neighbors of u
for(int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); i++)
{
// If neighbor is v, then skip it
if (g[u].get(i) == v)
continue;
// Call recursively with current
// neighbor as root
total = Math.max(total, dfs(
g, g[u].get(i), u));
// Get max from one side and update
if (curMax > max1)
{
max2 = max1;
max1 = curMax;
}
else
max2 = Math.max(max2, curMax);
}
// Store total length by adding max
// and second max
total = Math.max(total, max1 + max2);
// Update current max by adding 1, i.e.
// current node is included
curMax = max1 + 1;
return total;
}
// Method returns maximum product of
// length of two non-intersecting paths
static int maxProductOfTwoPaths(Vector g[],
int N)
{
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int path1, path2;
// One by one removing all edges and
// calling dfs on both subtrees
for(int i = 1; i < N + 2; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < g[i].size(); j++)
{
// Calling dfs on subtree rooted at
// g[i][j], excluding edge from g[i][j]
// to i.
curMax = 0;
path1 = dfs(g, g[i].get(j), i);
// Calling dfs on subtree rooted at
// i, edge from i to g[i][j]
curMax = 0;
path2 = dfs(g,i, g[i].get(j));
res = Math.max(res, path1 * path2);
}
}
return res;
}
// Utility function to add an
// undirected edge (u,v)
static void addEdge(Vector g[],
int u, int v)
{
g[u].add(v);
g[v].add(u);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int edges[][] = { { 1, 8 }, { 2, 6 },
{ 3, 1 }, { 5, 3 },
{ 7, 8 }, { 8, 4 },
{ 8, 6 } };
int N = edges.length;
// There are N edges, so +1 for nodes
// and +1 for 1-based indexing
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector []g = new Vector[N + 2];
for(int i = 0; i < g.length; i++)
g[i] = new Vector();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
addEdge(g, edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
System.out.print(maxProductOfTwoPaths(g, N) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh Python3
# Python3 program to find maximum product of two
# non-intersecting paths
# Returns maximum length path in subtree rooted
# at u after removing edge connecting u and v
def dfs(g, curMax, u, v):
# To find lengths of first and second maximum
# in subtrees. currMax is to store overall
# maximum.
max1 = 0
max2 = 0
total = 0
# loop through all neighbors of u
for i in range(len(g[u])):
# if neighbor is v, then skip it
if (g[u][i] == v):
continue
# call recursively with current neighbor as root
total = max(total, dfs(g, curMax, g[u][i], u))
# get max from one side and update
if (curMax[0] > max1):
max2 = max1
max1 = curMax[0]
else:
max2 = max(max2, curMax[0])
# store total length by adding max
# and second max
total = max(total, max1 + max2)
# update current max by adding 1, i.e.
# current node is included
curMax[0] = max1 + 1
return total
# method returns maximum product of length of
# two non-intersecting paths
def maxProductOfTwoPaths(g, N):
res = -999999999999
path1, path2 = None, None
# one by one removing all edges and calling
# dfs on both subtrees
for i in range(N):
for j in range(len(g[i])):
# calling dfs on subtree rooted at
# g[i][j], excluding edge from g[i][j]
# to i.
curMax = [0]
path1 = dfs(g, curMax, g[i][j], i)
# calling dfs on subtree rooted at
# i, edge from i to g[i][j]
curMax = [0]
path2 = dfs(g, curMax, i, g[i][j])
res = max(res, path1 * path2)
return res
# Utility function to add an undirected edge (u,v)
def addEdge(g, u, v):
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
edges = [[1, 8], [2, 6], [3, 1], [5, 3], [7, 8], [8, 4], [8, 6]]
N = len(edges)
# there are N edges, so +1 for nodes and +1
# for 1-based indexing
g = [[] for i in range(N + 2)]
for i in range(N):
addEdge(g, edges[i][0], edges[i][1])
print(maxProductOfTwoPaths(g, N))
# This code is contributed by PranchalKC#
// C# program to find maximum product
// of two non-intersecting paths
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
static int curMax;
// Returns maximum length path in
// subtree rooted at u after
// removing edge connecting u and v
static int dfs(List []g,
int u, int v)
{
// To find lengths of first and
// second maximum in subtrees.
// currMax is to store overall
// maximum.
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0, total = 0;
// Loop through all neighbors of u
for(int i = 0; i < g[u].Count; i++)
{
// If neighbor is v, then skip it
if (g[u][i] == v)
continue;
// Call recursively with current
// neighbor as root
total = Math.Max(total, dfs(
g, g[u][i], u));
// Get max from one side and update
if (curMax > max1)
{
max2 = max1;
max1 = curMax;
}
else
max2 = Math.Max(max2, curMax);
}
// Store total length by adding max
// and second max
total = Math.Max(total, max1 + max2);
// Update current max by adding 1, i.e.
// current node is included
curMax = max1 + 1;
return total;
}
// Method returns maximum product of
// length of two non-intersecting paths
static int maxProductOfTwoPaths(List []g,
int N)
{
int res = int.MinValue;
int path1, path2;
// One by one removing all edges and
// calling dfs on both subtrees
for(int i = 1; i < N + 2; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < g[i].Count; j++)
{
// Calling dfs on subtree rooted at
// g[i,j], excluding edge from g[i,j]
// to i.
curMax = 0;
path1 = dfs(g, g[i][j], i);
// Calling dfs on subtree rooted at
// i, edge from i to g[i,j]
curMax = 0;
path2 = dfs(g,i, g[i][j]);
res = Math.Max(res, path1 * path2);
}
}
return res;
}
// Utility function to add an
// undirected edge (u,v)
static void addEdge(List []g,
int u, int v)
{
g[u].Add(v);
g[v].Add(u);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]edges = { { 1, 8 }, { 2, 6 },
{ 3, 1 }, { 5, 3 },
{ 7, 8 }, { 8, 4 },
{ 8, 6 } };
int N = edges.GetLength(0);
// There are N edges, so +1 for nodes
// and +1 for 1-based indexing
List []g = new List[N + 2];
for(int i = 0; i < g.Length; i++)
g[i] = new List();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
addEdge(g, edges[i,0], edges[i,1]);
Console.Write(maxProductOfTwoPaths(g, N) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995 Javascript
输出:
6