有向图中的欧拉电路
欧拉路径是图中的一条路径,它只访问每条边一次。欧拉回路是在同一顶点开始和结束的欧拉路径。
如果一个图有一个欧拉循环,则称它为欧拉图。我们已经讨论了无向图的欧拉回路。在这篇文章中,同样讨论了有向图。
例如,下图的欧拉循环为 {1, 0, 3, 4, 0, 2, 1}
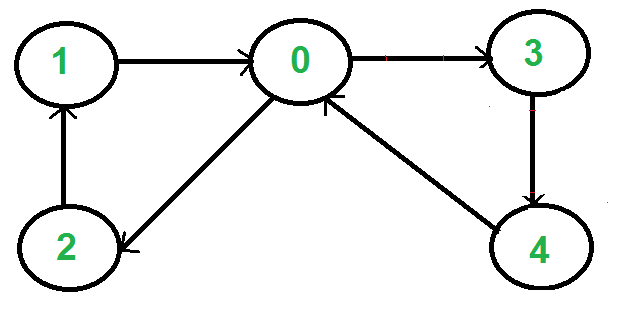
如何检查有向图是否是欧拉图?
如果以下条件为真,则有向图具有欧拉循环(来源:Wiki)
1)所有非零度的顶点都属于一个单一的强连通分量。
2) 每个顶点的入度等于出度。
我们可以使用 Kosaraju 的基于 DFS 的简单算法检测单连通分量。
为了比较入度和出度,我们需要存储每个顶点的入度和出度。出度可以通过邻接表的大小来获得。度数可以通过创建一个大小等于顶点数的数组来存储。
以下是上述方法的实现。
C++
// A C++ program to check if a given directed graph is Eulerian or not
#include
#include
#define CHARS 26
using namespace std;
// A class that represents an undirected graph
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // A dynamic array of adjacency lists
int *in;
public:
// Constructor and destructor
Graph(int V);
~Graph() { delete [] adj; delete [] in; }
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].push_back(w); (in[w])++; }
// Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not
bool isEulerianCycle();
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
bool isSC();
// Function to do DFS starting from v. Used in isConnected();
void DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[]);
Graph getTranspose();
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
in = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
in[i] = 0;
}
/* This function returns true if the directed graph has a eulerian
cycle, otherwise returns false */
bool Graph::isEulerianCycle()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isSC() == false)
return false;
// Check if in degree and out degree of every vertex is same
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != in[i])
return false;
return true;
}
// A recursive function to do DFS starting from v
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i, visited);
}
// Function that returns reverse (or transpose) of this graph
// This function is needed in isSC()
Graph Graph::getTranspose()
{
Graph g(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for(i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
{
g.adj[*i].push_back(v);
(g.in[v])++;
}
}
return g;
}
// This function returns true if all non-zero degree vertices of
// graph are strongly connected (Please refer
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/connectivity-in-a-directed-graph/ )
bool Graph::isSC()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited (For first DFS)
bool visited[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find the first vertex with non-zero degree
int n;
for (n = 0; n < V; n++)
if (adj[n].size() > 0)
break;
// Do DFS traversal starting from first non zero degrees vertex.
DFSUtil(n, visited);
// If DFS traversal doesn't visit all vertices, then return false.
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() > 0 && visited[i] == false)
return false;
// Create a reversed graph
Graph gr = getTranspose();
// Mark all the vertices as not visited (For second DFS)
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Do DFS for reversed graph starting from first vertex.
// Starting Vertex must be same starting point of first DFS
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited);
// If all vertices are not visited in second DFS, then
// return false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() > 0 && visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
if (g.isEulerianCycle())
cout << "Given directed graph is eulerian n";
else
cout << "Given directed graph is NOT eulerian n";
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java program to check if a given directed graph is Eulerian or not
// A class that represents an undirected graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list
class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
private LinkedList adj[];//Adjacency List
private int in[]; //maintaining in degree
//Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
in = new int[V];
for (int i=0; i i =adj[v].iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
n = i.next();
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n,visited);
}
}
// Function that returns reverse (or transpose) of this graph
Graph getTranspose()
{
Graph g = new Graph(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
Iterator i = adj[v].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
g.adj[i.next()].add(v);
(g.in[v])++;
}
}
return g;
}
// The main function that returns true if graph is strongly
// connected
Boolean isSC()
{
// Step 1: Mark all the vertices as not visited (For
// first DFS)
Boolean visited[] = new Boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Step 2: Do DFS traversal starting from the first vertex.
DFSUtil(0, visited);
// If DFS traversal doesn't visit all vertices, then return false.
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
// Step 3: Create a reversed graph
Graph gr = getTranspose();
// Step 4: Mark all the vertices as not visited (For second DFS)
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Step 5: Do DFS for reversed graph starting from first vertex.
// Starting Vertex must be same starting point of first DFS
gr.DFSUtil(0, visited);
// If all vertices are not visited in second DFS, then
// return false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
/* This function returns true if the directed graph has a eulerian
cycle, otherwise returns false */
Boolean isEulerianCycle()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isSC() == false)
return false;
// Check if in degree and out degree of every vertex is same
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != in[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static void main (String[] args) throws java.lang.Exception
{
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
if (g.isEulerianCycle())
System.out.println("Given directed graph is eulerian ");
else
System.out.println("Given directed graph is NOT eulerian ");
}
}
//This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
# A Python3 program to check if a given
# directed graph is Eulerian or not
from collections import defaultdict
class Graph():
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
self.IN = [0] * vertices
def addEdge(self, v, u):
self.graph[v].append(u)
self.IN[u] += 1
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
visited[v] = True
for node in self.graph[v]:
if visited[node] == False:
self.DFSUtil(node, visited)
def getTranspose(self):
gr = Graph(self.V)
for node in range(self.V):
for child in self.graph[node]:
gr.addEdge(child, node)
return gr
def isSC(self):
visited = [False] * self.V
v = 0
for v in range(self.V):
if len(self.graph[v]) > 0:
break
self.DFSUtil(v, visited)
# If DFS traversal doesn't visit all
# vertices, then return false.
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False:
return False
gr = self.getTranspose()
visited = [False] * self.V
gr.DFSUtil(v, visited)
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False:
return False
return True
def isEulerianCycle(self):
# Check if all non-zero degree vertices
# are connected
if self.isSC() == False:
return False
# Check if in degree and out degree of
# every vertex is same
for v in range(self.V):
if len(self.graph[v]) != self.IN[v]:
return False
return True
g = Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
if g.isEulerianCycle():
print( "Given directed graph is eulerian");
else:
print( "Given directed graph is NOT eulerian");
# This code is contributed by Divyanshu MehtaC#
// A C# program to check if a given
// directed graph is Eulerian or not
// A class that represents an
// undirected graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents a directed
// graph using adjacency list
class Graph{
// No. of vertices
public int V;
// Adjacency List
public List []adj;
// Maintaining in degree
public int []init;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[v];
init = new int[V];
for(int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
{
adj[i] = new List();
init[i] = 0;
}
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w);
init[w]++;
}
// A recursive function to print DFS
// starting from v
void DFSUtil(int v, Boolean []visited)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
foreach(int i in adj[v])
{
if (!visited[i])
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
// Function that returns reverse
// (or transpose) of this graph
Graph getTranspose()
{
Graph g = new Graph(V);
for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
foreach(int i in adj[v])
{
g.adj[i].Add(v);
(g.init[v])++;
}
}
return g;
}
// The main function that returns
// true if graph is strongly connected
Boolean isSC()
{
// Step 1: Mark all the vertices
// as not visited (For first DFS)
Boolean []visited = new Boolean[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Step 2: Do DFS traversal starting
// from the first vertex.
DFSUtil(0, visited);
// If DFS traversal doesn't visit
// all vertices, then return false.
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
// Step 3: Create a reversed graph
Graph gr = getTranspose();
// Step 4: Mark all the vertices as
// not visited (For second DFS)
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Step 5: Do DFS for reversed graph
// starting from first vertex.
// Staring Vertex must be same
// starting point of first DFS
gr.DFSUtil(0, visited);
// If all vertices are not visited
// in second DFS, then return false
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// This function returns true if the
// directed graph has a eulerian
// cycle, otherwise returns false
Boolean isEulerianCycle()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree
// vertices are connected
if (isSC() == false)
return false;
// Check if in degree and out
// degree of every vertex is same
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].Count != init[i])
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
if (g.isEulerianCycle())
Console.WriteLine("Given directed " +
"graph is eulerian ");
else
Console.WriteLine("Given directed " +
"graph is NOT eulerian ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh Javascript
输出:
Given directed graph is eulerian 上述实现的时间复杂度是 O(V + E),因为 Kosaraju 的算法需要 O(V + E) 时间。在运行 Kosaraju 的算法后,我们遍历所有顶点并比较需要 O(V) 时间的度数和度数。
请参阅以下内容作为此应用程序。
查找给定的字符串数组是否可以链接形成一个圆圈。