SciPy 线性代数 – SciPy Linalg
SciPy 包包含PythonNumPy 包的功能。它使用 NumPy 数组作为基本数据结构。它具有 NumPy 模块的线性代数中包含的所有功能和一些扩展功能。它由一个linalg子模块组成,SciPy 和 NumPy 子模块提供的功能有重叠。
让我们通过一些示例来讨论模块提供的一些方法及其功能。
求解线性方程
linalg.solve函数用于求解给定的线性方程。它用于自动评估方程并找到未知变量的值。
Syntax: scipy.linalg.solve(a, b, sym_pos, lower, overwrite_a, overwrite_b, debug, check_finite, assume_a, transposed)
让我们考虑一个示例,其中linalg.solve函数采用两个数组 a 和 b。数组 a 包含未知变量的系数,而数组 b 包含线性方程的右侧值。线性方程由函数求解以确定未知变量的值。假设线性方程为:
7x + 2y = 8
4x + 5y = 10Python
# Import the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# The function takes two arrays
a = np.array([[7, 2], [4, 5]])
b = np.array([8, 10])
# Solving the linear equations
res = linalg.solve(a, b)
print(res)Python
# Import the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix
x = np.array([[7, 2], [4, 5]])
# Finding the inverse of
# matrix x
y = linalg.inv(x)
print(y)Python
# Import the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix
x = np.array([[8 , 2] , [3 , 5] , [1 , 3]])
# finding the pseudo inverse of matrix x
y = linalg.pinv(x)
print(y)Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix A
A = np.array([[9 , 6] , [4 , 5]])
# Finding the determinant of matrix A
D = linalg.det(A)
print(D)Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix M
M = np.array([[1 , 5] , [6 , 10]])
# Passing the values to the
# eigen function
x , y , z = linalg.svd(M)
print(x , y , z)Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix M
M = np.array([[9 , 3] , [2 , 4]])
# Passing the values to the eigen
# function
val , vect = linalg.eig(M)
# Display the Eigen values and Eigen
# vectors
print(val)
print(vect)Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the input array
x = np.array([6 , 3])
# Calculating the L2 norm
a = linalg.norm(x)
# Calculating the L1 norm
b = linalg.norm(x , 1)
# Displaying the norm values
print(a)
print(b)Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix
x = np.array([[16 , 4] , [100 , 25]])
# Calculate and print the matrix
# square root
r = linalg.sqrtm(x)
print(r)
print("\n")
# Calculate and print the matrix
# exponential
e = linalg.expm(x)
print(e)
print("\n")
# Calculate and print the matrix
# sine
s = linalg.sinm(x)
print(s)
print("\n")
# Calculate and print the matrix
# cosine
c = linalg.cosm(x)
print(c)
print("\n")
# Calculate and print the matrix
# tangent
t = linalg.tanm(x)
print(t)输出:
[0.74074074 1.40740741]计算矩阵的逆
scipy.linalg.inv用于查找矩阵的逆矩阵。
Syntax: scipy.linalg.inv(a , overwrite_a , check_finite)
Parameters:
- a: It is a square matrix.
- overwrite_a (Optional): Discard data in the square matrix.
- check_finite (Optional): It checks whether the input matrix contains only finite numbers.
Returns:
- scipy.linalg.inv returns the inverse of the square matrix.
考虑一个示例,其中输入 x 由函数scipy.linalg.inv 获取。这个输入是方阵。它返回 y,它是矩阵 x 的逆矩阵。设矩阵为——
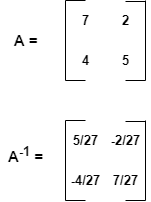
Python
# Import the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix
x = np.array([[7, 2], [4, 5]])
# Finding the inverse of
# matrix x
y = linalg.inv(x)
print(y)
输出:
[[ 0.18518519 -0.07407407]
[-0.14814815 0.25925926]]计算矩阵的伪逆
为了评估矩阵的 (Moore-Penrose) 伪逆,使用scipy.linalg.pinv 。
Syntax: scipy.linalg.pinv(a , cond , rcond , return_rank , check_finite)
Parameters:
- a: It is the Input Matrix.
- cond, rcond (Optional): It is the cutoff factor for small singular values.
- return_rank (Optional): It returns the effective rank of the matrix if the value is True.
- check_finite (Optional): It checks if the input matrix consists of only finite numbers.
Returns:
- scipy.linalg.pinv returns the pseudo-inverse of the input matrix.
示例: scipy.linalg.pinv将矩阵 x 进行伪求逆。它返回矩阵 x 的伪逆和矩阵的有效秩。
Python
# Import the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix
x = np.array([[8 , 2] , [3 , 5] , [1 , 3]])
# finding the pseudo inverse of matrix x
y = linalg.pinv(x)
print(y)
输出:
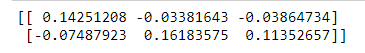
寻找矩阵的行列式
方阵的行列式是从矩阵的系数算术得出的值。在linalg模块中,我们使用linalg.det()函数来查找矩阵的行列式。
Syntax: scipy.linalg.det(a , overwrite_a , check_finite)
Parameters:
- a: It is a square matrix.
- overwrite_a (Optional): It grants permission to overwrite data in a.
- check_finite (Optional): It checks if the input square matrix consists of only finite numbers.
Returns:
- Floating point value
scipy.linalg.det采用方阵 A 并返回 D,即 A 的行列式。行列式是矩阵线性变换的特定属性。 2×2 矩阵的行列式由下式给出:
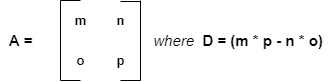
从上面的Python代码中,行列式计算为:
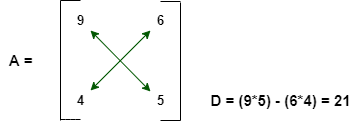
例子:
Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix A
A = np.array([[9 , 6] , [4 , 5]])
# Finding the determinant of matrix A
D = linalg.det(A)
print(D)
输出:
21.0奇异值分解
奇异值分解是一种矩阵分解方法,用于将矩阵缩减为其组成部分,以使特定的后续矩阵计算更简单。它是使用scipy.linalg.svd计算的。
Syntax: scipy.linalg.svd(a , full_matrices , compute_uv , overwrite_a , check_finite , lapack_driver)
Parameters:
- a: The input matrix.
- full_matrices (Optional): If True, the two decomposed unitary matrices of the input matrix are of shape (M, M), (N, N).
- compute_uv (Optional): The default value is True.
- overwrite_a (Optional): It grants permission to overwrite data in a.
- check_finite (Optional): It checks if the input matrix consists of only finite numbers.
- lapack_driver (Optional): It takes either the divide-and-conquer approach (‘gesdd’) or general rectangular approach (‘gesvd’).
函数scipy.linalg.svd采用矩阵 M 进行分解并返回:
- 以左奇异向量为列的酉矩阵。
- 奇异值按非递增顺序排序。
- 具有右奇异向量作为行的酉矩阵。
例子:
Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix M
M = np.array([[1 , 5] , [6 , 10]])
# Passing the values to the
# eigen function
x , y , z = linalg.svd(M)
print(x , y , z)
输出:

特征值和特征向量
令 M 是一个 n×n 矩阵,让 X∈C n是一个非零向量,其中:
MX = λX for some scalar λ.λ 称为矩阵 M 的特征值,X 称为与 λ 相关的 M 的特征向量,或 M 的 λ-特征向量。
Syntax: scipy.linalg.eig(a , b , left , right , overwrite_a , overwrite_b , check_finite , homogeneous_eigvals)
Parameters:
- a: Input matrix.
- b (Optional): It is a right-hand side matrix in a generalized eigenvalue problem.
- left, right (Optional): Whether to compute and return left or right eigenvectors respectively.
- overwrite_a, overwrite_b (Optional): It grants permission to overwrite data in a and b respectively.
- check_finite (Optional): It checks if the input matrix consists of only finite numbers.
- homogeneous_eigvals (Optional): It returns the eigenvalues in homogeneous coordinates if the value is True.
函数scipy.linalg.eig采用复数或实数矩阵 M,其特征值和特征向量将被评估。它返回矩阵的特征值的标量集。它找到矩阵的特征值和右或左特征向量。
例子:
Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix M
M = np.array([[9 , 3] , [2 , 4]])
# Passing the values to the eigen
# function
val , vect = linalg.eig(M)
# Display the Eigen values and Eigen
# vectors
print(val)
print(vect)
输出:

计算范数
为了定义两个向量或矩阵的接近程度,以及定义向量或矩阵序列的收敛性,使用范数。函数scipy.linalg.norm用于计算矩阵或向量范数。
Syntax: scipy.linalg.norm(a , ord , axis , keepdims , check_finite)
Parameters:
- a: It is an input array or matrix.
- ord (Optional): It is the order of the norm
- axis (Optional): It denotes the axes.
- keepdims (Optional): If the value is True, the axes which are normed over are left in the output as dimensions with size=1.
- check_finite (Optional): It checks if the input matrix consists of only finite numbers.
Returns:
- scipy.linalg.norm returns the norm of a.
函数scipy.linalg.norm返回七个不同的矩阵范数之一或无限数量的向量范数之一。
- L2 范数评估向量坐标与向量空间原点的距离。它也被称为欧几里德范数,因为它计算为与原点的欧几里德距离。结果是正距离值。
- L1 范数被评估为绝对向量值的总和。它是对距向量空间原点的曼哈顿距离的评估。
例子:
Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the input array
x = np.array([6 , 3])
# Calculating the L2 norm
a = linalg.norm(x)
# Calculating the L1 norm
b = linalg.norm(x , 1)
# Displaying the norm values
print(a)
print(b)
输出:

更多矩阵函数
| Function Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| scipy.linalg.sqrtm(A, disp, blocksize) | Finds the square root of the matrix. |
| scipy.linalg.expm(A) | Computes the matrix exponential using Pade approximation. |
| scipy.linalg.sinm(A) | Computes the sine of the matrix. |
| scipy.linalg.cosm(A) | Computes the cosine of the matrix. |
| scipy.linalg.tanm(A) | Computes the tangent of the matrix. |
例子:
Python
# Importing the required libraries
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
# Initializing the matrix
x = np.array([[16 , 4] , [100 , 25]])
# Calculate and print the matrix
# square root
r = linalg.sqrtm(x)
print(r)
print("\n")
# Calculate and print the matrix
# exponential
e = linalg.expm(x)
print(e)
print("\n")
# Calculate and print the matrix
# sine
s = linalg.sinm(x)
print(s)
print("\n")
# Calculate and print the matrix
# cosine
c = linalg.cosm(x)
print(c)
print("\n")
# Calculate and print the matrix
# tangent
t = linalg.tanm(x)
print(t)
输出:
